Catching predatory fish
a very popular activity among modern fishermen. Do you want to know what is most important when catching large predatory fish? The most important thing is not some secret lure, sensational tackle, particularly outstanding fishing spot or good time of day or year. Much more important is the quality of the fisherman himself! A good predatory fish hunter who wants to catch a worthy trophy needs above all three qualities: he must be flexible, have a creative approach and be able to concentrate his attention.
Types of fishing
Catching a predator
Sheer lure
The easiest way to catch bottom predators is vertical trolling. For vertical fishing, spinners of various shapes are used, cast from tin or made from other non-ferrous metals, usually in the form of a curved narrow spoon, weighted to a hook, 1 to 7 cm long.
The spoon is tied to a fishing line, and the fishing line is tied to a short fishing rod. With this gear, they get into a boat and float along a quiet stretch downstream, lowering the spoon to the bottom. The bait floats above the bottom towards the fish. At the same time, the angler shakes the spoon all the time, lowering and raising it. Small lures are used to tempt not only predatory fish, but also many peaceful fish - ide, roach, dace and others. Sheer lures are also successfully used in lakes, especially in the fall, in perch pits. On a boat they go to deep places and “play” with a spoon under the boat itself and around it.
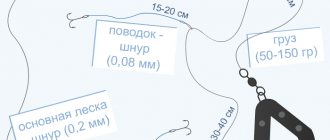
Fishing with live bait
Trophy predators are also caught using live bait. A sinker weighing 200-300 g is tied to a strong cord, and a special device is placed on the cord above the weight - a triangle made of thick wire. A live fish, placed on a single hook or on a special tackle, is suspended from the acute corner of the triangle. The fish serves as bait for a predator. Fishermen also use other devices with which live bait is lowered to the bottom.
This is how they are caught using live bait. They go out in a boat to the pit and lower the load to the bottom; the fish on the rig will swim above the bottom. The bait must be kept in one place or slowly pulled behind the boat, with the load stretching along the bottom or just above the bottom. They also catch predators by swimming, lowering live bait attached to a hook to the bottom. They swim with live bait with the current or in the pits, move it around the boat, raising or lowering it to the bottom.
Spinning fishing
When fishing with a spinning rod, the spoon is thrown to the bottom and then pulled towards you, winding the cord around the reel. But the spoon, pulled up by the tip of the rod, will gradually rise to the surface and thus go out of sight of the fish standing on the bottom. To avoid this, after casting the spoon to the bottom, pull it towards you, then stop the rotation of the reel for 2-3 seconds, and the spoon will sink to the bottom, then rotate the reel again, and the spoon will go to the shore. With this technique you can achieve the spinner being held above the bottom. However, this method of spinner fishing, as fishermen call it, “ledges”, even with good knowledge of the reservoir, is not always possible for an experienced spinning angler. Most often, the angler, afraid of landing the spoon on the bottom, leads it too high, the predator does not notice the bait, and the cast does not reach the target. Meanwhile, predators eagerly rush after the bait, which looks like a sick fish struggling with the current.
Fishing from a boat
When catching predatory fish from a boat, casting range is no less important, since in places with an average depth of more than 10 meters, the bait, after a standard 30-40-meter cast, makes only 15-20 meters of casting, and this is clearly not enough for a successful search for fish sites. Therefore, the casting range when fishing from the shore should be at least 50-60 meters.
Since fishermen often fish areas of the bottom with sharp changes in depth, it is clear that uniform wiring will not give practically any result: the bait will pass over all the depressions and ditches, often without even coming into the field of view of predatory fish.
The fact is that large fish in most cases choose for hunting or ambush places located below the upper edge of the edge, since in open areas of the bottom and especially on the tops of underwater mounds its silhouette is clearly visible to small fish. From under a dump, in the shadow of which it is easy to camouflage, a large predatory fish tracks down small fish feeding on the edge and attacks it. Small fish see the space around them well and can easily escape in case of danger. Successful catching of large predatory fish in pits is possible only with the use of special varieties of stepped fishing.
Fishing with a track
For fishing on the track, various rotating and oscillating spoons and other baits are used. All of these spoons are equipped with a tee in the tail, which, when moving the spoon close to the bottom, often clings to underwater snags and grass. In this case, you have to return to the place where it hit and unhook the spoon. When the spoon is driven too high above the bottom, it passes through layers of water where the predator does not stay.
Perch
Perch is an extremely common, schooling, freshwater fish. It is found in rivers and lakes throughout Europe, including Britain. It’s hard to believe, but relatively recently, perch was also introduced to Tasmania, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa! This comrade is one of those who is caught fishing with a spinning rod more often than others. It can be the size of a palm or reach the size of an elbow.
