Description
The chum salmon's head is large and conical; the upper jaw is straight, narrow, long; eyes are small. The body is elongated, somewhat laterally compressed. The dorsal and anal fins are located closer to the tail than to the head. There are 19-25 gill rakers (fewer compared to pink salmon), 12-15 gill rays. There are 9-11 rays in the dorsal fin III-IV, 13-15 in the anal fin III (12), 8-11 in the ventral fin I-II. The scales are larger compared to pink salmon (125-150). The tail stem is thinner and higher (compared to the red one). Pyloric appendages 135-185, vertebrae 69-71.
What are the differences between chum salmon and coho salmon caviar?
Coho salmon lay up to 7 thousand eggs in one go. Caviar is small in size, but its nutritional value is considered the highest among culinary specialists. The diameter of the eggs is no more than 4 mm, and the taste has a peculiar bitterness. At the same time, the caviar has a bright, rich red color, in contrast to the caviar of other salmon species, the color of which ranges from faint scarlet to red-crimson.
Chum salmon caviar is somewhat larger in size (5-9 mm) compared to coho salmon caviar. At the same time, the eggs have the shape of balls of regular geometry with a clearly defined red dot in the center of each egg. The color of the eggs is characterized as orange-amber, and there is no bitterness in the taste.
Difference between flavors
Naturally, there is a difference, but the preference of one caviar over another depends on the personal taste preferences of the consumer.
Coho salmon caviar may be characterized by uneven coloring and the presence of bitterness. Despite this, coho salmon caviar is considered quite tasty and healthy.
Chum salmon caviar is characterized by the presence of a pronounced taste. Despite this, it is not particularly popular among the population due to the hard shell surrounding each egg.
Properties of caviar
Coho salmon caviar is much more nutritious than the caviar of other salmon species, but its industrial value is not as high as compared to chinook or pink salmon caviar.
Chum salmon caviar has a slightly higher protein content, which is easily absorbed by the human body.
Many experts, as well as nutritionists, recommend regularly consuming caviar of various types of fish, at least 6-8 times a month.
Calorie content of caviar
100 grams of chum salmon caviar contains more than 300 kcal, and coho salmon caviar – 150 kcal
. This indicates that chum salmon caviar has more calories. Coho salmon caviar contains from 6.1 to 9.5% fat. In this regard, we can safely assume that coho salmon caviar is more suitable for dietary nutrition.
Harm and benefits of caviar
The presence of many useful substances in the caviar of salmon species helps to rejuvenate the body, helps to cope with male impotence, feel a surge of vital energy, and strengthen the immune system. The presence of iodine in caviar helps combat poor functioning of the internal secretion organs.
Despite the many positive effects of consuming red caviar, it is better to limit its use to people who have undergone surgery, for people suffering from rickets, and also in conditions where the human body is very weakened. Coho salmon caviar is not recommended for pregnant women, people suffering from poor functioning of the digestive system, or in cases of liver dysfunction.
Cost – is it worth paying more?
Due to the fact that most salmon species, including coho salmon, are caught at a high rate due to their nutritional value, the cost of caviar from these fish is quite high. Chum salmon caviar is in somewhat greater demand in restaurant chains, as well as in other areas of catering. In general, the cost of chum salmon and coho salmon caviar is practically the same on the market and is about 300 rubles per 130 grams.
How to choose red caviar
When choosing this delicious product, you should pay attention to the following nuances:
- It is better to choose a product packaged in glass containers, but not in cans, since there is no way to determine the quality of the product without breaking the packaging.
- A high-quality product is represented by the presence of grains of the correct geometric shape that do not stick to each other.
- If the color of the eggs corresponds to a red-crimson hue, not counting Chinook salmon caviar, then this indicates a fake.
- Caviar packaged in cans may be a product containing an increased amount of liquid, with grains of irregular shape, and also with the presence of preservatives.
- The shelf life of the packaged product is no more than six months, which must be indicated on the label.
- Caviar can correspond to the first grade, when the salt concentration is no more than 6%, as well as the second grade, with a salt concentration of up to 8%. First grade caviar must have whole eggs, without the presence of blood and without the presence of parts of the egg, as indicated in the technical specifications.
In addition, each variety has special requirements for the aroma, which must be attractive and not contain any other odors, as well as for the homogeneity of the product.
