Types of feed
Feeds are divided into artificial (granulated feed and feed mixtures) and live (account for 25-25% of the fish diet and includes natural live feeds). They are also divided into other criteria, which are described below.
By composition
The food must be selected according to its composition - it must contain certain nutrients and microelements.
- Proteins occupy an important place in metabolism. The protein content in the diet should be from 30 to 60% of the total amount of dry food. It is especially important to provide the right amount of protein to young animals. It contains essential amino acids and their absence can lead to decreased growth and disease. Protein foods include beef heart, chicken eggs, fresh frozen and boiled fish, shrimp and krill meat.
- Fats are the main source of energy, their deficiency will lead to a decrease in growth rates and cause physiological disorders. The need varies depending on the type of pet (for example, for carp - 1%, for eel and trout - no more than 0.5%). Fat is contained in various seeds (flax, for example) and cake.
- Carbohydrates - the amount should not exceed 25%, which is a complete source of energy, but the need for different types of fish is different. For example, for carp or eel, a high fiber content threatens to slow growth and increase the fat content of the meat. Also, the amount of carbohydrates should be calculated not only by breed, but also by age of the fish. Contained in plant and grain raw materials.
- Minerals – some minerals (calcium, phosphorus, chlorine) are obtained by fish from the water. The rest must be given to them artificially, carefully selecting elements of the diet. If there is a slight lack of minerals, then this affects the growth rate, but if there is a severe deficiency, then this ends in a decrease in appetite or even the death of the young. Fish get minerals from plants and algae.
- Vitamins - all vitamins are responsible for certain processes in the body - vitamin A controls the state of metabolism, D is responsible for the formation of bones, E - promotes the formation of caviar. But vitamin B is considered especially important, with the help of which proteins and carbohydrates are absorbed. The source of vitamins is live food - insects, crickets, dodrophila flies.
Depending on the type of fish
Fish have their own feeding habits - some feed in the upper layers of water, others in the lower, and others in the middle. And it is on the basis of these physiological characteristics that feed is selected:
- Fish are surface feeders - feed them food in the form of chips, sticks and flakes as they are light in weight and help keep them afloat.
- Fish in the middle layers of water can also eat cereal and chips, because when wet they become heavier and sink lower to the bottom. Another solution is pellets, as they sink slowly, allowing the fish time to eat them.
- Fish on the bottom - eat pellets, tablets and wafers. They are heavier than chips and immediately begin to sink to the bottom.
By manufacturer
When choosing food, you should pay attention to high quality food that has proven itself in the market. Some of these foods have a healing effect:
- Tetra is a leader in the production of products for aquariums and garden fish farming. The following types are offered for cold-water fish: Tetra pond sticks – universal food for pond fish in the form of floating sticks. The price varies depending on the packaging of the feed. For example, a 1 liter jar (that’s 100 g of food) costs 250 rubles.
- Tetra pond sticks mini – granulated food for small pond fish (up to 15 cm) and fry. The price is about 350 rubles for a 1 liter jar (this is about 135 g of food).
- Tetra goldfish (Goldfish, Goldfish Granules, Goldfish Pro, Goldfish Color, Goldfish Energy Sticks) – flakes and sticks for goldfish. Price - from 50 to 3,500 rubles, depending on packaging and type of food (for example, for a jar with a capacity of 1 liter you will need to pay 700-1,000 rubles).
- Tetra pond holiday is a “long-lasting” food for pond fish during holidays (provides fish with nutrients for 14 days). Price – 260 rubles for 98 g.
- JBL NovoRed – food in the form of flakes. Price - from 700 to 1200 rubles per jar with a capacity of 1 liter (190 g of feed). JBL NovoRed refill will cost much less , which is sold in a spare package at a bargain price (450 rubles for 750 ml/135 g).
- Aller ArtEx is a premium food for sturgeon, whitefish and pike perch.
Aller Parvo EX is a starter food for carp.
A 25 kg bag costs from 2300 to 5500 rubles.
Growing fish in the country: what types to choose
Each type of fish requires not only certain feeds and conditions, but also breeding technology.
- Carp
The easiest way is to introduce yearlings into the pond in the spring and catch them in the fall. But if it is not possible to buy grown-up young animals, the pond is stocked with fry and raised using the method of breeding commercial fingerlings.
When independently breeding carp from fry, it is necessary to equip several types of ponds for spawning, rearing of young animals and winter maintenance. Breeding young animals is a great way to save money on the purchase of ready-made planting material.
Note: The most suitable carp breeds are those that are common in the region of your homestead. For example, in the south it is better to grow the Stavropol and Krasnodar varieties, in a temperate climate - Parsky and Central Russian, and in the north - Sarboyan and Altai.
Since female carp are highly fertile, only a few males and females are needed for full breeding. As a rule, fish are used for spawning for no more than seven years. Producers are kept separately from other fish. In addition, during the spawning period they need to be fed intensively. Only high-quality males and females without defects are suitable for breeding.
Note: It is difficult to determine the sex of carp. This can only be done in sexually mature individuals and only during the spawning period. At this time, in females, the genital opening becomes enlarged and red, and the abdominal cavity becomes soft. During the spawning period, males develop warts on their gills and head.
The productivity of spawning depends not only on the quality of males and females, but also on the preparation of the reservoir. Since carp lay their eggs in the substrate, the bottom should be covered with soft vegetation, turf or pine needles. Sometimes artificial spawning grounds are set up. The water temperature should be no higher than 18 degrees. Females lay eggs and males fertilize them. The caviar matures in 3-5 days, depending on the water temperature. The optimal figure is 18-26 degrees.
For normal growth of young animals, it is necessary to provide them with good protein food: small crustaceans, insect larvae, etc. Since quite a lot of larvae hatch from one nest, after they grow up, they need to be seated, since the natural food base of the pond will not be enough.
Recommendations for breeding carp also include:
- When purchasing fry, you must first keep them in water for a while for transportation, and only then transplant them into a new pond. This is necessary to equalize the temperature. If this is not done, the fry will experience temperature shock and die.
