Determining the depth of the reservoir
Fishermen use a variety of fishing methods in their practice, and each of them has its own specifics. Some of them are simpler, others are more complex, but all of them will require you to know the depth of the intended fishing spot. But to be called a versatile angler, you must learn all these methods.
Determining the depth using a fly rod
This tackle is considered the easiest to use and is used for fishing relatively small fish. It is with its study that fishermen begin their journey in fishing. Unfortunately, this method is not as effective as a plug, as this method requires time and several casts to one point to determine the depth.
The equipment consists of a regular float, sinker and hook, the only difference is that a depth gauge weight is fixed at the end. Under the weight of the sinker, the float will sink, i.e. if the depth is greater than that set by the float, then the float will sink, if on the contrary, it will lie down. And in order to achieve the desired result, you need to manually move the float along the fishing line and ensure that the float stands level, as with normal loading of equipment.
You can measure in the same way without this weight, but then the result will be less accurate. Also, using this method, the bait can be placed exactly on the bottom of the reservoir so that it does not lie or float above the bottom.
Plug as a depth gauge
Undoubtedly, a shortened plug is the most suitable gear for determining the thickness of the water layer and the bottom topography. To take measurements, you will need to equip your rod with a relatively heavy depth gauge sinker. And since the fishing line in this case will stand vertically along its entire length, the measurements will be jewelry-accurate. The length of the measurement will be limited only by the length of the gear. It is clear that if the plug is thirteen meters long, then it is unlikely that it will be possible to measure the reservoir beyond this distance. This, one might say, is the only disadvantage of this method.
You also don’t have to constantly re-cast the fishing rod: you only need to lift the depth gauge from the bottom and take it to another place. If the equipment comes off easily, the bottom is hard. In the case when the weight seems to get stuck in the ground and reluctantly comes out of it, then with a high degree of probability it can be assumed that the bottom of the reservoir is muddy.
Let's say a few words about the models of plug-in depth gauges. Their optimal weight ranges from 10-40 grams, and these indicators do not depend on their design. If you need to examine a closed body of water, then a device weighing up to ten grams will be enough, but for a fast river you will have to take a depth gauge with a maximum weight (otherwise the readings may be erroneous due to the windage of the fishing line).
Basically, a plug fishing rod is equipped with a conical depth gauge, on top of which there is a ring attached, and at the bottom there is a foam layer. This model is especially convenient if the fisherman needs to set the parameter “to the bottom”, or slightly above it. After this, the float moves upward along the main line so that a small piece of the leash is on the bottom relief.
You can also use the STONFO push-button depth gauge. When you press the button, a recess appears from the device into which the hook is inserted. When pressed again, the spring is activated and everything returns to its original place.
Another type of depth gauge is the so-called “toad”. These are lead rounds that open when pressed under the action of a small spring. An additional shed is placed inside the device. These models are used to determine the immersion depth of the tackle when fishing on a flat float (“lollipop”).
Electrical sensing method
To identify promising areas for water, the method of electrical probing is most often used. It is carried out by vertical probing of the soil. The electrical resistivity of rocks and underground aquifers varies. Thus, water-saturated soils have a lower electrical resistance than the mineral skeleton of low-moisture rocks.
Using current recorders, you can determine the resistance at each horizon, identifying for yourself those areas where there is a layer of groundwater
The only drawback of this method is that there is always a possibility of calculation errors if there are iron ore deposits in the ground or the proximity of metal fences and railway networks.
Seismic survey method
The seismic exploration technique is based on measuring wave kinematics. Using instruments, places are determined where there is an increased seismic background, the peak values of which reach frequencies from 4 to 15 Hz.
The essence of seismic exploration is that the measurements are first carried out in an area located in close proximity to the groundwater search site, which has a similar geological section.
The downward generated waves, having reached the rock, which differs from the overlying layers, are reflected upward, like an echo. Then, within an hour, the same measurements are carried out in the area where groundwater is being searched.
The depth of the reflecting boundary is calculated based on the obtained values of the sensitive devices of geophones. The presence of artesian waters is judged by a 5-10 times increase in the level of seismic background in the area of the study areas.
Frequency values in the range of 4-15 Hz, which exceed the level of the natural background of the Earth, arise due to the fact that water-filled reservoirs are a denser environment for the passage of the acoustic environment
When acoustic waves pass through liquids that have a high density, a change occurs towards higher frequencies.
Drilling exploration wells
This method allows you to most accurately determine the geological rocks forming the site. But since it involves large financial costs, it is used only in situations where it is planned to equip a large water intake designed for several houses.
