About spinning rods
The spinning rod consists of a handle (butt), a reel holder, a blank, which is equipped with guide rings for guiding the cord or fishing line, the last ring at the tip is called a “tulip”.
Spinning rods are distinguished by the type of connection of the knees:
- Plug-in. The most popular among spinners. They have two, less often three, elbows that are inserted into each other. Lungs.
- Telescopic. Retractable, heavier, less durable and sensitive. Convenient to transport.
There are rods of one-piece designs on sale, usually short (up to two meters).
They are called one-part ones. Consist of one knee. The most “sensitive”, but often inconvenient to transport. The material used to make the form determines its weight and strength:
- Fiberglass.
- Carbon fiber (graphite, carbon).
- Composite (a mixture of fiberglass and carbon fiber in various proportions).
- With Kevlar admixtures (super strong material).
Pay attention to the material used to make the handle: smooth artificial polymers will slide in your hand, choose natural ones, for example: cork.
Rings are one of the most important elements; the reliability and sensitivity of spinning tackle depends on their quality. But it should be noted that expensive samples are not always necessary.
For example, when fishing exclusively with monofilament, it is not necessary to use expensive SIC ceramic inserts; they are necessary when fishing with braid, since it, like a saw, leaves deep cuts in conventional plastic ring inserts.
Accordingly, for a spinning rod on which it is possible to use braided wire, we check the quality and material of the inserts and the rings themselves; for a regular rod, more budget solutions are also suitable.
The test form indicates the weight of acceptable baits, divided into:
- Ultra-light (UL – Ultra-Light) – up to 6 gamma.
- Light (L – Light) – from 6 to 11 grams.
- Medium-light (ML – Moderate Light) – from 11 to 19 grams.
- Medium (M – Moderate) – from 19 to 23 grams.
- Moderate Heavy (MH – Moderate Heavy) – from 22 to 37 grams.
- Heavy (H – Heavy) – from 35 to 45 grams.
- Super heavy (XH – Extra Heavy) – over 45 grams.
Lures that are too light or too heavy and exceed the test limits can lead to loss of control when retrieving or damage to the rod when casting.
The structure of the form is an important characteristic that determines its flexibility.
The play of the bait when retrieving and the casting distance depend on this:
- Extra Fast – when loaded, 1/5 of the form will bend.
- Fast – 1/4 part.
- Medium (Moderate) – 1/3 part.
- Slow – 1/2 part.
The length of the rod allows you to vary the casting distance:
- Long rods over three meters are used for sea fishing, on large rivers, and when fishing from the shore of large bodies of water.
- Medium length (2.10-3.00 m) - used on lakes, small rivers and rivers, canals, etc.
- Short (1.50-2.10 m) – when fishing from a boat.
Keep your spinning rod clean and transport it carefully. If the knee joint gets stuck, cool the rod and release it without sudden movements or force. Do not allow sand particles to get into the joints.
How to choose the right fishing rod
We recommend taking into account several important points:
- Fishing conditions. Fishing will take place from the shore or from a boat.
- When fishing from a boat near a coastline filled with vegetation, you need to take short tackle up to 2.1 m long. On clean beaches, from the bridge, a spinning rod up to 3.5 m long is preferable.
- To catch a predator, a plug rod is considered the most convenient.
- The optimal gear material is a carbon fiber composite. It is light and even during long fishing your hand will not get tired.
- The test and system are selected based on the type, weight of the bait used, and wiring options.
- It is believed that fast action rods effectively perform hooking, but do not absorb well the jerks of the fish when playing. Slow ones are less sensitive, but work great when fishing, softening sharp jerks.
- For beginners, to practice the accuracy of casting and wiring techniques, you can opt for medium tackle or another universal option. And by acquiring skills, gradually move on to more narrow-profile products.
What is a spinning test
Test – weight range of baits used. Indicates the maximum permissible bait weight limit.
Depending on the indicator, rods are divided into the following classes:
- Ultralight. UL marked. Lightweight spinning rod with a weight of up to 5 g. Suitable for catching small perch or even chub and roach. The casting distance does not exceed 20 m.
- Light. Marked L. This type of rod is used for fishing from the shore. The dough is up to 15 g. The average pike and perch take this bait. The casting distance does not exceed 35 m.
- Medium or average (medium). Marked M. Test up to 30 g. It is considered a universal rod because it is suitable for any predatory fish. You can fish both from the shore and from a boat.
- Heavy. Marked H. Used for large specimens of catfish, pike, asp, and bream. Test from 40 g and more.
Products are produced marked MH, ML - intermediate classes, which stand for medium-heavy, medium-light. If you come across other variants of unfamiliar markings, then look carefully at the grams. This will make it easier to navigate.