- Slaked lime should be added to the pond to normalize acidity and prevent disease.
- Regular application of mineral and organic fertilizers contributes to the formation of a natural food base. However, when adding too much manure, the hydrochemical composition of the water deteriorates, so organic matter must be supplemented with mineral fertilizers (nitrogen and phosphorus). They must first be dissolved in water. But if the pond is intensively overgrown with algae, fertilizers are not applied.
- Special ponds should be prepared for wintering. If the reservoir is covered with a thick crust of ice, its depth should be about two meters. The water needs to be further aerated by making holes or connecting compressors. If possible, clean water can be added to the pond. In winter, carp are not fed, as at low temperatures they stop feeding. In the spring, the carp begin to be fed, and the amount of food supplied in the summer reaches two times a day. In addition, the fish must be caught gradually. Reducing the number of individuals will help to grow higher quality products.
Young carp need additional feeding. Food is introduced once or twice a day. The number of feedings is increased as the water temperature rises.
Note: You can determine the need to apply fertilizer using a white disc. It is immersed in water to a depth at which it will be visible. If the visibility line is at a depth of 25-30 cm, fertilizers need not be applied, but if it is more than 50 cm, the pond is fertilized.
When growing carp, you need to control the size of the fish by conducting control catches. The fish are measured, weighed and released back into the water. If individuals begin to lag in growth, the water quality, food supply and oxygen content should be checked.
- Goldfish
This is a fish that is unpretentious to water quality and can be bred in a wide variety of water bodies. Usually crucian carp feed on small crustaceans, but the natural food supply can quickly become depleted, so additional mineral and organic fertilizers should be applied. This stimulates the formation of food, since crucian carp does not consume artificial food well.
In winter, crucian carp do not feed, and food consumption begins only after the air temperature rises to 6-8 degrees. Of particular value is the hybrid of silver crucian carp and carp, which is distinguished not only by its resistance to living conditions, but also by its undemandingness in feed.
- White amur
It can be grown either alone or together with other fish that feed on vegetation. Planting density depends on the amount of aquatic vegetation. If the pond is moderately overgrown, you can grow 1-2 fish per 10 square meters. If there is a deficiency of vegetation, artificial food is introduced, but cupid eats it much worse.
- Silver carp
It can be grown at high densities. This is explained by the fact that silver carp eats mainly aquatic vegetation. For full growth, individuals need not only a good food supply, but also a favorable regime. The water temperature should be 25-27 degrees, and the oxygen level should be at least 5 mg/l.
Typically, ponds for silver carp should not be deep. The penetration of sunlight into the water column not only promotes warming, but also stimulates the growth of algae.
- Bighead carp
Unlike white carp, bighead carp feeds on zooplankton, not algae, although the growing regime for these varieties is the same. Considering that there is usually more algae in ponds than plankton, the stocking density of bighead carp should be less than that of white carp. However, it can be grown together with carp without the risk of food competition.
- Rainbow trout
Grows and develops quickly in cool, oxygenated water. The optimal temperature is 14-18 degrees. The fish feels good even at lower temperatures, but if it exceeds +22 Celsius, the trout stops feeding and growing.
Ponds for trout must be flowing, but they can also be raised in cages or pools. Spawning is stimulated artificially by collecting eggs and sperm. Subsequently, dry or semi-dry insemination is carried out (Figure 1):
- When dry, the caviar and sperm are mixed, poured with water (so that the liquid covers the caviar), mixed again and washed after 5-10 minutes. After this, the caviar must be left in water for 3 hours to swell.
- In semi-dry, the sperm is diluted with water and added to the eggs immediately before insemination. The products are immediately mixed, and when the caviar swells, it is transferred to a special incubation apparatus. Water is constantly supplied to it. Hatching occurs in approximately 5-7 days.
Figure 1. The procedure for inseminating trout eggs
The incubation apparatus must be covered, since the larvae do not tolerate light well. The fry are transferred to the pools after the gall bladder has completely dissolved. Examples of incubation apparatus for hatching trout fry are shown in Figure 2.
- Peled, pelchir
These are demanding fish, preferring cool reservoirs with oxygen-enriched water. Preference should be given to flowing reservoirs, but fish can also be grown in stagnant ponds, but care must be taken to ensure that the water contains a sufficient amount of oxygen (6-7 mg/l).
- Sturgeon
They can be grown in small ponds, pools and cages. They must be flowable, and the slopes must be strengthened. The fastest growing species are beluga, bester and paddlefish, which is why they are mainly bred in homestead farms.
- Som
Growing channel catfish is economically profitable. It adapts well to various growing conditions, is undemanding when it comes to feed and grows quickly. When introducing artificial feed, preference should be given to foods rich in protein. In addition to ponds, catfish can be raised in pools and cages, but a more intensive feeding regime should be provided.
- Pike
This is a predatory fish that increases the productivity of water bodies. If there is enough food, pike can be raised together with crucian carp or crucian carp. As a rule, the stocking density is 2 individuals per 100 square meters, but if there is a lack of feed, the stocking density should be reduced.
- Buffalo
Heat-loving fish, ponds for rearing which must meet standard requirements for ponds for herbivorous species. Buffalo feeds on aquatic vegetation, and to achieve a good weight of individuals it is necessary to provide a complete food supply.
- Acne
One of the most valuable species due to its high taste. In addition, eels are quite easy to breed. The larvae are caught in the coastal waters of natural reservoirs and transplanted into ponds. Planting density can reach 2 thousand individuals per square meter. The larvae stay here for about a month, after which they are sorted by size and placed in different reservoirs.
Figure 2. Examples of incubation apparatus for hatching fry
When grown in pools, the fish will be ready for sale after 3-4 months, but for this, high water flow and good aeration must be ensured.
- tilapia
In temperate climates, tilapia can only be grown in artificial reservoirs with controlled temperatures. If this condition is met, further breeding of tilapia is not difficult. They multiply quickly and easily, tolerate transportation well and are not very demanding when it comes to feed.