Color
In the sea, the head and body are on top, the fins are dark blue with a metallic tint, and the sides and belly are silvery-white. In breeding plumage, the head and body are black on top; there is a clear, dark gray spot behind the eye, and dark purple or dark crimson stripes on the body. In females during the spawning period, the proportions of the body and head almost do not change. In males, the overgrown upper jaw hangs in the form of a powerful hook over the lower one. The body becomes even flatter due to the development of a large hump behind the head. By spawning, the body, palate, tongue, and bases of the gill arches become black. The meat becomes flabby and whitish. Juveniles in the river have black stripes on the sides of their bodies.
How to distinguish stale fish from fresh OR “Anatomy of falsification”
A whole segment of defrosted products has appeared on the Russian fish market, which are sold under the guise of chilled ones. To see this, let’s take a look at one of the most expensive and prestigious chain supermarkets.
... And you don’t need to go to the circus. The specialist here has something to laugh at: we enter one of the most expensive and prestigious chain supermarkets. We move to the fish department. Beauty! It's quite elegant here. A spacious counter with a wide assortment attracts attention. 27 types of fish and seafood are neatly laid out on ice. This is where the pleasant impressions end.
First of all, let me remind you that the phrase “chilled fish” is a very specific commodity term, a technical condition with a very specific GOST 814-96. That is, this is one of three generally possible options for selling fish. In the store it can be either live in aquariums, or frozen in freezers, or chilled on so-called glaciers.
To ensure the quality of chilled fish, it is not at all necessary to ask a question to the seller, who will most often answer that “the fish was brought in the morning.” He will not say exactly how long the fish spent traveling from the place of catch to the counter. Moreover, you will not understand this even if you look at the documents accompanying the fish. But a superficial knowledge of geography and fishing will help you avoid running into falsification. It is enough to look at the fish itself and touch it.
Tips for fisherman: How to choose trout with caviar based on appearance - Answers for beginners
Professional advice: the simplest and most obvious signs of how to distinguish fresh fish from stale fish
The surface of the fish must be clean, without damage, only slight bruising of scales is allowed. The scales on the body of fresh fish are naturally colored, shiny, hold tightly, and there is no mucus. The body of stale fish is dull or completely dull, the scales are knocked down in places, do not hold tightly, and fall off easily.
An unpleasant fishy smell should also alert you. Fresh fish of normal quality smells of the sea, fresh clean water or ozone, or has no smell at all.
The back and muscles of fresh fish are dense to the touch, the dimple from the pressure of a finger quickly evens out, leaving no marks. The meat of stale fish is darkened, easily separated from the bones, the pit is sluggish under finger pressure and slowly levels out. We look at the abdomen. It is not swollen in fresh fish. In stale ones, it often bursts with or without prolapse of the insides.
And now the simplest thing is to put the fish on your hand or lower it into the water. If the fish does not bend in the palm of your hand and sinks in the water, it is fresh. If it does not sink in the water, but when placed on the hand it bends in an arc, then the fish has gone rotten. You can use a spatula instead of your palm. It is from this absolutely precise point of view of GOST that we continue to examine and feel the product.
Wild species of ocean trout from sea waters go to spawn in mountain rivers and lakes. The males go first to prepare spawning grounds, as with all wild salmon. Males, like all males in nature, are much larger than females, and have a very formidable, intimidating appearance, and also, for their size, they have enormous strength, it is not for nothing that during their journey to spawning grounds, all river species of fish hide in secluded places.
Trout belongs to the salmon family of fish. You can distinguish salmon fish by the adipose fin on top near the tail.
I believe there are two types of trout. This is a freshwater river trout, a very valuable and beautiful type of fish. And very tasty, by the way. There it is possible to distinguish a male from a female only at autopsy. The female has mature or embryonic eggs in her abdomen, and the male, respectively, has milt.
But there is a second type of salmon trout - wild ocean trout, which was cultivated and bred in special reservoirs.
Wild species of ocean trout from sea waters go to spawn in mountain rivers and lakes. The males go first to prepare spawning grounds, as with all wild salmon. Males, like all males in nature, are much larger than females, and have a very formidable, intimidating appearance, and also, for their size, they have enormous strength, it is not for nothing that during their journey to spawning grounds, all river species of fish hide in secluded places.
