Spinning wiring: ways and methods
Content
Let's look at how to do spinning wiring. In most cases, fishing with spinning wobblers and their wiring is significantly different from fishing with spinners or microjigs. Moreover, the same types of spinning retrieves performed by different anglers or by the same angler using different gear will differ noticeably from each other. The most indicative in this regard is twitching - a wiring technique that changes not only for each wobbler model, but also taking into account the type of fish, biting activity and other factors.
Thus, we can talk about the general principles of performing different types of wiring, suitable for certain baits and fishing conditions. And the criterion for correct wiring is the size of the catch.
Different baits require different types of wiring
Gear used
Rod
A spinning rod is designed for casting a fishing line with heavy bait. When feeding such baits over a considerable distance, the rod experiences great stress, so it must be elastic and durable, but at the same time flexible. A rod that is too rough and powerful will tear thin fishing line when hooking and retrieving fish.
Modern spinning rods are usually made of carbon fiber, fiberglass, and metal.
For uniform retrieving, middle-class rods with a test weight of 15 to 40 g are suitable. The action should be slow. This combination of characteristics allows the tackle to spring softer, which is important in this fishing technique.
Coil
There are no special requirements for the coil for uniform wiring. The only thing is that when fishing with large rotating spoons against a strong current, you should prefer a power reel to the more common high-speed reel, since it bears a serious load.
fishing line
Fishing line for spinning fishing can have different thickness, color, and breaking capacity. But most importantly, the fishing line can be one of three types of cords:
- Monofilament fishing line (monofilament);
- Wicker;
- Fluorocarbon.
All three types are characterized by different strength, stretchability, and refractive index. The choice of fishing line depends on the size and habits of the fish, the characteristics of a particular body of water, the size and weight of the bait, as well as the preferences of the fisherman.
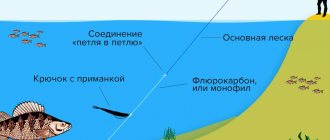
Leash
Metal leashes are used to catch pike with uniform fishing.
Uniform wiring
Uniform retrieving - retrieving a bait with a spinning rod at a constant speed by reeling out the fishing line with a reel. Wiring speed can vary from very slow to very fast. In turn, the speed of the retrieve determines the depth of the bait: the faster the retrieve, the sooner the bait will reach the surface of the water.
Uniform wiring is a simple type of wiring with which it is recommended for beginners to start getting acquainted with spinning. Although simple, uniform wiring can be quite effective. This applies to fishing with rotating spoons with a core weight, for which this type is considered to be practically the only fishing method. In addition to rotating spoons, using uniform fishing, you can fish with:
- front loaded spinners;
- oscillating spoons;
- wobblers with their own game;
- active plastic baits and many others.
Uniform wiring of the wobbler with different depths
Fishing technique and tactics
Uniform retrieval of the bait consists of a smooth rotation of the spool (line guide). Thus, it turns out that the bait moves smoothly in the water without any jerks or deviations to the sides. With this wiring technique, only the speed of rotation of the reel can change, and, naturally, the speed of movement of the bait will change. The faster you turn the spool, the faster the bait will move and vice versa.
During uniform wiring, you need to correctly select the diameter of the fishing line and the weight of the bait. Unbalanced equipment leads to the rapid emergence of the bait and movement on the surface of the water, or vice versa, the movement of the bait along the bottom. Only with the help of properly balanced equipment can you guide the bait along the required trajectory. By uniform retrieving you can identify fish at different depths. But when the bait turns out to be heavy, you can get out of this situation by increasing the speed of rotation of the spool. Only then will the bait pass near the bottom and not come into contact with it. And light bait with a large-section fishing line must be carried out slowly, only then the bait will have time to sink and will not rise. It should be noted that very slow or fast wiring may frighten or not attract the predator. We must not overdo it here.
In reservoirs with high currents, uniform wiring must be done more vigorously than in stagnant reservoirs. Since fish in rivers are more mobile than in lakes, accordingly, in a lake the fish will simply get scared or will not keep up with the gear, and in rivers during a slow retrieve the bait will not work or will not attract a predator.
During uniform retrieving, the depth of immersion can be adjusted by the position of the spinning rod. By lowering the spinning rod to the water, we force the bait to move near the very bottom. And vice versa, by lifting the spinning rod to the top, we force the bait to move higher. This may be necessary when there are sunken trees or other obstacles in the path of the bait.