In addition, tilapia can be bred together with other fish that feed on aquatic vegetation.
From the video you will learn how to properly incubate eggs and keep fry.
How to choose the right food for your fish?
If your choice falls on ready-made food, then you should understand that not all of them are the same and healthy, so you should pay attention to some characteristics:
- Purpose of feed. Take balanced food for pond fish, not aquarium fish;
- Balance. The food must be balanced and include proteins, minerals, and vitamins to ensure healthy and complete nutrition.
- Digestibility. The diet you choose should be well absorbed and promote good digestion, as this will help keep the water clean for a longer time.
- Components. They must be selected, so there is no need to buy economy-class food made from low-quality raw materials, since this does not provide any nutritional value for the fish and accelerates water pollution with organic matter and the growth of algae due to poor digestibility.
- Package. You should not purchase food in bulk or in damaged packaging, as there is no guarantee that such food remains fresh or of high quality. The packaging must be made of dense material, not allow light to pass through and have a lock;
- Immune protection. Particularly useful food for fish are those that help increase the body's defenses.
Protein as a source of fish growth
The protein content in fish food should be optimal because it is the basis for starting a full metabolic process. The amount of protein for fish as a percentage of the total dry matter of the diet should exceed this figure established for farm animals. Fish require two to three times more protein than mammals. The volume of this element is 35 - 60% of the total diet.
Young fish especially need a large amount of protein, as it contributes to their intensive growth. If we consider how much protein is required using the example of carp, then young fish whose weight does not exceed 1g will need from 13 to 59 grams of protein per day, with a weight over 1 gram the calculation is as follows: from 4 to 7 g of protein per kilogram of body weight fish individual.
The benefits of protein for fish are explained by the richness of its composition. It contains several unique amino acids:
- valine;
- threonine;
- methionine;
- lysine;
- arginine;
- histidine;
- phenylalanine tryptophan;
Each amino acid performs a specific function - transport or construction. The experiment showed that with a lack of amino acids, within 14 days the fish's appetite is disrupted, growth is stunted and various fish diseases occur.
Calculating the optimal amount of protein in the diet is not difficult if you pay attention to the temperature conditions at which the fish are kept. So, at an average temperature of 8°C, a protein content of 40–42% of the total dry matter mass of the diet will be sufficient. An increase in temperature to 15 degrees necessitates an increase in the amount of protein to 52 - 55%.
Features of feeding
When growing fish in a pond, the feed requirements are slightly lower, because in natural reservoirs there is natural food that needs a little supplementation. Typically, fish food is introduced in the form of granules, briquettes or dough-like mass. Pay attention only to granules or briquettes, as they have high moisture resistance, while the dough-like mass will soon lose half of its useful substances.
In early spring, when the fish wakes up, feed it more nutritiously than in summer. In hot weather, the fish do not eat as much, as they can find food in the pond itself. And in the fall, when the water temperature drops below 10 degrees, stop feeding the fish completely, since in winter most species go into a dormant state.
How to feed fish correctly?
While the feeding process is taking place, you need to observe how the fish eats the food. The amount of food should be such that there are no leftovers. If what the fish were unable to eat accumulates, then the feeders and pond need to be cleaned, otherwise the remains will begin to decompose and contribute to the development of pathogenic microorganisms.
The state of appetite is assessed about 40-60 minutes after the food has been distributed.
Rules
In order for feeding fish to give the desired result, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Don't just throw dry food on the bottom of the pond. Add a little water to it and make the consistency of a thick dough, and only then add it to the pond.
- Feed the fish at the same time to develop their reflex.
- When feeding in the evening, add lighting so that the fish begin to reflexively react to this light, which will simplify the catching process in the future.
- Provide the feeding area with a metal tray made of galvanized iron and equip it with a lifting device. This is necessary in order to raise and lower the tray into the pond at any time and monitor the process of eating food. You can also regulate the amount of food dispensed and ensure that the food does not begin to rot or sour, which will help maintain the purity of the water.
More information about feeding pond fish is written here.
Compliance with conditions
Feeding fish in a pond depends on a large number of factors, which include:
- Water temperature - in the summer months, if there is a large natural food supply, feeding occurs 2-3 hours after the sun rises. The water temperature should be from 12-15 degrees and above;
- Age – Fledglings need to be fed twice a day – morning and evening, in small portions. Two-year-olds are fed once a day - in the morning.
- Eatability - in order not to overfeed the fish, you need to monitor the rate of food disappearance. If the food is eaten too quickly, it means the fish are not getting the amount of food they need. If the food remains untouched for three hours, then it is worth reducing the norm.
Feeding the fish in your pond
Of course, carp and crucian carp released into the pond must be fed periodically.
Although the water in a small pond contains some natural food base in the form of daphnia, bloodworms and other small animals, this fish food in a small pond is unlikely to be sufficient to ensure the required weight gain in your pets. Therefore, you need to be a hospitable and generous owner, providing the necessary ration of additional nutrition “at hand” for the inhabitants of your pond in order to ensure the desired result of fish farming. The solution to this problem is made easier by the fact that carp and crucian carp are not picky about food and are omnivores. For complementary feeding, plant foods and feed for pigs or chickens are suitable. Excellent plant food for carp fish are: flour, bran, lupine, corn, vetch, rye and boiled potatoes. There is a tradition of going to Akhtuba for fish. You can read about one of the databases here. Your own pond cannot be a worthy substitute for such a vacation.