To catch a perch, no special tricks are required. As a rule, this fish rushes to any bait if it finds it appetizing enough, be it a wobbler, streamer or an ordinary spoon. In addition, perches hunt in schools. So, if you hook a perch while standing in one place, there is a good chance that while standing in the same place you will pull out several more. Large perches should be caught from a boat, in the deepest parts of the reservoir.
Lures for predatory fish
Both peaceful and predatory fish serve as food for predatory fish in water bodies. A predator that eats peaceful fish does not spare its relatives. There are frequent cases when a pike grabs and swallows, gradually pushing another pike into the stomach. Burbot can also swallow burbot, which is not much smaller than itself. As for small fish, they are eaten by predators in huge quantities. Suffice it to say that to gain 1 kg of its own weight, a perch needs to eat up to 50 kg of fish.
Predatory fish are very indiscriminate in their choice of food, so a variety of fish can be used as bait when catching them. Large predators are caught equally well with both small and large live bait. But predators such as asp, grayling, salmon, trout, perch and pike perch, grab mainly small fish and fry, preferring live fish, although they are often caught on pieces of fish.
Some good baits for predatory fish - pike, perch, burbot, catfish and chub - include the grass frog, found throughout the northern regions and central Russia, and the green frog, common in more southern regions.
Many amateur fishermen are so successful at catching frogs, especially pikes and catfish, that they prefer them to any other bait.
Also, when catching predators, artificial baits are often used.
Equipment for catching predatory fish
- Lightweight float rod for catching live bait.
- Canna for storing live bait.
- A spool of thick fishing line 0.5mm, large single hooks, sinkers of any type.
- Kukan for storing caught fish.
- Landing net, yawner and extractor for fishing and releasing fish from the hook.
Catching predators
Pike
When fishing with a pop-up wobbler, step-by-step wiring is used. First, the wobbler is sent in a steep arc to the bottom, and after a few seconds the reel is stopped so that it begins to float - this is repeated until they pass through a deep water section.
Stepped fishing is no less effective when fishing with a vibrotail. It is very important to cast in such a way that the bait rises from the bottom of the deep area into shallow water, where it should be led above the bottom, making additional jerks with the rod.
It is best to fish with a rotating spoon near algae or snags, launching it along the border of a difficult place and clear water. A twister connected to a spinner improves the game somewhat. Moreover, the choice of spinner or twister is not decisive. The pike takes the larger “spinner”.
Oscillating spoons are most often used to catch fish in areas with strong currents. The cast can be made at right angles to the shore, then the spoon is allowed to move freely with the current. From time to time they jerk it up from the depths, avoiding snags, and reel it in.
There is one feature: in cloudy weather, bait can be cast in any direction, and in sunny weather, so that the sun is on the side. A pike caught on the bait suddenly rushes to the side, so you need to tame its burrows in a timely manner, otherwise it may lead the tackle into snags or grass.
Zander
The behavior of pike perch differs from the behavior of other predators mainly in that during daylight it always stays at depth, and with the onset of darkness it goes ashore to hunt. Pike perch has a narrow pharynx structure, so any fish with a narrow, slanted body is ideal food for it. The wobbler must also have an appropriate design, otherwise the pike perch may remain indifferent to it. The best wiring with a wobbler is horizontal, uniform or with slight accelerations.
Fishing with a heavy Kastmaster spinner is good in fast sections of rivers. The wiring in this case is fast and uniform.
Pike perch are caught with twisters and vibrotails with less effect. Of the soft baits, the most catchy one is considered to be a foam fish, which is caught using the method of step-by-step retrieval.
It is good to fish with spinners during the period when pike perch is actively moving in a flock in search of food. At this time, it can feed in different layers of water. Usually these are places saturated with oxygen, where there are a lot of fry. The spinner rig should be light enough, and the spinning rod should have the appropriate characteristics for long-distance casting of such bait.
Perch
Catching perch with a twister gives good results. All types of retrieves are suitable for this, but there are times when the fish goes all the way to the shore for a uniformly moving bait and does not take it - then a slight disruption in the rhythm of the retrieve can lead to success. The mass of the twister is selected depending on the strength of the current. In very strong currents, the use of this bait is ineffective.
Small rotating spoons of yellow or white color in combination with a red, yellow or black twister are very attractive for perch. Another good bait for perch can be fly spoons.
Sometimes the hunting location of a perch can be determined by schools of fry: jumping out of the water, they scatter in all directions.
Ide
It takes well on a perch lure. The smallest rotating petal with a tee No. 7–8 is quite suitable, since the ide has a small mouth. The French spinner Aglia-1, small spinners from Mepps, and domestic spinners and spinners are also suitable. It has been noticed that with sunrise, ide prefers dull, copper, sometimes even black spoons and spinners that have a brownish-pockmarked coloring with a red triangular plumage, and at dusk or in dim lighting - shiny baits. Combining a spinner with a vibrating tail or artificial fly often produces better results.