Uneven wiring
Uneven wiring is a logical development of uniform wiring. In order to attract the attention of a predator, the speed of the retrieve changes randomly; jerks with the rod and stops of the bait are added to the retrieve, creating the chaotic movement characteristic of living nature.
Read more
How to catch asp using a spinning rod?
The number of options for uneven wiring is practically unlimited, so finding out how to correctly make uneven wiring with a spinning rod can only be done experimentally.
Stepped wiring
Stepped wiring is associated with jig fishing. This is not entirely true, except for jig baits, you can use a step to move completely different baits in different layers of water.
Retrieving a floating wobbler with stops creates steps that are opposite to those of a jig - when stopping, the bait does not sink, but floats up. Using a wobbler, you can implement wiring with a step height from the working depth of the wobbler to the surface of the water. Bites can occur at any time during the retrieve.
Stepped wiring is carried out similarly to jigging with active sinking baits:
- oscillating spoons;
- sinking wobblers;
Stepped wiring of a floating wobbler
- bladebaits (cicadas);
- spinerbaits.
For step-by-step retrieving, it is desirable that the bait has a play not only during retrieving, but also during a pause - when falling.
Stepped
This wiring is primarily used in jig fishing. It consists of an alternating reeling of the line, during which the bait rises up, and a pause, when it freely falls down. It can be done using a reel or rod. Both options have their place and are equally effective.
Mostly step animation is performed in the lower layers of water with direct contact of the bait with the bottom. The spinner makes two or three turns with the reel or throws the rod, and then there is a pause. Similar wiring can be done in the water column. It works well on passive pelagic fish, especially asp.
Stepped wiring is designed for different types of baits:
- jigs (silicone, foam rubber, polyurethane foam and others);
- jigs and other narrow-bodied jigs;
- front-loaded turntables;
- spinnerbaits and tail spinners.
Stepped fishing is used for catching pike perch, pike perch, catfish and pike perch. With its help, you can effectively examine the bottom, “tapping” each pit and tubercle. This animation is productive in snags, on a rocky bottom, on sharp edges and slopes.
Photo 1. Stepped wiring diagram.
By varying the height of the bait, the duration of the free fall and subsequent stay at the bottom, the angler can select the optimal presentation for the depth of fishing, the strength of the current and other fishing conditions, as well as the mood of the predator:
- If the fish is pressed to the bottom and behaves inactively, then the height of the “step” is selected small, as is the subsequent time for the bait to fall. But it is advisable to increase the duration of its stay at the bottom.
- If the fish stands above the bottom at a distance of a meter and a half, then it is necessary to reduce the weight of the load. At the same time, the height of the toss increases, and the time of fall is extended. It’s good when the bait hangs in the water column, very slowly gliding towards the bottom.
- The classic “step”, two or three turns and a pause, is suitable for active fish that actively feed and respond well to the offered bait.
In general, the classic step-by-step retrieve is the basic animation for jigging. Beginners should first master this serve. Then you can add various elements and techniques to it, adapting to the mood of the predator.
Twitching
Twitching, or twitching (jerk) wiring, is a method of animating wobblers such as minnows and poppers. It is carried out by jerking the tip of the rod with different amplitudes and frequencies, with pauses between them. Under the influence of water on the blade of the wobbler during amplitude movements of the rod, the bait deviates from the direction of the wire, first in one direction, then in the other, creating the illusion of a rushing fish.
Today, this is one of the most popular and productive methods of spinning fishing.
The twitching rule, common to all baits, is that the less active the fish, the softer the retrieve should be, and the longer the pauses between twitches.
Twitch wiring options
Spinning casting technique
There are several basic rules. Following them will help a novice spinning player avoid initial mistakes and cast correctly, far and accurately.
Overhang of the bait
Overhang is the distance from the bait to the tip of the spinning rod. It is often recommended to make the overhang of the bait 30-40 centimeters from the tulip, as the most optimal. But here you need to take into account such characteristics as:
- Spinning rod length.
- Rigidity. Different types of bait load the spinning rod differently. If the overhang is short, the cast will be short, since the form will not be loaded enough. With an increased length, casting accuracy suffers, and inconveniences arise for the spinner.