If you stocked your pond with yearlings, it is enough for them to sprinkle flour on the surface of the water, since it floats on the surface of the water for a long time until it gets wet. Rye can be served raw. Lupine is a legume and therefore, like corn, it is better to grind it coarsely, then they quickly soak in water and carp eat them more willingly. It is better to steam legumes and grains in boiling water. Compound feed should be prepared in the form of balls of thick dough. To create the most economical menu, you need to monitor the growth of the fish. The average consumption of grain feed per fish is no more than 3 - 5% of its weight. Feeding the fish should be done once or twice a day and preferably at the same time. It is advisable to immediately decide on the place of feeding in the pond and it is necessary to prepare a “feeding table” for this. For a small pond, you can use a simple table made of a plastic cover with perforated holes secured with a cord to a fishing rod. The table with food should be lowered to a depth of 30 - 35 cm. Fresh food should be added only to the empty table. The use of a “feed table” allows you to constantly monitor how much food is eaten and remove its excess so as not to spoil the water in a small pond, which occurs when uneaten food sours. The volume of a portion of food must be determined taking into account the water temperature, since the lower the water temperature, the less carp fish consume food. The water temperature favorable for their life is +24° − +26°С. When it decreases to +12°C, their feeding intensity will decrease and they will stop growing. With a further decrease to +4°C, or an increase to +30°C, cyprinids will completely refuse food. Therefore, feeding can begin at the end of April or beginning of May, if the water is already warm enough (usually from mid-May), and it should be stopped around mid-September, depending on the weather.
You need to make so many of these tables in the pond so that the fish don’t get too crowded when feeding. By autumn, carp lose their appetite, so the portions of food should be reduced at this time, otherwise the food will only be wasted and will not be useful to the fish.
The fish that live in the pond eat with great pleasure all insects that fall on the surface of the water. To increase the supply of this free food, you can use night decorative lighting on the pond using lanterns with solar panels, which are placed along the shore of the pond or float on its surface. Most of the insects that fly into the light will become a high-calorie snack for your pets. In addition, such illumination will save you or your guests from unexpected night swimming in the pond.
That's all I wanted to tell you about fish food in the pond and feeding them.
Feeding regimen for different fish
The differentiation of fish by species plays an important role in feeding efficiency, since each food has specific nutritional requirements.
Carp
The daily feed requirement for carp breeding is determined by the weight of the fish and the water temperature. If the weight of the carp is up to 0.5 g, then the daily norm is 100% of the weight, if 500 or more, then 2.8% of the total weight.
Fingerlings and two-year-olds are fed pellets, which are placed in special feeders. The young are fed every hour, reducing the amount of food given as they gain weight. Also, the number of feedings decreases when the water temperature drops. You can feed carp with protein food (worms, bloodworms, snails and shells), potatoes, cake and bread, as well as finely chopped soft grass and special feed (which it is advisable to pre-mix in a bucket until a dough-like mass is formed).
If the water in the pond is very warm - 23-26 degrees, then the fish's appetite increases and they need to be fed more often. Feed the young almost every hour. It is enough to feed carp weighing from half a kilo to 2 kg 4-5 times a day. If the water temperature is 22-24 degrees, then the number of feedings reaches 5-6 times a day, if 14-20 degrees, then 4 times a day, and at temperatures less than 14 degrees - 2-3 times a day.
crucian carp
Crucian carp is a fish that is considered almost omnivorous. Nothing will happen to her, even if you forget to feed her, because in reservoirs she will always find the necessary minimum of food, especially if an ecosystem has already formed in the pond.
Crucian carp eat best algae, steamed beans and cereals, worms, insect larvae, and bloodworms. It is not advisable to feed bread.
The amount of feed introduced should be no more than 5% of the weight of the fish. Calculating the norm is simple - if about 30 individuals of 200 grams each live in a pond, then the total weight of the fish is 6 kg, which means that the one-time feed norm should not exceed 300 grams.
Feed the crucian carp 1-2 times a day, at the same time.
Read about breeding crucian carp, including feeding them, here.
Salmonidae
Fish of the salmon family are fed with meat waste, low-fat dry milk, as well as meat and bone, fish and krill meal. These components can be mixed with each other or you can immediately buy ready-made feed, which differ by age group: for example, for fry weighing up to 5 grams, take RGM-6M and S-112-Lat, and for young animals - LK-5P.
Som
Catfish is a special fish, since by the time it begins to eat properly, its stomach and intestines have already developed, which makes it possible to form special enzymes for digesting food. This feature makes the fish less demanding on the composition of the feed - for catfish, SB-1 and SB-3 are usually used, supplementing them with calcium if rearing occurs in soft water.
You need to feed catfish fry 8 times a day, gradually reducing the number of meals to 4 times. The volume of a single dose of food depends on the temperature of the water - the warmer the water, the more food you need to give.
Acne
To successfully breed young fish, you need to monitor the amount of animal proteins in the eel’s food; the more there is, the more intensive the growth of the fish. The young are fed up to 10 times a day in the shaded parts of the pond and use mainly animal feed for feeding. For fish weighing up to 2 grams, the daily norm is 16%, weighing 2-4 grams - 12%, 4-8 grams - 10% and 8-25 grams - 8%.
Sturgeon
Sturgeon need to be given food with a high fat content, this is especially important for juvenile besters. The number of feeding times depends on age: larvae and fry are fed up to 12 times a day, and adult fish - from 4 to 8 times a day.
tilapia
For tilapia, feed of both plant and animal origin is excellent, and protein foods are a priority.
Grain waste, meal and mixed feed are suitable for feeding tilapia. The larvae begin to consume artificial food as soon as they switch to active external feeding and therefore they are excellent for breeding in pools and ponds.
For juveniles weighing up to 50 grams, take feed VBS-RZh-81, RZGK-1, and weighing from 50 grams and above - PK-Vr, RGM-2Ke, etc. The food supply per day is determined based on the weight of the fish.
Feeding pond fish
Artificial feeding
Before populating a pond, it is necessary to determine: how many fish can be planted in each specific reservoir?
This is not an idle question. The answer to this depends on whether your “pets” will receive additional food or not. In general, a fish will always find a certain amount of food in a reservoir, but on natural food it will not fatten up a lot of meat. On average for the season from 1 sq. m of water area, you can get 10–20 g of growth. It's not thick. The natural productivity of a home pond is quite low. If you focus only on it, then each fish should be provided with up to 20 square meters. m of reservoir area. Can everyone afford such luxury? Most likely no. And in order to have more fish from a small area, you need to feed it. Then in a stagnant pond you can get 0.3–0.5 kg of weight gain per square meter. And if, in addition, you saturate the water with oxygen, that is, use aeration, carry out water exchange and other reclamation measures, then you can reap a much larger “harvest.” Thus, when feeding the inhabitants of a home pond, from 0.5 to 5 two-year-olds can be grown on each square meter (depending on their weight).