To increase the reliability of research, two or three exploration wells are drilled at the designated groundwater search site.
Experts distinguish three methods of exploration drilling:
- Core
- used when drilling to great depths. The principle of operation is based on the fact that a rotating core pipe, the end of which is equipped with a drill bit, cuts through the rock. And then the destroyed rock, under the pressure of the washing solution or compressed air supplied through the pipe column, is pushed to the surface. - Rotary
– based on the transmission of rotational motion to the drill string through a surface rotor. This type of drilling is accompanied by flushing the rock face with a special solution or ordinary water. - Impact-rope
- works due to the destruction of rocks under the action of a falling drill projectile, the end of which is fixed to a rope. The tool simply breaks off the rock and crushes the soil, and then uses a bailer to extract it to the surface.
The choice of drilling method depends on the type of rock, the depth of the formation or lens and the financial capabilities of the customer. But in terms of drilling speed and productivity, rotational methods win in this regard.
The price of an exploration well is determined by multiplying the cost of one linear meter by the depth of the wellbore. The total amount is calculated based on the complexity of the excavation, the diameter of the trunk and the need to use casing pipes.
Hydrogeological data obtained from drilled wells is taken into account when preparing a forecast assessment of the promising area. They help to study changes in the properties of water-bearing rocks in a vertical section.
Ways to measure the depth of a reservoir with float tackle
The easiest way to measure depth when fishing from the shore with a float (if long casting is not intended) and from a boat, when the depth is measured plumb. When float fishing there are two measurement methods:
1.
A sinker is tied directly to the hook.
2.
The measurement is carried out using gear configured for fishing, when the weights are at a certain distance from the hook.
In the first case,
Having moved the float a certain distance from the load, the tackle is thrown into the fishing spot. If the float has disappeared under the water, then you need to increase the depth (raise the float higher); if it lies on the surface of the water, the depth is reduced exactly until the float appears slightly out of the water. This is the depth in this area.
The second method already requires some logic.
So, if the float is lying on its side, it means that the weights are on the bottom, you should reduce the descent slightly - the float will take its working position.
At the same time, it should be understood that this is not the true depth yet - there are still leads. So, by reducing the depth by another length of the leads, you can get an accurate idea of the true depth, and the hooks will be located directly above the bottom.
On the current
To measure depth in currents
It is advisable to use a heavier sinker, and at the same time try to ensure that the line forms a smaller angle.
In still water
To determine the exact depth in a still body of water
You can use special marker floats, which can be purchased, or you can make it yourself, fortunately there is nothing complicated about it. Having thrown the tackle with a marker float to the fishing point, releasing the fishing line from the reel (you must remember the footage of the fishing line), you need to track the moment when the float emerges from the water. That length of the drawn line is the depth. To make it easier to measure the distance, you can pre-mark the length directly on the knee of the rod - a very simple and effective way that allows you to measure depth in still water at different distances.
How to determine the best place for fishing
The most difficult thing, perhaps, but also very necessary, is to learn to identify, in large areas of the bottom with a large amount of silt, places with a more or less hard surface
It is important to learn to recognize the moment when a weight stuck in the silt comes out of the silt and the rod blank levels out and begins to tremble slightly. This is a sign that such a place has been found
Measure the depth in these places and remember this place using landmarks, after which you need to make a couple or three fan-shaped casts. This is done so that you can accurately determine the dimensions of the space on the left and right sides. After all the measurements, we recommend installing a marker there to guide you when casting equipment and bait mixture.
Working with a marker, despite its apparent simplicity, requires some skills and consistent training to improve them. And since this method creates a lot of noise, it is better to hone your skills before fishing in places that are already familiar to you or after it and somewhere on the side, so as not to scare away the fish and not spoil fishing and the enjoyment of communicating with nature for others.
And to improve the skill of “sense of the bottom”, I would recommend the following exercise, but which is easily feasible only in water heated to a temperature suitable for swimming. To do this, you need to swim to bring the marker 70-100 meters, then dive with a mask and walk along the fishing line along the entire route of the future movement of the cargo, remembering all the features of the bottom along the route. And then practice pulling up the load while measuring the depth, comparing your visual sensations and signals coming along the fishing line to the rod and further into your hand with the picture of the bottom that you saw during the dive. In general, these are all the points that my partner and I use in practice.
Thank you all for your attention! No tail for you, dear fishermen, no scales!