Unlike females, which are much smaller, have a round nose and do not have a nuptial plumage, male beres dress in nuptial plumage during spawning, these are multi-colored stripes, and, most importantly, they have a huge head ending with a humpbacked nose and a mouth with large fang teeth .
They say that you can look at the heads! I even took a photo of them and thought it didn’t help to compare them, but it’s a little smaller in females (but in relation to the body!) and when there’s one or two fish it’s hard to compare. When they just bring it and there are a lot of them, then it helps (there is something to compare the brightness and heads with)
Posted on 03/05/2018
What to always buy with caviar..
old higher new higher rated
more than a month ago
A funny folk game “Buy trout with caviar.” Answering the question, what would always be with caviar? No way, this is from experience, but to increase the chances of buying trout with caviar, I can tell you how it was for us.
We sell fresh local trout all year round (rainbow trout is what they call it in my opinion). You can buy caviar only in April-May. Caviar is what fish reproduces with (spawning), and fish cannot have caviar all year round!
The age of the fish and the weight (I’m talking about the rainbow fish that are bred on farms) is from 1.5 kg and above, and it is in April-May with a protruding belly, a bright red scarlet/crimson stripe and light scales, and males have bright fins, females do not .Here the chances are high, but buying every week (we eat fish often) it was like everything was as described above, but there was no caviar! The fish had already released the caviar and the stripes became faded and the cup was missing in places.
They say that you can look at the heads! I even took a photo of them and thought it didn’t help to compare them, but it’s a little smaller in females (but in relation to the body!) and when there’s one or two fish it’s hard to compare. When they just bring it and there are a lot of them, then it helps (there is something to compare the brightness and heads with)
But there were heads like females and a large belly and color, but no caviar (as the locals say, fish do not rest every year and go to spawn, there are such things, it turns out). So, in principle, it’s always not possible. And age is important (sexual maturity!) otherwise You can catch up on the weight and feeding conditions and the conditions of detention, but if the age does not apply, where will the caviar come from?!
Tips for fisherman: How to make lightly salted trout at home - Detailed review
As for the frozen/imported one, I would choose the largest of the lot in size, with a small head (small teeth / but in comparison with others), even scales, a large belly. And if it was caught during the spawning period and it has not yet had time to release eggs, then maybe and you'll be lucky.
Schools of large trout have fewer brethren. Adults hunt alone, finding the best places and protecting their area from competitors.
Talgar, st. Abay (up 3 km.)
Copyright © 2021 | Subject of copyright
Several species of salmon, including 19 subspecies, are called trout. The most famous: rainbow, lake, brook and brown trout, as well as char.
It is capable of reaching speeds of up to 16 km/h. The trout escapes from the predator by jumping out of the water to a height of up to 2 meters, while its speed exceeds 30 km/h.
Schools of large trout have fewer brethren. Adults hunt alone, finding the best places and protecting their area from competitors.
Interestingly, for some reason trout do not like the moon. According to rumors, trout do not hunt and “do not walk” on a moonlit night. Scientific explanations for this phenomenon have not yet been found.
However, there is also a pattern in its behavior - trout comes out to feed (hunt) at dawn and dusk, and prefers to hide during daylight hours. For places of shelter where it stops, it chooses areas near depressions and rifts. There, the trout positions itself with its muzzle against the flow of water, counting on prey accidentally brought by the water. In this position, it is easiest for the fish not to be spooked and not to miss it.
Trout is a very interesting fish, which is good not only on a plate, but also, first of all, on a hook: belonging to the salmon family, when caught it shows remarkable dodging abilities, being considered the most valuable trophy for an angler. Trout fishing is extremely popular in many countries as sport fishing.
Description of trout
The trout's body is slightly flattened laterally, so the fish looks a little flat. The muzzle is truncated and short. The standard size of trout is from 25 cm to 35 cm in length and from 0.2 kg to 0.5 kg in weight. The largest specimens of trout are found in Karelian streams and rivers, which are rich in food - some trout individuals can reach from 1 kg to 2 kg of body weight (a record weight of 5 kg is also known).
The trout has teeth on the vomer: two rows - on the palatal part of the vomer handle and three or four teeth - on the back of the anterior triangular plate. The dorsal fin has 910 branched and 3-4 simple rays, the caudal fin - 17-19, the anal - 317, the ventral - 118, the pectoral - 112. The dorsal fins are covered with dots, the ventral fins are yellow.