- Bait type. Throwing a spinner (oscillating or rotating) is different from throwing a wobbler. Pinocchio is voluminous and has additional long-casting systems inside its body. In order for the system to work, the bait should be thrown with acceleration.
Line retention when casting
There are two types of line retention when casting:
- The first is when you press the line against the side of the reel spool with your index finger.
- The second, most common, is holding at the handle of the spinning rod (as in the photo).
The position of the spinner's hands when casting
Casting a spinning rod with one hand looks beautiful, but I still recommend giving up the apparent beauty and grasping the handle with both hands. Regardless of the blank length, weight and type of bait. Each hand performs its own function.
In principle, these are the main points that first of all need to be paid attention to when mastering the technique of casting a spinning rod for a novice fisherman. Of course, there are quite a lot of nuances and you will have to get acquainted with them
For example, the fight against overlapping tulip fishing line.
For clarity, I can offer a video about the technique of casting a spinning rod from Kirill Gushchin, where all the episodes are perfectly described.
The video is wonderful, I just want to warn beginners against completely copying the actions of a professional when working with a loaded form. Kirill has a lot of experience and good spinning. With budget Chinese chopsticks, such tricks may not work and will lead to breakdown.
Jig wiring
Well-known to the vast majority of anglers, jigging involves guiding the bait in a step, taking into account different characteristics:
- bait speed;
- bait fall time;
- length of the horizontal part of the wiring and others.
The attractiveness for fish, and therefore the high efficiency of jigging, is explained by the constant control of the bottom, where the fish usually stays, and the presence of a vertical phase, during which most bites occur.
A huge number of jig baits allow you to catch almost any fish using this method - from pike perch and catfish to crucian carp and roach. Fishing can be done in most bodies of water.
Classic wiring
Animation of the bait in classic fishing is carried out using a reel. After the bait touches the bottom, the angler makes two to four turns of the reel at a fairly fast pace. This is followed by a pause until the bait falls to the bottom, after which the cycle repeats.
Read more
How to choose the right spinning rod for trolling?
Jigging with a floating wobbler
Most bites occur in the free-fall phase of the bait, so its weight is selected so that the fall time is from two to four seconds. If the bait falls to the bottom faster, the predator does not have time to react to it, and if it falls slower, the bait rises too high from the bottom.
Classic wiring is most effective if the movement of the bait is directed from the shallows to the depths.
Types of postings
Experienced fishermen resort to an endless variety of fishing variations:
- Pumping;
- Stop and go stop and go;
- Uniform;
- Uneven;
- American;
- Stepped;
- For demolition;
- Ripping;
- Near;
- Dzhigova
- Classic, etc.
Uniform
Uniform broaching (compared to the stepwise or jerky method) is the simplest. A fisherman does not need to have any special skills or knowledge. After throwing the bait, you need to wait until it goes down to the required depth. Then slowly and steadily rotate the coil.
Take short breaks periodically and rewind after certain intervals. Most often, predatory fish bite precisely at the moment of such a pause.
Uneven
With this method of fishing, the pace of reeling the spinner either speeds up or slows down. The breaks between these phases are also uneven. Any bait can be used.
Stepped
The movements of the spoon are chaotic; it walks along the bottom in a zigzag pattern, sometimes moving away from it, sometimes approaching it. A coil is wound between the wires. When the spinner reaches the bottom, make a couple of turns with the reel, wait again until the spinner reaches the bottom again, make a couple of turns with the reel again, and so on.
The zigzag movement pattern of the bait and its amplitude directly depend on two factors. This is the speed at which the coil is turned and the number of turns between stops.
The step method is universal; it can be carried out simply with a fishing rod. At the moment when the spoon reaches the bottom, you need to raise the spinning rod sharply up. But not too high from the bottom, 15-20 cm will be enough. Then reel in the slack line, let the spoon fall to the surface again, and jerk again.
Sooner or later, the predator begins to become interested in such a game, reminiscent of the behavior of a wounded or weakened fry. When the bait hits the bottom, it creates a noise that provokes large fish to attack. Often the bite begins at this moment.
For demolition
This method is most catchy when the water in the river has not yet warmed up enough. The point is that the wiring is carried out not by the fisherman, but by the current. You need to choose a bait of the right weight. If you take it too heavy, it will either not budge at all or will cling to the bottom.