By the time of the drop of the load
You can approximately determine the depth by counting the time until the load reaches the bottom. The method is relatively accurate, especially in still water and if you know how long it takes your load to travel a certain distance in the water. I have two weights that I experimentally selected for myself: one of them travels a meter in 2 seconds, the other in one. Knowing this, I cast to the fishing point and mark the time until the weight reaches the bottom (this is marked by the sag of the line and the tip of the rod). For example, I counted 4 seconds using my weight, which sinks at a rate of 1 meter per second. Therefore, the depth is approximately 3.5-4.5 meters. Ideally, you should make several casts to improve accuracy.
As I already said, there are other methods, but I use the ones listed above. I hope the information was useful to you.
How to determine the depth of a reservoir without an echo sounder
Water depth is one of the most important indicators for a fisherman.
And if in familiar bodies of water the fisherman already roughly knows the depth map, then when choosing a new place, determining the depth is a priority. Of course, today there are a lot of modern technical means - echo sounders, depth gauges, but their use is not always possible. To use these devices, you need ideal conditions - free access to water, a flat shore, the ability to launch a boat, etc. But there is another reason, and it is the most significant. Initially, many fishermen rushed to purchase these newfangled aids, but very soon realized that fishing with their use loses, in fact, the very spirit of competition, hunting, and the unknown and turns into some kind of automated event based on the achievements of electronics. In addition, this equipment, mainly made in China, is very capricious, requires maintenance and costs, at least for the same batteries, and can fail at any time. Therefore, having played enough with these miracle devices, the fishermen safely threw them into the far corner and returned to the proven old-fashioned diagnostic methods. So, there are several ways to measure the depth of a reservoir
.
If you plan to fish from the shore with a fishing rod, then cast a float tackle with an arbitrarily set depth level (float). If the float lies on its side, then the load is on the bottom. You need to lower the float down and cast again until it reaches a vertical position, and then carefully level it so that the float on the surface of the water is slightly inclined. This will mean that the sinker has barely touched the bottom. In this position, fishing is most preferable, since the fish feed mainly at the bottom. But if you wish, you can fish from any horizon by moving the float in the desired direction. If necessary, you can use a tape measure or “by eye” to measure the distance between the float and the load and determine the exact depth in centimeters.
If you plan to fish from a boat, then in addition to the first method, you can also use a regular plumb line made from several meters of twine and any weight. To determine the depth, you can make meter marks on the twine in any convenient way, for example, using knots.
When fishing from the shore using a bottom fishing rod or feeder, the depth is determined by the moment the line weakens after casting the tackle and its complete immersion. The load sinks at a speed of approximately 1 meter per second. At this time the line will be stretched. Once it touches the bottom, the line will weaken. Thus, we can calculate the approximate depth of the casting point.
When fishing from ice, it is best to use a regular bottom feeder to measure depth. After unloading the feeder at the bottom, pull it out to the edge of the hole and determine the footage in steps. It is not recommended to make knots on the twine, as in the cold they will freeze and make it difficult to unwind.
These, in fact, are all the main ways to determine the depth of a reservoir without the use of any technical means.
As already mentioned, the correct choice of depth is the key to a good catch. To illustrate, I’ll give you a story from personal experience.
Determining the depth of the reservoir
Fishermen use a variety of fishing methods in their practice, and each of them has its own specifics. Some of them are simpler, others are more complex, but all of them will require you to know the depth of the intended fishing spot. But to be called a versatile angler, you must learn all these methods.
Determining the depth using a fly rod
You can measure in the same way without this weight, but then the result will be less accurate. Also, using this method, the bait can be placed exactly on the bottom of the reservoir so that it does not lie or float above the bottom.
Aquifer and its quality
Water accumulates in underground storage facilities thanks to waterproof layers consisting of clay, which do not allow moisture to pass through and protect the aquifers from all kinds of pollution. The layers of sand located between the clay layers also help to accumulate and retain water.
To accurately determine the aquifer, it is better to contact specialists
Before drilling a well, it is important to determine the quality of water you want to obtain. Depending on the method of formation, groundwater is divided into:
Depending on the method of formation, groundwater is divided into:
- Verkhodka - located near the earth's surface and filled due to precipitation. It is characterized by low quality due to dirt washed off from the surface, so it is most often used for technical purposes.
- Groundwater - collected in the first permanent aquifer, the depth of which starts from 1.5 m, and the composition depends on the frequency and amount of precipitation, the proximity of the reservoir and the condition of the surface soils. Most often, due to harmful impurities, it is not suitable for drinking.