Trout color
The color of trout is unstable and prone to transitions: from the back its body usually has a greenish-olive tint, on the sides - yellowish-green, with spots of black, white or red (sometimes with a bluish border), along the belly - grayish-white, often with yellow-copper tint. It often happens that there is a predominance of one tone - for example, a dark color that turns almost black, or, conversely, a light color that turns colorless.
Differences between male and female trout
Female trout differ from males in their larger body size, smaller head size and fewer teeth. Consequently, males, on the contrary, are smaller in body, with a large head and an abundant number of teeth. In mature males, the end of the lower jaws is often bent upward, which makes them just as easy to distinguish from females. The meat of both can be colored in different colors - white, yellowish or reddish.
Trout species
Trout is a comprehensive concept that includes several species of fish (all of them belong to the Salmonidae subfamily of the salmon family). Trout is recorded in 3 of 7 genera of the subfamily.
Trout Habits
Trout is a cautious and fast fish that requires increased patience from the fisherman. Distinguished by her excellent eyesight, she perfectly sees everything that is happening on the shore, so it is very easy to scare her. It is extremely demanding and pretentious in relation to water, which leaves an imprint on the behavior of the fish: the habits of trout change depending on the reservoirs and conditions in which it has to live.
However, there is also a pattern in its behavior - trout comes out to feed (hunt) at dawn and dusk, and prefers to hide during daylight hours. For places of shelter where it stops, it chooses areas near depressions and rifts. There, the trout positions itself with its muzzle against the flow of water, counting on prey accidentally brought by the water. In this position, it is easiest for the fish not to be spooked and not to miss it.
What do trout eat?
In terms of nutrition, trout is completely unpretentious, so it grows very quickly. She knows how to find the larvae of any aquatic insects and catch moths fluttering over the river, boldly jumping out of the water. In the spring-summer season (especially in May-June), flying “feed” allows the trout to gain fat again after the spawning period. At this time, its food consists of mayflies.
Where are trout found?
Trout are abundant in the United States, where they are popular sport fishers. A similar situation is observed in Norway. There are even special fishing and tourism centers dedicated specifically to trout. In general, trout occupies a leading position in countries where a large number of mountain rivers flow.
Tips for fisherman: How to cook fish soup from a trout head - What to choose for fishing
Trout habitats
Trout Spawning
Spawning of pied trout occurs at the very beginning of autumn - in September. For spawning, it selects shallow water areas, pebbly and rocky soils and fast currents. The laid eggs reach a diameter of 4-5 millimeters and have a reddish or yellowish tone. It has been noted that during the development of a trout embryo, various deviations from the natural course are most often observed. These include albinism, hermaphroditism, deformities in the form of two-headed individuals, etc.
As a rule, salmon, especially wild salmon, costs significantly more than trout . Yes, the final price that the buyer sees in the store consists of many factors, but it is still better to know about the main differences between these two representatives of the salmon family when planning to buy trout or salmon in the store if you doubt the seller.
Differences
Chum salmon differs from pink salmon in having larger scales and fewer gill rakers. There are no black spots either on the body or on the caudal fin. Secondary sexual characteristics are not as pronounced as in pink salmon.
Summer Amur chum salmon are morphologically different from autumn ones in size - they are noticeably smaller than autumn ones. Biologically, it varies greatly: it enters the Amur earlier than the autumn one, and its course usually stops when the autumn one begins. Summer eggs spawn a month earlier than autumn eggs; the number of eggs is less than that of the autumn eggs. Summer chum salmon in the Amur reach the same age as autumn chum salmon (3-6 years), and also enter the river in the 4th year of life.
The distribution area along the Amur River is also different: summer chum salmon does not rise so high. The main spawning grounds for summer chum salmon are currently: river. Amgun, lake Orel and tributaries of the Amur to the river. Mad. In the Ayano-Okhotsk region and on Sakhalin, as well as on the Amur, the course of summer and autumn chum salmon is well defined, but on Iezo (Hokkaido), apparently, there is a course of one autumn one.