What is rod action?
Action is the amplitude of flexibility of the tackle under the influence of load. Displays the hardness of the blank. Affects the speed and accuracy of spinning control.
There are 4 types:
- Very fast. Only the tip of the rod is flexible. Allows you to cast with high precision. Provides high-quality hooking. It is distinguished by high sensitivity and durability. Disadvantages: short casting range, poor shock absorption when fishing, which can lead to the loss of the bait.
- Fast. Flexible ½ part of the tackle. Half formation.
- Average. Flexible ¾ part of the rod.
- Slow. The entire working part of the rod is flexible. Possibility of using thin lines in equipment. Long cast. Excellent cushioning when playing. But with this system, casting accuracy suffers, hooking occurs with a delay. Low sensitivity.
For beginners in fishing, a quick action will suffice. You can check the system for compliance with what is specified in the instructions even upon purchase. You need to lightly wave the rod. If the tip bends and immediately returns to its original position, then it is very fast. When the top bent forward, it returned back and took its starting point - a fast formation.
Types of spinning fishing
Spinning rods are selected depending on:
- Weight and size of the desired catch.
- The baits used and the method of conducting them.
- Conditions of the planned fishing.
- Kind of like a pond.
Catching a predator with a spinning rod
Catching predatory fish with a spinning rod is carried out using artificial baits that imitate fry or insects on which the predator feeds.
The attractiveness of the bait is created by the wiring technique. And also using live bait - fish secured with hooks (single, double, treble) or special tackle.
Types of the most popular spinning baits.
Spoons
They are divided into two types: rotating and oscillating.
Rotating ones consist of a core, a hook (with or without “feathering”) and a petal; there are different types:
- Spoons are insects : the core of the spinner copies the larva or insect, the petal is its chitinous cover. Can be supplemented with hook feathering.
- Spoons are “condoms” : a heavy core dressed in a bright rubber cover with “tails”.
- Bell spinners : an acoustic spinner with a bell core, which is a resonator and a load at the same time.
- Container cargo . Installation of a container on the core of the turntable for aromatic gels or pastes that dissolve during the wiring process and create a “fragrant trail”.
- In combination with a system of changing hooks for additional equipment of the spoon with artificial bait.
- Spinner with natural bait.
- Two-leaf spinners in tandems on a rigid, composite rod, or on a flexible cable.
- Spoons with twin blades or screws.
- Spinnerbaits are a hybrid of a jig head and a rotating spoon mounted on one wire frame. The design is designed for fishing in snags.
By type of shipment they are divided into:
- Spinners without loading for fishing in the upper layers of water.
- Front-loaded spoons - the sinker is located in front of the blade. Sometimes such a load is called a head.
- Rear-loaded spoons - the sinker is located after the rotating blade.
The game can be divided into:
- with a narrow game;
- with a wide game;
- with a fixed blade deflection angle.
Petal shape:
- With a rounded petal - for fishing in reservoirs without current.
- With oval - for flow.
Oscillating spinners. In essence, it is a piece of metal of a special shape with a hook. Can be equipped with various additional elements.
Can be classified:
- in appearance: classic flat, stamped, three-dimensional, made by cutting or casting, with additional equipment;
- by weight: light, medium, heavy and extra heavy;
- by purpose: models for uniform, stepped, jumping or semi-plumb wiring;
- by relative width: narrow, medium and wide.
The shape of the spinner affects the game during the retrieve. The longer the spoon, the slower it oscillates in the water column (and is better suited to the current).
Some types:
- Spoon.
- Fish.
- Storling.
- Wave.
- Plate.
- Castmaster.
The thickness of the spinner also has a strong influence on the game: the thicker and heavier, the slower the game.
The depth of the stamping determines the nature of the game: flat ones play easier, but are more prone to spin; with increasing stamping depth, it is less active, but more stable during insertion.
The shape of the longitudinal bend most determines the nature of the movements of the bait and there are four options:
- arc;
- caterpillar;
- wave;
- snake
Jig head
It is an element of equipment designed to increase the weight of the hook and deliver the bait to a given depth. A distinctive feature is the location of the load in the head of the bait. They differ in weight, material of manufacture, shape, type of construction.
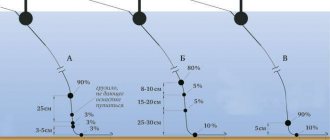
The weight of the jig head is selected depending on the depth and presence (speed) of current in the reservoir so that the duration of pauses between retrieves (the length of time during which the jig reaches the bottom after the completion of the retrieve) remains within 2-5 seconds. The casting distance depends on the weight of the equipment.