- Interstratal waters - collected between two waterproof layers that formed the bed and roof of an underground lake at a depth of at least 15 m. This water can be used for drinking, although it is often characterized by increased hardness.
- Artesian waters - located at a depth of 100 m or more, are the most environmentally friendly source of water intake, as they are purified from all types of contaminants, passing through layers of clay, sand and gravel. Artesian water is often highly mineralized, and its composition and taste are determined by the presence of minerals dissolved in it.
The depth of occurrence of aquifer veins depends largely on the surface topography. On the plains the depth is one, but in lowlands it is completely different. In addition, aquifers never come into contact with the ground.
Determining the bottom topography and its structure
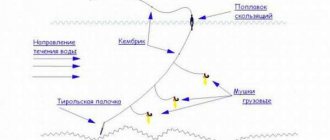
At the moment, the most common way to determine the relief and structure of the bottom is using marker equipment with a sinker. It can be made at home. You need to take a marker sinker with spikes or protrusions, a steel leash, a pass ring on the leg (preferably with a ceramic layer inside), a bottle cap, a swivel, a snap hook, and a special float. The leash will protect your equipment from mechanical damage, the cork will help it float, and the line will glide much better in a ring with ceramics.
Currently, to determine the bottom relief and its features, fishermen use several methods and their combinations. Let's take a closer look at them.
Jig wiring
This method is easy to perform and requires only basic knowledge of jig fishing from the fisherman. The main condition for this is the uniformity of the wiring and its pace. From the moment the jerk is made until the subsequent fall of the sinker to the bottom, the fisherman counts the time as quickly as possible. The relief of the reservoir (holes, edges, etc.) will depend on the difference in the count in different areas. It is clear that if the count increases, then the depth in this area is greater, and vice versa.
Broaching method (drawing)
If the tip of the tackle trembles and ringing movements are heard in your hand, then it is clear that the bottom of the reservoir is pebbly. If nothing interferes with the passage of the weight, then there is a sandy bottom below, and in the case where the movements are dull, it is shell rock. With long jerks of the rig, there is algae in front of you. If the movements are light, even with some slack - a slope, and if the movement is tight - an ascent. In the case of drawing equipment, you only need a cord. Please note that a lot depends on the action of the rod: the faster it is, the more effectively you can examine the selected bottom relief. In sport fishing, ultra-fast marker rods are used for these purposes. However, for experienced fishermen there are no problems in measuring using almost any gear.
Marker float tackle
The line is then manually released from the reel. In this case, the fisherman needs to control the mark on the fishing rod (if a marker is used), or monitor the first ring. It is imperative to count how many bleeds are made before the float floats to the surface.
You can do the opposite: make the float float up, then wind the main line onto the spool until it stops, while counting the revolutions of the reel. Now all that remains is to drag the weight along the bottom relief for a few meters (in order to determine its structure), and measure the depth again.
This method is used by matchmakers. When fishing with a feeder in fast rivers, it is of little use due to the drift of the float by the current, and, as a result, incorrect results of your research.
How to increase site browsing depth
- Work on the design and usability of the resource. Imagine a website with a bright green background and lots of colorful images. It is quite difficult to find the necessary information on it, so you should not be surprised when you see low viewing depth values. The design should be changed to make it easy for visitors to understand the text.
- Properly arrange internal linking. For information resources, hyperlinks in articles to other interesting sections are suitable. You can add blocks such as “Related materials” or “Popular”. If the resource is a trading platform, the “Recommended”, “Similar Products”, “Popular Sections”, etc. blocks will be of great help.
- Diversify your content and improve its quality. Interesting texts, pictures and videos best increase viewing depth. Structure your texts, break them into blocks, add lists, infographics, and then visitors will stay on your site longer.
The viewing depth, along with other characteristics, signals how interesting the resource is for users. The main thing is to design the site so that the audience wants to return to it again and again, and also to work on the quality of the content. Then the viewing depth will be higher, and the resource itself will be more popular.
How is depth measured?
Along the shore and in the distance
If you need to measure the depth not far from the shore (3–5 meters from it), then this task can be easily accomplished with the help of an ordinary float rod. The depth at which the float begins to lie horizontally on the water is the depth of the reservoir in this place.
It is more difficult to determine the depth at a further distance - 25–35 meters from the shore. If you have a boat, then everything is simple: you drive up and measure using a depth gauge or echo sounder. There are methods using a marker float.