Summer chum salmon are distributed in the northern part of the Pacific Ocean, along the American coast - from the Bering Strait south to San Francisco, along the Asian coast - from Providence Bay (Chukchi Land) to the Gulf. Peter the Great. Chum salmon is found in small quantities in the lower reaches of the Lena, where it is even a commercial item. There are also in Kolyma, Indigirka and Yana. It is abundant in Anadyr, along the shores of Kamchatka (chum salmon is rare on the Commander Islands), along the shores of the Sea of Okhotsk, the Kuril Islands, and Sakhalin. It used to rise to the Amur in masses.
The summer chum form grows more slowly than the autumn form. 88% of individuals in schools of summer chum salmon are almost 4 years old (less than four years, counting from the time the fry hatch from the eggs; males are 63 cm long, females are 60 cm long). In autumn chum salmon, it happens that more than half are five-year-olds.
General information
Included in the order Salmonidae, family Salmonidae. Sometimes in everyday life it is called red fish because of the color of the meat. Other salmon, such as pink salmon or trout, received the same simplified name. In fact, red fish are representatives of another family - sturgeon.
Chum salmon has always been of industrial value, especially for the peoples of the Far East. In the second half of the last century, the number of red chum salmon greatly decreased due to uncontrolled fishing. The state took her under protection and now the situation has changed dramatically for the better.
The life of a fish is divided into two main stages: before and after puberty. Young individuals live in the seas, often near the coast.
When a fish becomes an adult, its habitat and behavior change greatly. She becomes more aggressive and gathers in large schools. To lay eggs, they need to make a difficult journey to the mouths of rivers, and then to their upper reaches. Usually you have to move against the current. After spawning, the chum salmon dies.
The fry are in fresh water for the first time. When forces appear, they go to sea, and the cycle repeats again.
Appearance
What a chum salmon looks like depends on its age. Its appearance changes greatly after ripening. Until this time, it has an elongated shape, a massive body, and a silvery color, for which another name for chum salmon is received - silverfish.
After ripening, the color of the scales becomes brownish-yellow. Other changes in chum salmon include:
- Purple spots appear on the body.
- The scales become rougher, the skin becomes thicker.
- The body becomes wider.
- The shape of the jaw changes. The teeth increase in size and become curved.
- At the moment of spawning, the color of the fish turns black. It is no longer suitable for fishing.
- This is a big fish. As a rule, adult individuals are 0.5−0.7 m. The largest known specimen is 1 m and weighs 16 kg. However, these are official data. In the Khabarovsk Territory, local residents claim that from time to time in the Okhota River they come across specimens measuring about 1.5 m.
Habitats
Lives in the Pacific Ocean . Chum salmon goes to spawn in fresh rivers:
- Far East,
- North America: from California to Alaska,
- Asia.
For moving from salty sea waters to fresh waters, the fish is called migratory. Prefers the northern part of the ocean near the Kuro-Sivo current. The area includes the seas:
- Beringovo,
- Okhotsk,
- Japanese.
The fish is found at a depth of up to ten meters. In the spring, it gathers in schools and moves towards the fresh water bodies of Canada, the USA, South Korea, and Japan. It can often be found, for example, in the Sea of Okhotsk basin, in the following rivers:
- Lena,
- Indigirka,
- Kolyma,
- Yana.
Spawning process
Schools are divided into sexually mature individuals and those who are not yet ready to reproduce. The latter head back to the coast. The salmon, ready to spawn, move on.
The fish reaches sexual maturity at about four years of age. Chum salmon can spawn in summer and autumn. In warm weather, this occurs from August to September. River places are selected by fish very carefully. Usually there is a weak current and pebbles at the bottom.
If the water freezes to the bottom, the fry will die. The autumn chum salmon also takes this into account, so it chooses places where there are underground springs nearby. Moving water does not freeze to the bottom.
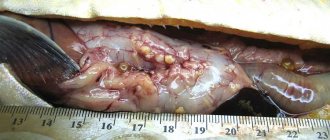
The caviar is large, approximately 7.5 mm in diameter. Females carefully prepare the place and level the bottom. After throwing, the eggs are carefully covered on top with pebbles and gravel. The resulting hills are 2-3 meters long and 1.5-2 meters wide. At this time, the males drive the fish away so that they are not tempted to feast on the eggs.