If the bait is too light, it may not reach the bottom at all. Experimentally, you need to find a balance in which the bait, without burrowing into the bottom sediments, will seem to float above them.
Classical
This method of spinning fishing is considered the most active and fastest type of fishing using a reel. When the bait reaches the bottom, you need to make 3-4 turns, pause, during which the jig bait again lies on the ground.
The pause between revolutions is the moment for the most intense bite, when the nozzle freely falls to the bottom. This procedure must be repeated until the hook with bait reaches the shore. If there is no bite, the spinning rod is cast again.
American
The bait is moved with the help of a rod, as with classic wiring. The length of the spinning rod is selected based on the fishing characteristics. The length of the step depends on the size of the fishing rod. The American method is considered the most sensitive to the bait, since it has to be controlled at the time of retraction. The bait, fishing line, spinning rod and fisherman’s hand can be considered a single system.
Jig
People go on this type of fishing using jig baits with a rigid spinning rod and braided cord. The lower horizons of the water column are the optimal place for fishing. Often this is where hunters guard their prey. The bait is moved in jerks (jumping), copying the behavior of a sick, weakened fry.
Several types of ging wires are used:
- evenly;
- stepwise;
- aggressively;
- for demolition;
- jumping.
Ripping
A type of jerking technique. They fish with a wobbler and make amplitude swings with a spinning rod in a vertical plane (from top to bottom). Ripping is carried out with a short spinning rod, then the wobbler will dive to greater depths.
Pumping
The method is similar to the previous one. But the strokes are made from bottom to top.
Stop and go stop and go
This method works if caught using composite wobblers. This is the slowest way. Do not use it to catch a predator in a large area of water; use it for spot checking in limited areas.
This method works great if the object is inert. After throwing the lure, wait until it stops at the required depth. Spin the coil 4-5 times, pause for three seconds. Then pull the spinning rod up and reel in the line. It often bites when it stops.
Near
The method is successful in reservoirs with a quiet current, at medium and great depths. With this technique, it is better to fish near the shore, no further than 10-15 meters. It is considered a universal method and is suitable for hunting large (bream, chub, ide) and small (roach, silver bream, crucian carp) fish.
Twitching
This is a jerk technique for spinning rods. When twitching, they catch predatory fish using a wobbler, while sharply jerking the form from side to side.
The important role of pause
With different techniques, it is important to correctly distribute the number of spinning jerks and pauses. If you move evenly, without pauses, then the bait also moves steadily. Take long pauses between bursts. Increasing pauses when hunting pike is especially effective.
Slow wiring
Slow retrieving is performed similarly to the classic one, but there is a pause of 1-3 seconds between the bait falling to the bottom and the next retrieving cycle. This wiring is shorter (1-2 turns of the coil) and slower.
Slow retrieving works well in cold water, when the fish are inactive and do not have time to react to a fast-moving bait. In places with a clean bottom, it is good to periodically supplement the wiring by slowly dragging the bait along the bottom for a short distance. This technique works especially well on pike perch and pike perch. Slow retrieval in the autumn sometimes attracts peaceful fish - bream or carp.
Classic wobbler wiring
Using fishing lines
- Posting bait for perch.
Perch does not really like simple, even movement of the bait. Only twisters and vibrotails, which have a high-frequency tail action, are at least somehow suitable for catching a striped predator on a simple uniform. More successful movements of soft bait for catching perch are: uniform with frequent pauses, short, rather sharp jumps. Large perch love intermittent dragging of the bait along the bottom. The use of microvibration, small tremors with the tip of a spinning rod, is one of the important techniques when fishing, specifically for perch. - Posting bait for pike.
Pike, unlike perch, on the contrary, accepts uniform bait movement very well. This does not mean that you should fish exclusively this way. But God himself ordered the use of active baits, in particular large vibrotails, and the inclusion of even stages in the wiring pattern. If fishing is done with wobblers, then jerk retrieves are perfect. - Posting bait for pike perch.
Pike perch prefers stepwise and jumping bait movement along the very contour of the bottom. Steps, jumps, at the same time, it is better to do medium and short ones. The size of pauses needs to be adjusted, because At this point, pike perch's taste may change. Note that pike perch is more picky and capricious about fishing than perch and pike. - Posting bait for catfish.