Some examples of choosing a sinker weight for different fishing conditions:
- Nanojig – up to 3 grams. Standing water and depth up to 2 meters;
- Microjig – from 3 to 7 grams. Depth up to 4 meters and current speed up to 2 m/s;
- Light - from 7 to 21 grams. Depth 4-6 meters, speed – 3 m/s;
- Average - from 21 to 42 grams. Depth – 4-6 meters, speed – more than 3 m/s;
- Heavy - from 42 grams or more. Great depths and/or high current speeds.
Jig heads are made from lead, tungsten alloy and brass. They vary in price, size and durability.
There are two types of jig head designs: cast and collapsible. The cast design involves the weight and the hook as a single unit, the collapsible design involves offset installation of the weight and the hook.
Offset installation involves the use of a weight with two fastenings (popularly called “Cheburashka”) and a hook (simple or offset). A hook is attached to one ring of the weight, a leash carabiner is attached to the other, or a cord is tied. A silicone bait is put on the hook.
In addition to jig heads, other weights are also used. Some are used as a “flexible”, “jointed” version of jig heads - these are “Cheburashkas”, “drops” and “sticks” with built-in swivels and hooks attached to them using a winding ring.
They can be of different shapes, with soldered “ears” or with collapsible ones.
Others are used in rigs with a “retractable leash” and the like. They have the shape of a bullet (in the case of the Texas rig), a ball, a drop, a stick, etc.
Types of fishing for predators: trolling, fly fishing, jig fishing, microjig, casting, etc.
Trolling fishing. This is spinning fishing from a boat with a motor. This type of fishing from a rowing boat is called “track”. The bottom line is that at low speed the fisherman lowers the bait into the water and, without using wiring, but only the movement of the boat, “combs” the reservoir in search of prey. The presence of an echo sounder optimizes the process.
Fly fishing. This is fishing for artificial or live insects using a spinning rod with special equipment and casting and retrieving techniques. With this type of fishing, floats and sinkers are not used; fishing takes place on the surface of the water or its upper layers. Casting is primarily carried out using a special cord, and not a spinning rod blank as in classical fishing.
Mormyshing. Jigs are traditionally a winter bait, but there are already exceptions. Spinning fishing with jigs is becoming increasingly popular. Refers to ultralight fishing. Jigs work more effectively in early spring and late autumn.
Microjig. A type of jig spinning fishing using light baits. These include marmodroch, nanojig, etc.
Casting. It is distinguished by the use of special gear: spinning rod and reel.
The rods are shorter, specialized, and have an inertial baitcasting reel – all this allows for more accurate and longer casts, more sensitive and smooth movements of baits.
Overview of the main parameters for choosing a rod when fishing from the shore
As mentioned above, spinning is a universal tackle. However, if when fishing from a boat the set of criteria is very limited, since fishing is actually carried out in open space, then when casting from the shore, all possible influencing factors must be taken into account. It is necessary to pay attention first of all to the following characteristics:
- Coastline. It is worth carefully looking around to see how overgrown the approach to the reservoir is, whether there are bushes or trees growing along the water. It should also be remembered that spinning is a sporting tackle and the angler has to move often, so you need to study the condition of the shore along the entire expected length of the route.
- Size and nature of the reservoir. Determines how far you need to cast. Depending on the area and the presence of flow, these can be large and small rivers, streams, flowing and stagnant lakes. Also, the choice of fishing rod is influenced by the topography of the bottom and how swampy the reservoir is.
- Bait used. Everything here is quite simple, since there are several main branches of spinning tackle. This is fishing with oscillating spoons and their varieties, rotating spoons, wobblers and poppers, as well as silicone. The use of a certain type of bait determines the tactics and methods of fishing, for example, when installing a silicone fish, the angler will most likely choose jig wiring. From here the class of the rod will be determined.
- Estimated catch. It also dictates what kind of rod you need to use. For example, to catch small perches you will need lighter tackle, but if the angler is counting on catching a large specimen of pike or pike perch, the spinning rod should be much tougher.
Neglecting at least one of these factors can lead to complete discomfort during fishing and its accompaniment by constant snagging on coastal vegetation, tangling of the fishing line and, as a result, the end of fishing. In order to wisely choose a spinning rod for fishing from the shore, you need to understand the parameters described below.
Price and type of rod
Before buying a spinning blank, you need to carefully study the market, since there are a huge number of offers there. And very often you can find a budget rod within 3,000 rubles, which in its characteristics will be similar to a product produced by a famous brand and having a retail price of 30,000 rubles and above.
And yet, despite the fact that the brand is a significant, but not fundamental, circumstance, it should be noted that among both beginners and experienced fishermen, rods from Daiwa and Shimano have a good reputation; manufacturers Banax, Nissin, Tenryu are a little less known. The range of these companies is very large and allows you to choose a set of rods for the required type of fishing.