If you grow silver carp or other phytoplanetophagous animals, then you do not need to feed them in the usual sense, that is, give them food. But it is necessary to create good conditions for the intensive development of phytoplankton directly in the reservoir itself. For this purpose, mineral and other fertilizers are applied. Thus, phytoplanktivores (silver carp and other similar fish) are not fed, but only activate the productive capabilities of the pond.
No additional feeding is required for macrophytophages - for example, for grass carp, when it is grown in polyculture (together with carp and other fish) as a secondary species.
If several species of fish are raised in one reservoir, for example, silver carp and peled (representatives of zooplantophages), then in this case direct feeding is also not required; It is necessary to develop food organisms directly in the pond.
Carp and other benthophages that feed on organisms living at the bottom of a reservoir and in its soil are most often grown as the main species in polyculture. Their planting density is quite high, so the lack of natural food must be covered by artificial food. For this purpose, specialized feed is best suited, and it is advisable to prepare specific food for each type and age of fish.
If you have the means or the fish population is small, you can purchase complete feed. They are expensive and are used in industrial fish farming, when the stocking density is 100–250 specimens per 1 sq. m. m. The requirements for pond feed are not so stringent, so they are 2–3 times cheaper. At the same time, pond food (for example, for carp) must contain the necessary set of nutrients: crude protein - at least 23%, fat - 3.5%, phosphorus - 0.7%, and fiber - no more than 9%.
When growing trout, only complete feed is used. To feed larvae and juveniles weighing about 5 g, they usually take starter feed, then production feed. In addition, trout feed must contain all ten essential amino acids. These are feedstuffs RGM-6M, RGM-5V, RGM-8V (for fish of different weights). In addition to specialized trout feed, you can also feed slaughterhouse waste (meat and animal entrails), low-value fish, krill meal, skim milk and other products.
Sturgeon fish require a higher fat content. In starter feeds they should be 16–20%. Compound feed for bester and its relatives – ST‑4AZ, BM‑1. Like trout, sturgeon can be fed with paste-like feed, the basis of which is minced meat from low-value fish with the addition of fish, blood, meat and bone meal, egg powder, silkworm pupae, and waste from slaughterhouses. You can use up to 20% of loose feed for cattle or pigs, but the effectiveness of such mixtures will be lower than special feed.
If the family budget does not allow the use of specialized feed, then feed mixtures can be prepared at home yourself, using all kinds of cakes and meals, legume waste (beans, peas, soybeans, lentils, vetch, lupine), animal feed (fish, blood, meat - bone meal, dried shellfish meat, silkworm pupae, etc.), waste from grain crops, waste from the flour milling industry (flour scraps, flour dust, bran), food residues and other feed products of plant and animal origin containing proteins (proteins), fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals.
The nutritional value of protein is determined primarily by the quantity and quality of its most important components - amino acids, which are divided into replaceable and essential. Essential amino acids must enter the animal's body along with feed, and non-essential amino acids are formed directly in the body. The absence or deficiency of certain amino acids can lead to disruption of the physiological activity of individual organs and the entire body of the fish (metabolism is disrupted, growth stops, hemoglobin in the blood decreases, etc.).
Feed mixtures for pond fish must be balanced in amino acids. It is recommended to include both animal (fish and bone meal - 5-10%) and vegetable (sunflower and flaxseed meal - 20%) in the diet of growing carp fingerlings. In addition, the fish must be given food rich in vitamins (special substances necessary for the body for normal growth and development) - for example, crushed aquatic or terrestrial vegetation or protein-vitamin paste from it, brewer's grain, waste from vitamin production, etc.
Fresh green vegetation is crushed in a feed crusher and mixed with the main feed (up to 30% of the main mass). Aquatic vegetation in the diet of carp includes duckweed, pondweed, hornwort, etc. At the end of the growing season after the death of aquatic vegetation, green tops of carrots and beets are included in the feed mixture (no more than 20–25% of the bulk weight).
For feeding fish in ponds, cakes and meals are widely used - peanut, castor bean, flaxseed, sunflower, rapeseed, soybean, rapeseed, etc.
Fish food must be fresh and of good quality, since spoiled, sour, moldy, rancid food can cause the death of fish. Store feed in dry, well-ventilated areas.
Feeds differ in chemical composition, calorie content (nutritional value) and feed ratio (a number indicating how much feed must be fed to obtain 1 kg of pond fish growth). First of all, the feed ratio depends on the composition (nutritional quality) of the feed, its content of proteins (proteins), fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals. The feed coefficient varies even for the same feed, depending on the conditions of the aquatic environment (temperature and hydrochemical conditions, etc.), the age and health status of the fish, the quality and method of preparing the feed, feeding technique, etc. For example, the feed coefficient of soybean meal ranges from 3 to 6, cotton meal - from 4 to 7, etc. The feed coefficient of meal is approximately the same as that of meal (for example, flax and hemp - 4, cotton meal - 7, etc. ).
To establish the efficiency of using feed in pond farms, a certain indicator is used - payment for feed, i.e. the ratio of the amount of feed introduced (specified) into the ponds to the weight gain of the fish. The rate of payment for feed increases when feeding fish in thickets of aquatic vegetation, in silted areas of the pond, when the rate is too high, when all the feed is not eaten by the fish in the feeding areas, remains and rots, as well as when the fish becomes sick and unfavorable environmental factors.
The indicator “payment for feed” allows you to assess the correctness of feed consumption from an economic point of view. The feed ratio will always be lower than the feed payment rate, since some of the feed is not used by the fish and is lost in the pond.