Catfish most often attacks the bait during a pause, free fall. Yes, and all the other predators mentioned in the paragraphs above also often attack the bait during the fall. But, with catfish, this is even more critical. So, take long, long pauses when trying to purposefully catch a catfish. - Fishing for peaceful fish.
Catching peaceful fish with a spinning rod using edible silicone, although it is gaining momentum, cannot yet be considered a fully formed direction. So, this is just a small subjective recommendation. To increase the chances of catching peaceful fish with microjig tackle, you need to use a slow, smooth retrieve, without sudden movements and hysterical trembling, which perch loves.
American wiring
American retrieving is carried out similarly to the classical one, but to animate the bait they use not reeling with a reel, but movements with a rod. After the bait falls to the bottom, the angler pulls or jerks the rod, and then returns it to its original position, while simultaneously picking up the resulting slack in the fishing line with the reel. The next time the bait touches the bottom, the wiring cycle is repeated.
The advantage of American wiring is the close contact of the angler with the bait and the ability to more easily diversify the wiring with the movements of the rod.
The disadvantage of American wiring is that when the fishing line is reeled in, it is difficult to detect bites, and it is at this time that the fish most often bite.
Jig wiring methods
Jig fishing is very diverse not only in the baits used, but also in the options for their animation. You can hold a conditional twister, mounted on an offset hook and an eared sinker, evenly, with a classic “step”, or with jerking elements in an aggressive manner, or simply drag along the bottom. Methods of placing jig baits depend on the fishing location and the mood of the predator.
The most commonly used feed variations are:
- Classic stepped.
- Sharp accelerated.
- Slow with dragging along the bottom.
- With jerky elements.
- Using a fishing rod.
- Undulating pelagic.
Each method of placing a jig gives results, the main thing is to use it at the right time, in the right place and with the right bait.
Classic "step"
This is the basic wiring in jig fishing. It is carried out as follows:
- After touching the bottom, make several turns of the reel at a fast or medium pace. The bait comes off the bottom and begins to accelerate upward.
- Then there is a pause, and the bait begins to free fall to the bottom.
- After the bait falls, several turns of the reel follow again.
You need to strive to select the weight of the sinker so that after 2-3 revolutions, the bait sinks to the bottom in no longer than 3 seconds - this is the “classic”. Naturally, by changing the size of the load, you can increase or decrease the free fall time. This way, passive fish react better to the “hanging” of the bait, and a heavier load allows you to fish the area in a high-speed manner and quickly detect an active predator. The use of a cord is mandatory to record any contact between fish and bait.
Aggressive wiring with jerky elements
This wiring method is used by advanced jig masters, who thus diversify the behavior of the bait. Various jerky manipulations give her a more natural, realistic behavior. It begins to resemble a prowling or wounded fry, which provokes the fish to grab.
This wiring should not be confused with jerk wiring. In essence, this is a classic step serve, into which various jerking elements are only additionally introduced. It can be twitching, chaotic jerks, all sorts of delays and tossing. Such methods of jigging are designed to increase the number of bites on passive fish or on pressed-in reservoirs.
Wiring in the “American” style
This method of retrieving differs from the “classic” one in that the bait is thrown using a rod and not a reel. The fisherman makes a sweeping acceleration with the spinning rod, and while lowering the bait to the bottom, he takes out the slack in the fishing line. This type of jig wiring is more complicated, but it does exist and should definitely be mastered.
Dragging along the bottom
Ultra-slow feeding of the bait, almost without lifting off the bottom, is used when catching a passive predator. In this case, the load is applied heavier than conditions require. Drawing is carried out by slow winding with a reel. It is advisable to make short stops in the wiring; bites often occur at this very moment. Dragging along the bottom is very promising when hunting for passive pike perch and large perch. Good results are shown by passive type silicone worms without a twister tail. The bite often feels like a hang, then the weight gradually begins to move. To detect such a bite, hook and remove the predator, you need to use a sensitive spinning rod for jigging.
Wave-like wiring in the water column
This type of wiring is often used when fishing for pike. The toothy predator usually stands not at the very bottom, but above it at a distance of 1–2 meters, and looks more upward, and does not control the bottom layer. Pelagic wave-like wiring does a good job of imitating a lost fish, which is rushing about in confusion in the water column. Can be used both when mounted on a regular jig head and on an articulated jig rig.