How to find out the depth of a reservoir and bottom topography using fishing gear
A mechanical lot is a more optimal solution compared to a manual one, because... transport speed can be quite high, up to 28 km/h. This is due to the fact that the vertical use of the device is not particularly important.
Measuring with a mechanical lot occurs by lowering a tube sealed at the other end into water. There are marks on the walls of the tube that indicate the depth of the reservoir.
4
An echo sounder is an electronic device that meets modern requirements of science and technology. The greatest depth that the device can determine is 12 km, and measurements can be carried out at high speeds, up to 50 km/h.
There are many companies that produce echo sounders, but they all consist of a sensor, transmitter, screen and receiver. 5 When turned on, the sonar transmitter sends an electrical impulse to the sensor, which, in turn, forms a sound wave from it and sends it into the water.
Counting method
But the easiest way to determine depth is the method used by many experienced spinners. This is a counting method: you need to count the seconds from the weight's contact with the water until it falls to the bottom in a given place. This is done simply: the weight is thrown into the point of the reservoir where you need to measure the depth. After touching the water surface (it is advisable that there is no slack on the line at this moment), you begin a second-by-second countdown: one, two, three, and so on. The end of the countdown is considered to be the moment when the line sag sharply. This means that the cargo has already landed on the bottom.
The best standard for such measurements is a weight or spoon weighing 17–22 grams, since in the water column they drop 1 meter in about 1 second. There will undoubtedly be an error with this method, but within 0.5 meters at a depth of 3 to 5 meters and about 1 meter at a depth of 6-10 meters.
Preliminary determination of well depth
There are several ways to find out the approximate depth of a well before drilling:
- Survey of neighbors in the area. If your neighbors use a well or well, you can always get this information from them. It’s even better if there is technical documentation for the well: it usually indicates not only the depth, but also the flow rate.
- Study geological research data. Such a plan is the result of engineering and reconnaissance activities carried out in the area. It contains information about the specifics of the soil and the pattern of aquifers. Having such documentation in hand, drilling a well is much easier.
- Test drilling. If accurate data on the depth of the aquifer in a specific area is required, exploration drilling can be ordered. This service is quite expensive and is used for private needs only in exceptional cases.
Test drilling
Identifying stuck places
As for the snags of the bottom, to determine it, use the spoon you are going to fish with, which is not equipped with hooks. After casting, you also count down until the spoon reaches the bottom, then begin reeling. The characteristic blows and shocks transmitted along the fishing line from the contact of the spoon with snags and the bottom at a standard fishing speed will tell you almost everything about the topography and the snags of the bottom in a given place. Unexpected troubles during such a bottom check can be either a fish biting on a spoon that is not equipped with hooks, or the fishing line getting stuck between the knots of a snag.
After checking, you can start fishing, of course, equipping the lure with hooks. Taking into account the information received about the relief, after the spoon hits the water, count again, but start reeling in the line a little earlier than the bait hits the bottom. For example, if during the control cast you counted to ten, then start reeling the spoon at the count of eight or nine.
Did you know?
Is the thunderstorm far away?
If you measure the time that elapses between the flash of lightning and the clap of thunder, you can determine the distance at which the thunderstorm is located. The speed of sound is approximately 360 meters per second. By multiplying time by the speed of sound, you can determine the distance to the thunderstorm (since the speed of light is much higher than the speed of sound, it can be neglected). Typically, thunder can be heard at a distance of up to 15-20 kilometers, so if an observer sees lightning but does not hear thunder, then the thunderstorm is more than 20 kilometers away.
Venus on the face of the Sun
“I say: I saw Venus like a mole on the face of the Sun.”
These lines are written on parchment that is over a thousand years old! The author is the scientist-encyclopedist of the Ancient East al-Farabi.
Was the medieval astronomer wrong? After all, in order to see the passage of Venus across the disk of the Sun, he first had to accurately calculate the movement of the planets and determine the day and hour of the eclipse.
Calculations by modern experts have shown that in 910 AD, from the territory of modern Kazakhstan, it was indeed possible to observe a “mole on the face of the Sun.”
The sky is in diamonds
This expression comes to mind when you read the message that the production of integrated circuits has recently been launched, in which sapphire crystals are used instead of a semiconductor substrate.
Such microcircuits are many times more expensive than traditional ones. But it is also many times more reliable in space, where a failure in the operation of any microcircuit can lead to the death of a spacecraft: gem crystals, as studies have shown, have special anti-radiation properties that protect microcircuits from cosmic rays.
Source: “Young Technician” magazine