To feed fish, various waste from agricultural production, the flour-milling industry, food residues from public catering establishments, etc. should be widely used. Of particular importance are grain cleaning waste, which accumulates on the currents during grain harvesting in the form of defective grains of wheat, rye and other grain crops. This coincides with the period of the most intensive growth of carp, when it especially needs food. Timely use of grain waste contributes to a significant increase in fish productivity of ponds and an increase in the yield of marketable products.
In non-draining, swampy, acidified ponds and overgrown with hard vegetation, feeding fish does not give the desired result. The effect of feeding is also reduced in reservoirs contaminated with “weed” fish, which destroy the given food in large quantities.
When feeding fish, take into account the density of its planting. When it is relatively small, you can feed a relatively uniform food. At high planting densities, specially prepared feed mixtures and feed mixtures balanced in nutrients are provided. Proper nutrition of fish is impossible without the inclusion of various minerals in the feed. Potassium, sodium, calcium, phosphorus, iron and other minerals are necessary for any body. They are used to build the skeleton and are part of the organs and tissues of fish. If there is a lack of these elements in the food, the fish's metabolism is disrupted, abnormal development of bone and other tissues is observed, and growth slows down. All this can lead to illness and even death of the fish.
In some cases, microelements should be added to fish feed - in particular, cobalt salts, which have a beneficial effect on the blood composition of fish, their growth rate and health. The use of cobalt chloride salts in an amount of 0.08 mg (in terms of cobalt) per day per 1 kg of live weight of fish allows you to increase the weight of two-year-old carp by 16–30%, and of fingerlings by an average of 30%.
2 mg of cobalt salts are added per 1 kg of feed mixture in the first half of summer, and 4 mg in the second half of the growing season. Cobalt salts are dissolved in water and the solution is poured into the prepared feed, kneading it until it forms a dough. If there is not enough cobalt solution for mixing feed, add the required amount of water from the pond. The dough-like food is immediately laid out on the feeding areas. Since cobalt salts quickly become saturated with water, they should be stored in glass jars with ground-in lids. The use of cobalt as a fish feed additive is most effective in those geographic areas where there is a deficiency of this element in soil and water.
Growth substances and antibiotics used in animal husbandry are also successfully used in fish farming. When feed terramycin is included in the diet (at the rate of 5-10 thousand international units per 1 kg of feed), the total fish productivity of ponds increases to 220 kg per 1000 square meters. m of pond area. Add 2–5 g of feed terramycin per 10 kg of feed, mixing the mixture thoroughly.
Among other substances that stimulate growth, noteworthy is the protein-vitamin concentrate (synthetic protein), which increases the fish productivity of the pond by 12.4%.
When compiling a diet, it is very important to take into account the protein ratio of the feed (the ratio of digestible protein to digestible nitrogen-free substances), i.e. how many parts of digestible nitrogen-free substances (carbohydrates, fats) are per part of digestible protein (nitrogenous substances). For example, with a feed protein ratio of 1:3, one part of digestible nitrogenous substances accounts for 3 parts of digestible nitrogen-free substances. When calculating the protein ratio, it is assumed that the caloric content of proteins, carbohydrates and fats is different. The amount of fat, as the most high-calorie substance, is multiplied by a factor of 2.25‑2.5.
To determine the protein ratio, you need to know how much digestible protein, fat and nitrogen-free substances the feed contains. The amount of vegetable fat is multiplied by a factor of 2.25, and animal fat by 2.5. Next, the result is added to the amount of nitrogen-free substances. The resulting amount is divided by the amount of protein.
A mineral additive in fish feed mixtures can be rotted sludge - sapropel. It contains vitamins (D, B1, B2 and B12), folic acid, calcium, phosphorus, iron, microelements (iodine, cobalt, manganese, bromine, etc.). Sapropel also contains antibiotics that suppress pathogenic microbes, as well as proteins, carbohydrates, organic acids and other substances. When it is added to the main fish food in an amount of 20%, the fish productivity of the pond increases by 51.9%, and carp fingerlings survive better. Before using sapropel as a mineral additive in fish feed, it is necessary to do a chemical analysis to determine its composition.
The second significant question that invariably arises when feeding fish is: in what form should the food be given?
Until recently, different types of feed were used in fish farming: loose, dough-like, pasted (in the form of a paste), briquetted and granulated. Today, all fish food is produced only in the form of granules or grits (for juveniles). The rest of the food is prepared independently. The fact is that if you introduce dry loose food into a reservoir, it dissipates very quickly and becomes inaccessible to fish. Loose food mixed with water (pasty) does not improve the situation: almost half of it does not reach the fish either. Briquetted feed can reduce nutrient losses by 15–20% compared to paste feed. Briquettes falling into water disintegrate after 1.5–2 hours. During this time, the carp manages to eat most of the given food. However, even in this case, the losses are quite large. Therefore, it is more effective to use granulated feed.
When feeding with granules, the contamination of the pond with food debris is reduced. The overall productivity of a reservoir when feeding fish in this way increases by about 13% or more.
Granular feed can be prepared independently in a meat grinder from a wet (14–18%) feed mixture consisting of sunflower cake ground into flour (70%), hydrolytic yeast (5%), flour mixture (25%) and water (30% to weight of the feed mixture).
Granules for fingerlings are passed through grates with 3 mm holes, for two-year-olds - with 5 mm holes, and for producers - with 9 mm holes. The strength of granules increases when crushed green mass is added to the feed mixture in an amount of up to 30%. Before feeding the prepared pellets to the fish, they are dried, dried for 3–4 hours and laid out on feeding areas - areas located in the coastal zone of the reservoir at a distance of 30–50 cm from each other at a depth of 0.6–1.5 m. Placed under the area a surface with hard soil measuring 2x2 m, clear it of vegetation and mark it with numbered poles. One feeding place is designed for 5 thousand fingerlings in nursery ponds, for 200–250 two-year-olds in feeding ponds or for 20 breeders in brood ponds.