Chum salmon nutrition
After spawning, the chum salmon dies and becomes food for its fry. The emerging young also feed on insects . Then the diet includes:
- shellfish,
- smaller fish, such as smelt or herring,
- crustaceans.
During the last trip to the spawning site, the chum salmon does not eat anything. The digestive tract does not work and atrophies. It is believed that she thereby protects the offspring from potential threats. At this time, regular baits do not work. The exception is live bait or artificial bait.
Industrial significance
Compared to other salmon, there is a lot of catch of Far Eastern chum salmon. In terms of catch volume, it is second only to pink salmon. It is mined using nets:
- at or near river mouths,
- in other areas where industrial mining is permitted.
Seasonal enterprises often appear near the fishing site. They allow you to reduce costs and better preserve the product.
Nutrition
During the freshwater period of their life, chum salmon fry feed on aquatic organisms that live on the bottom. During downstream migration, juveniles eat small aquatic invertebrates. It feeds very actively and gains up to 2.5-3.5% of body weight per day. In rivers, competitors of juvenile chum salmon are juveniles of grayling, whitefish, whitefish, minnows, sticklebacks and smelts.
In the sea, small immature chum salmon (30-40 cm long) eat copepods, amphipods, fish (juvenile flounder and gobies, anchovies, sand lance, smelt, herring), pteropods, tunicates, ctenophores, euphausiids and juvenile squid.
Reproduction
Chum salmon enter rivers at the 3-10th year of life; 4-6 year olds take part in reproduction. It enters the Amur in masses. Among the fish entering the Amur Estuary and the mouth of the Amur, fish with not yet fully mature reproductive products predominate. These fish - silverfish - have a shiny, silvery color without spots; The meat is fatty and pink in color. Silverfish are very similar to sockeye salmon; fishermen distinguish them by appearance mainly by the caudal peduncle, which in chum salmon is thinner and higher. A few days after the chum salmon enters the river, as it approaches the spawning grounds, its appearance begins to change: the shiny, silvery color of the chum salmon disappears, the color becomes brownish-yellow, and the back darkens.
Development
The fry hatch on the 69-108th day after fertilization of the eggs. They begin to feed even before the yolk sac is completely absorbed. 2 months after hatching, the fry grow in length to 3-3.5 cm; they have 8-11 dark spots visible on the sides of their bodies. On the 152nd day, the juvenile chum salmon grows up to 4 cm. The juveniles that have escaped take longer to fatten in the rivers than other salmon species. At the beginning of migration from spawning grounds in May - June, the length of downstream juveniles is up to 31-40 mm, weight from 188 to 457 mg (values vary depending on feeding areas). During the migration period, juveniles form small schools capable of performing passive and active migrations. When coastal shallow waters warm up to 14°C, intensive migration into sea waters begins.
What does salmon look like?
The appearance of salmon has several common features that are characteristic of the description of all representatives of salmon:
- The body of the fish is elongated, flattened laterally.
- The head is small in comparison with the overall length, the eyes are small, the large mouth is sloping downwards.
- Between the dorsal fin and the tail there is a small adipose fin.
You can distinguish salmon from other varieties by the following characteristics:
- In sexually mature individuals, the lower jaw has a hook-like protrusion, and the upper jaw has a characteristic depression.
- The pectoral fins are located well below the midline, the caudal fin has only a small notch.
- The scales of salmon are small, silver in color, the back has a greenish or gray tint, and the belly is light, almost white.
- Along the entire body above the midline of the salmon, small black spots are visible, the shape of which resembles the letter X.
The color of salmon changes noticeably during reproduction. The fish acquires a bronze tint, in addition to black spots on the back, orange and red dots appear, and the shade of the fins becomes more intense.
The male salmon differs from the female in its more massive jaws, size and head shape. Females have fewer teeth, they are even and identical; males have sharp, different lengths and grow in different directions.
Size and lifespan
Salmon is considered one of the largest representatives of salmon. Fish that live in the ocean or sea reach their maximum size, since that is where they have a sufficient amount of food. In addition, salt water accelerates metabolic processes, promoting more intensive growth and weight gain.
The largest salmon grown in the sea weighs 40-45 kg, and its length can reach 1-1.5 m. Individuals inhabiting freshwater reservoirs are smaller in size, their weight, depending on the availability of food, can range from 5 to 15 kg.