It is necessary to properly balance the load of the spinners. Excessive weight is of no use: it does not allow the spoon to play correctly and contributes to greater clinging to the bottom and algae. On rotating spoons, two types of sinkers are used and sometimes both at the same time: a head sinker and a sinker on a rod.
Chub
To catch this fish, first of all, the smallest rotating spoon of the Aglia-0 type is used. Casting is done in the feeding areas of the chub - it often reveals itself by hunting for fry at the border of fast and slow water. The bait is placed near the surface or in the water column, sometimes with slight jerks.
A hybrid of a rotating blade with a twister or streamer often brings success. It is very important for the fisherman to understand what color bait the chub likes in a given body of water. For example, during the period when the May beetle emerges, brown or brown baits with black specks are effective. The chub is cautious, often staying near overgrown, poorly accessible shores, so it often has to be caught by stealth, using a pendulum or catapult cast.
From the oscillating spinners, choose small, oblong-shaped ones, equipped with two small tees in the middle and in the tail, of different, but not bright colors.
For chub fishing, the best rod is at least 3 m long with a soft tip that can respond well to sudden jerks of the fish when fishing.
Bait casting technique
To learn how to cast correctly, you don’t have to have great talent - just follow the basic rules.
In order to cast the bait over and over again in a strictly intended place, you must first choose for yourself a method that allows you to hold the rod most correctly and comfortably. I call it "grip."
For me, as for the vast majority of athletes I know, the most comfortable and only grip when casting with a spinning rod is the position when the handle of the spinning reel is clamped between the middle and ring fingers of the right hand, while the thumb resting on the rod acts as a “guide” casting Just as when shooting at targets, a sniper needs to fix his hands in one position, and a spinning player must always hold the reel the same way. Such consistency will allow you to achieve filigree precision when sending the bait to the intended location.
The casting technique is best practiced on a wide river, where snags on snags or overhanging branches sticking out of the water are excluded. Depending on the environment, the strength and direction of the wind and the specific task facing the spinner, different casts are used. If the shore where fishing is to be done is deserted, it is best to use the simplest and most convenient casts from the right or left over the shoulder; if the bank turns out to be overgrown with bushes or tall grass, you should throw the bait over your head; if there are tree branches hanging over the angler’s head, you can use a pendulum cast, albeit not very far, but the only one possible in such a position.
To ensure that the casts are similar to each other, before making them, it is recommended to monitor the overhang of the bait (that is, the distance from the upper end of the bait to the tulip of the spinning rod). The swing can be greater or less if the bait changes from light to heavy, from large to small. But when fishing is carried out with baits of the same parameters and before each cast the distance from it to the tip of the spinning rod fluctuates significantly, then you are unlikely to be able to hit the same point twice.
On a wide river, however, this is not as important as on a narrow winding river. But casting range plays a very big role here. After all, often the catchable underwater edge is located at a considerable distance.
If this is really the case, then it’s time to remember such an important thing as the spinning test, in other words, the manufacturer’s recommended minimum and maximum weight of lures for a particular rod. If, for example, the test of your spinning rod ranges from 10-20 g, then trying to forcefully cast a bait weighing 40 g will most likely lead to breakage of the tackle.
It is rare to fish in completely calm weather, and when the wind blows, often, according to the law of meanness, It is rare to fish in completely calm weather, and when the wind blows, often, according to the law of meanness, it is head or side.
In such weather, it is desirable that the flight path of the bait be as low as possible. Considering the strength of the side wind, it is necessary to make appropriate adjustments when casting. For example, if the wind blows from the left, then the cast should be made with a large deviation to the left...
But even on a wide river, it is not so much the casting range that is important, but its accuracy. Sending the bait vertically over the head (in a straight line) is not particularly difficult. It is more difficult to exclude the undershoot/overshoot factor. And if undershooting means that you wasted your time, then the flight is sometimes not entirely in vain, because the bait can still “light up” in a promising area. In addition, we can correct the overshoot: just slow down the line running off the spool with the pad of your index finger. If the flight is insignificant, braking occurs by light touches (short presses of the fishing line) to the outer edge of the spool; if the cast turns out to be too powerful, the braking of the running line can be increased, stopped, and, if necessary, even jerked back to the bait under your feet.
Proper braking of the bait must also be practiced in order to soften its splashdown, that is, to eliminate the effect of a strong splash, which can frighten the fish.
see also
- About Fishing Seriously - Issue 12 - Catching pike perch with a jig
- About Fishing Seriously - Issue 27 - Fishing for pike perch
- About Fishing Seriously - Issue 32 - Fishing with live bait
- About Fishing Seriously - Issue 39 - Fishing with girders
- About Fishing Seriously - Issue 46 - Asp Fishing
- Shcherbakov brothers - Issue 10 - Wobblers (part 1)
- Features of the selection and use of artificial baits
- Making foam rubber baits
- Wobblers for pike
- Pike fishing, great relaxation and fun pastime
- Perch fishing - a universal recreation