They feed the carp 1–2 times a day at the same time (early morning and evening), spreading the food with a shovel, bucket or special scoop. The palatability of the given feed is checked daily by inspecting the feeding areas (in shallow places). If the fish eats the food well, then the daily norm is gradually increased. If there is a lot of feed left on the site, a new portion is not added, but the reasons for poor feed consumption are found out and eliminated. Most often, fish do not take food if it is of poor quality, the feeding areas are contaminated, the remains of uneaten food have become sour, the water temperature is low, the feeding doses are incorrectly calculated, the fish is sick, etc. If the food is not eaten well, it is necessary to change the feeding places, arranging them in areas largest concentration of fish.
Diagram of the Reflex automatic feeder: 1 – hopper; 2 – feed dividing cone; 3 – hopper hole; 4 – feed cone; 5 – aft table; 6 – ring ejector; 7 – pendulum-rod; 8 – hemisphere with a screw for adjusting the height of the ring ejector; 9 – nut for adjusting the height of the feeding table; 10 – ring ejector limiter
The ideal option is to feed the fish only when it wants it. This problem has haunted many generations of fish farmers. And so, about forty years ago, the first feeders appeared, dispensing food only at the request of the fish itself. Today, the best among them is considered to be an automatic feeder of the “Reflex” type. It is a bunker with food located above the water. Through a hole in the bottom, the food spills out onto the locking table, and the resulting cone of granules closes the hole. On the table there is a ring ejector with a pendulum rod that goes under the water. The fish, having touched it, transfers the movement to the thrower, and he throws off several pellets of food. In order to get a new portion, the fish must push the rod again. The position of the feed table under the hopper opening can be adjusted to position the cone closer to or further from the edge. The fish quickly masters this device. First, the fish farmer himself dumps the pellets. Attracted by the food, the fish begin to frolic under the feeder and touch the pendulum. As a result, a new portion of food is poured out. Very soon they develop a conditioned reflex: if you touch the rod, you will get food.
Aero feeder diagram: 1 – frame; 2 – mesh; 3 – pasty food; 4 – water level
Experience in operating self-feeders has shown that fish do not push the pendulum and do not pour out food simply out of curiosity. If they have no appetite, they will not come to the feeder. The device differs favorably from its analogues in that in order to receive the next portion of food, it is necessary to push the pendulum.
Automatic feeders can be used to feed almost all types of fish. However, there are some peculiarities: for example, feeding salmon requires special adjustment of the table, and for sturgeon, which take food from the bottom, it is necessary to install trays with sides. It is not difficult to make an automatic feeder: a bucket can serve as a hopper, and a wire with a diameter of 2 mm can serve as a rod.
When providing paste-like feed to salmon, you can use an air feeder. It is a floating frame made of wood or other lightweight material, covered with a metal mesh or latex frame with a mesh size of 30–35 mm. The distance from the net to the water should be from 1 to 3 cm when loading it with food, which is placed on top. Falling through the holes of the mesh, it becomes accessible to fish. Moreover, in order to receive food, it must momentarily rise above the surface of the pond.
To accustom the fish to such a device, it is first placed in the water column, then raised to the surface, and then above the water.
Breeding live food
In the early stages, fry and fingerlings are fed with live food - planktonic crustaceans, daphnia. For breeding daphnia, small ponds or daphnia pits with an area of 1–2 square meters are arranged. m and a depth of 5 to 60 cm. You can also use concrete pools, canvas and wooden vats, bathtubs, barrels where the water is heated.
Fresh horse manure is added to such reservoirs or pools at the rate of 1.5 kg per 1 cubic meter. m of water. The next day, live daphnia are planted there (5-10 g per 1 cubic meter of water), caught in nearby reservoirs, pits with water or in puddles, which are located in open places and are well warmed up by the sun. After 8-10 days, manure is added to the reservoir at the rate of 750 g per 1 cubic meter. m of water. In warm weather, on the 18th-20th day, daphnia are caught with nets from a shallow mill basin and transferred to spawning and nursery ponds. In 1 cubic m of water, daphnia can grow up to 1 kg.
If daphnia ponds or pits are located on the shore of a fish pond, then after the planktonic crustaceans mature, grooves are dug and the water along with the daphnia is released into the pond.
For fry and young of the year, the larvae of bloodworm mosquitoes (chironomids) are also grown as the most valuable food for pond fish. To do this, in a pond, near the shore, soft aquatic vegetation is placed in a pile (height and width 1 m) and mixed with manure mixed with soil. When laying heaps, the water should not be heavily polluted with manure. This can affect the gas regime of the reservoir and worsen the conditions for growing pond fish.
The title of the book is Fish and Crayfish. Breeding technology
What determines the effectiveness of feeding?
The conditions in which fish are grown have a direct impact on the growth rate and quality of fish meat. An important point is water temperature - a large number of species increases their growth rate when the water temperature in the reservoir rises. If the readings drop to 0 degrees, then food digestion first slows down, and a little later the process stops altogether.
The quality of food also matters (protein food accelerates the growth of fish) and the amount of oxygen in the water (a value of 1 mg/l is too low for fish, and it stops growing and eating). The big disadvantage of low oxygen levels is the increase in ammonia and nitrate concentrations, which also negatively affects growth.
Take care about the length of daylight hours. Since daylight hours tend to decrease with the approach of colder seasons, it makes sense to use artificial lighting to stimulate the production of growth hormone and improve food digestion.
Keep an eye on the salt level in the water because some fish species can only be kept in either fresh or salt water. The exception is tilapia, as it can grow in any type of reservoir.
To dispense food, use special feeders that you can make yourself. You will find detailed instructions on how to make such a feeder in this video:
Freshwater Aquarium Population
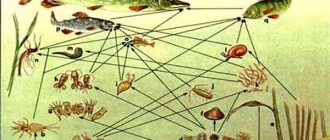
A living ecosystem is a symbiosis of various micro- and macro-level organisms. The ability to coexist and complement each other, thereby forming a constant interaction of all its participants in a closed cycle, biotope.
Nuances of the biotope
According to Wikipedia,
Biotope (from the Greek βίος - life and τtoπος - place) is a relatively homogeneous area of geospace (land or reservoir) in terms of abiotic environmental factors, occupied by a certain biocenosis.