The average lifespan of salmon in its natural habitat is 12-15 years. When artificially reared, fish reach marketability and the required weight at the age of 3 or 4 years, depending on the conditions of detention.
How to distinguish salmon from trout by appearance
Not all commercial red fish are valued equally. There are often cases when unscrupulous sellers try to pass off cheaper varieties of salmon, most often trout, as salmon.
How can you differentiate between these two types of fish?
If salmon and salmon are sold whole, their main difference is their size. Thus, the average weight of trout usually does not exceed 1-2 kg, while a salmon carcass, depending on the place of catch, can weigh 5-10 kg or more. In addition, trout can be distinguished by a soft pink stripe that stretches from the head to the caudal fin along the midline.
When comparing fillets of these types of fish, the differences are practically unnoticeable. The variety can be determined only after cooking the meat: trout becomes lighter during heat treatment, while salmon’s flesh color remains the same. Salmon tastes more pleasant and juicier, since its fat is evenly distributed throughout the body, and not just near the belly, like trout.
Economic importance
Chum salmon is a very important fishery target. In Russia, chum salmon are caught during the run in summer (July-August) and autumn (August-September). It is obtained on the approaches to rivers and in the rivers themselves, mainly with fixed, cast seines and floating nets.
Chum salmon is the second most important species after pink salmon on the mainland coast of the Sea of Okhotsk. More than half of the total chum salmon catch is salted in various ways. Its caviar is especially prized. The waste obtained from cutting chum salmon is used to make feed fishmeal and fat. The hides are used to make shoes and haberdashery goods. Chum salmon is an object of artificial fish farming.
Literature: 1. Lebedev V.D., Spanovskaya V.D., Savvaitova K.A., Sokolov L.I., Tsepkin E.A. Pisces of the USSR. Moscow, Mysl, 1969 2. L. S. Berg. Freshwater fish of the USSR and neighboring countries. Part 1. Edition 4. Moscow, 1948 3. Chereshnev I.A. Freshwater fish of Chukotka. – Magadan: NESC FEB RAS, 2008. – 324 p. 4. A.N. Makoedov, M.I. Kumantsov, Yu.A. Korotaev, O.B. Korotaeva. Commercial fish of inland waters of Chukotka. M.: UMK "Psychology", 2000. 208 p. 5. Atlas of freshwater fish of Russia: In 2 volumes. T.1. / Ed. Yu.S. Reshetnikova. -M.: Nauka, 2003. – 379 pp.: ill. 6. Commercial fish of Russia. In two volumes / ed. O.F.Gritsenko, A.N.Kotlyar and B.N.Kotenev. - M.: VNIRO publishing house. 2006.- 1280 p. (Vol. 1 – 656 pp.).
Oncorhynchus keta
Walbaum, 1792
Chum salmon
[1] [2] [3] , or
chum salmon
[2] [4] [5] (from Nanai keta -
fish
[2]; lat. Oncorhynchus keta [5]) - one of the most widespread among salmonids (second place after pink salmon) and the most common species of anadromous fish of the salmon family [6]. Valuable fishery object.
Varieties
Ichthyologists distinguish 2 independent forms of chum salmon: Asian and North American. They do not overlap geographically, choosing different places for spawning and living until sexual maturity.
An Asian taxon occurs in Russia. Regional subspecies of such individuals:
- Sea of Okhotsk - lives in the northeast, as well as in the southern part of Sakhalin;
- Amur - found in the northern part of the Tatar Strait, other habitats - Zeya, Amgun, Bikin;
- southern - lives in Kunashir, Primorye;
- Sakhalin - in the southwestern part of Sakhalin;
- northern - in Chukotka and Kamchatka.
What is chum salmon of the autumn and summer races?
During spawning, individuals are divided into autumn and summer. The summer one spawns from August to September. And autumn chooses those places where springs are located.
Description [edit | edit code ]
The maximum recorded body length is 100 cm, weight is 15.9 kg; life expectancy is up to 7 years [7]. According to other sources, the largest specimen of chum salmon was recorded in Alaska - 109 cm long with a body weight of 20.8 kg [6].
There are 19-25 gill rakers, 12-15 gill rays, 135-185 pyloric appendages.
Female chum salmon in “nuptial” coloration.
Females and males of chum salmon.