Everything is important in this matter - the chemical composition of water, lighting, temperature, species composition of fish, plants, diversity of zooplankton.
The slightest imbalance leads to changes in the environment, illness and death of “pets”. Therefore, you need not just to contemplate the beauty of the underwater world, but to skillfully care for and maintain certain living conditions of its inhabitants.
If the biotope is a pond, then you need to select fish and plants that are resistant to existing in standing water.
In a river biotope there are wider possibilities, but here too the natural biocenosis must be taken into account.
You cannot interfere with predators and their prey; the little things will simply be mercilessly eaten away.
It is necessary to take into account the volume of the aquarium and the number of fish. They should not be crowded so as not to disturb each other. Water must be added, its level and degree of contamination must be monitored. Periodically clean the walls from organic matter and the filter element.
Next, we will dwell on the main points of keeping domestic fish in an aquarium, invertebrates, mollusks, insects and plants.
Fish
Of the river candidates for pets, small freshwater fish up to 10 cm long, and even better up to 5-7 cm, are most suitable for an aquarium.
These are verkhovka, bleak, mustard, char, gudgeon, and spike. The larger ones include roach, rudd, and perch.
In nature, river “residents” prefer to stay with the flow, in conditions of a comfortable oxygen regime and clean water. Such an environment needs to be artificially recreated, right down to the flow.
That is, good aeration and clean water are the key to a “healthy” ichthyofauna of the ecosystem.
Pond and lake species adapt well to stagnant water. These are the fish that can live without oxygen in an aquarium. For them, minimal water aeration is sufficient.
In our reservoirs, loach, rotan, crucian carp and tench can survive practically without oxygen.
The temperature regime should be close to natural. In summer it is 14-20 degrees, in winter a couple of degrees lower.
It is advisable to take water from a reservoir, spring, well, if from a water supply system, then it must be left for at least a day.
Invertebrates
From this category, you can keep leeches and crayfish in the aquarium. For example, the lake false horse leech survives well in an artificial environment.
The large false horse leech is a predator, but is harmless to humans and does not feed on blood.
In nature, its prey is insects and snails. You can feed it pieces of meat, which the leech swallows whole.
It is advisable to keep crayfish separately from fish, the smallest of which they hunt. Even if you throw fish at crayfish, it’s not a fact that they will survive. The crayfish won't eat them right away, but over time they will eat them.
When keeping crayfish, you need to keep the water clean, change it more often and aerate it well.
You can get the smallest (from 1 to 5 mm long) invertebrates - daphnia, rotifers, flagellates, cyclops. In summer, it is enough to scoop up a few liters of water from a pond and pour it into the aquarium. But maintaining the population will be difficult. They are all natural food for fish and are practically eaten away.
Shellfish
River gastropods - snails.
Bivalves and barley snails with large shells look great on the bottom of the aquarium. It is interesting to watch how they open the doors and filter the water through themselves.
Gastropods or river snails are good at cleaning algae from the walls, crawling endlessly over them. In addition, they eat rotting organic matter at the bottom and periodically nibble on algae.
In a word, snails - pond snail, lithoglyph, bassoon, meadow - are excellent orderlies and are irreplaceable in an autonomous environment.
It is better not to take coil and bitinia snails; in nature, they are intermediate hosts of parasites dangerous to humans.
Insects
There are a lot of insects and their larvae suitable for an aquarium. It is best to take original and large ones. They are beautiful and clearly visible.
As an option, you can consider introducing water-loving and spinning beetles, water scorpions, water striders, and smoothies.
Aquatic insects for an aquarium
It is better not to take the latter, they bite, it feels as if they were bitten by a wasp.
You can add a few caddis larvae. Their straw houses are original and educational for the younger generation of young naturalists.
Plants
Aquatic plants are needed to create a biotope. Any of our reservoirs will do. However, they need to be selected according to the volume of the aquarium. After all, there is no point in planting a cattail in the ground, which grows a meter high, and then you have to remove it.
So, the best plants that will decorate and create a natural habitat for fish, shellfish, and invertebrates are:
- hornwort
- conferva
- Elodea canadensis
- polushnik
- pondweed
- watercolor
- water ranunculus
- urut,
- body cutter
- duckweed
The choice is yours…
Self-preparing food
There are situations when it is not possible to purchase ready-made food. In such cases, you can always prepare it yourself.
For example, you can make a long-term storage feed mixture, which will include the following components:
- fishmeal – 15 parts;
- shrimp – 5 parts;
- dried bloodworms – 5-10 parts;
- boiled egg – 5 parts;
- dry daphnia, cyclops and gamarus - 5-10 parts;
- powdered milk – 5-10 parts;
- bread crumbs;
- red bell pepper (for coloring) – 5 parts;
- underwater plants;
- yeast – 6-10 parts;
- shoots of nettle, dandelion and plantain scalded with boiling water - 10-14 parts.
All ingredients need to be ground and supplemented with multivitamins, then mixed in boiling water to a paste-like state and boil for another 2-3 minutes. Divide into molds and freeze. The dish is given to the fish both frozen and melted. Freshly cut herbs or ground green peas are used as a garnish.
Nutrition of fish is an important issue if you want them to live a long time and be pleasing to your eyes (when decorative breeding of koi carps, for example). Therefore, you should be very careful when choosing food, read the composition of ready-made feeds and do not hesitate to ask questions to more knowledgeable people who will help you figure it out.
0
2
Copy link
Catching, transportation
It is better to “harvest” future pets in the spring, especially if we are talking about large specimens. When fishing, the main task is to inflict as few wounds on the fish as possible. From this point of view, it is preferable to use a net or a net, and if it is worth catching with a fishing rod, it is with a small and sharp hook.
Everyone chooses which individuals to release and which to take, but younger individuals take root faster and are easier to transport. Newly-made pets should be placed in containers that are wide and low, with 5-6 fish in each container.
It is recommended to regularly change the water and keep the vessel out of direct sunlight. These measures will prevent oxygen starvation of fish and heating of water. It is important to avoid shaking during transportation.