Based on their technical design, forms are divided into plug-in and telescopic. The first ones consist mainly of two parts and are connected end-to-end using a plug connection. This guarantees them high strength, uniform load distribution and, accordingly, excellent balance.
Rods of the second type are very outdated; their only advantage is their compactness during transportation, which made them popular mainly among lovers of float and bottom tackle. Accordingly, when fishing with spinning tackle from the shore, it is better to give preference to a plug form.
Primary parameters for choosing a fishing rod: test and length
These characteristics almost completely describe the fishing rod for a particular body of water. So, the length allows you to determine the casting distance, having a direct relationship - the longer, the further. The test, in turn, shows how heavy the bait can be delivered to the desired area of the reservoir and partially determines what weight of fish is expected to be caught.
Rods have a very different test, and extreme values can be from tenths to a unit of grams when fishing with ultra-light baits, and from tens to hundreds of grams when hunting fish such as taimen, salmon, catfish or very large pike using special oscillating spinners. Universal values for most reservoirs when fishing from the shore will be 7-30 grams, 5-15 grams, 5-25 grams or close to them, i.e., no more than 30 grams and lying in a wide range.
It should be remembered that it is better to choose a test with a small margin, ideally so that the mass of the bait is its average value. As an example, if you plan to cast a spinner weighing from 7 to 15 grams, then a rod test of 5-25 grams would be ideal.
Recommended reading: Everything for winter fishing
The choice of length is motivated not only by the casting range, but also by the nature of the shoreline of the reservoir. If the coast is clean, without high coastal vegetation, then there is the possibility of a large sweep, which allows the use of a blank length of up to 3.3 meters. As an example, these could be large lakes or reservoirs. If the reservoir is located in a wooded area and is bordered by lush vegetation, even coniferous trees, then it is best to use rods with a length of 1.8 to 2.1 meters. In general, as practice shows, even when alternating fishing on forest streams with a transition to a large forest lake with partially clear banks, a rod 2.1 meters long is quite universal.
Here you can immediately give a specific example, which may be useful to beginners. So, the intended fishing location is a small river flowing from a forest lake and flowing into a huge water area. The width of the stream does not exceed 3 meters, with riffles leading to places with a moderate current. The species of inhabited fish with prospects for catching are pike, pied trout and brown trout. Accordingly, rotating spoons weighing 6-7 grams will be used for trout, a Castmaster-type spinner weighing 13 grams for trout, and it is also possible to use a popper and wobbler weighing 15 grams for catching pike. From these considerations it is clear that a Daiwa rod with a length of 2.1 meters and a test weight from 5 to 21 grams will be universal. With its help, you can easily make both pendulum and side casts without fear of making a shore hook.
Rod build
This parameter should be displayed in a separate column, since it ultimately characterizes the form of the rod and determines what baits will be used for fishing. In fact, it indicates the information content of the tackle when casting, retrieving and retrieving, depending on the type of equipment. Despite the fact that this is a separate and very large topic, you should at least superficially study this parameter in order to correctly select a spinning rod for fishing from the shore.
The action is indicated on the form of the rod; it is convenient to divide it into three types:
- Extra fast and fast. These are rigid rods in which only the whip is used during casting, retrieving and retrieving. When fishing from the shore, it is well suited for jigging or twitching, where the sharpness of both the hook and the transfer of impulse to the bait should be maximum.
- Medium. If the angler does not fully know what kind of fish lives in the reservoir and is going to use a wide range of baits, this is the ideal rod setup. In all modes, exactly half of the form functions. It can be used with both jig baits and all spinners; landing fish is very simple, since its jerks are effectively dampened.
- Slow. As the name implies, the rod responds to the load with its entire length. This type of blank is used when fishing with large spoons and, accordingly, trophy fish. Good shock absorption allows you to effectively fight against a massive predator. Also suitable for some types of twitching.
So, as can be seen from the description, for beginners or anglers who do not have sufficient information about the reservoir, it is recommended to use a medium or, as it is called, semi-parabolic system. This rod will allow you to use a wide range of baits, provide optimal casting and comfortable fishing.
The quality of the rod blank
As mentioned above, there are a huge variety of fishing rods on the market from different manufacturers. One of the pricing factors is the material from which the form, handle and fittings are made, as well as the quality of the assembly itself. That is, with the same characteristics, a more expensive fishing rod may be more durable. However, sometimes the principle works, which is based on the fact that it is impossible to buy an exclusive product for too little a price, but for a large specific fake it is quite possible. Therefore, it is necessary to examine the rods as carefully as possible, examine the surface for chips and cracks, check the alignment of the guide rings, the integrity of the fastening, etc.
Most rod blanks are made of carbon fiber. This material is distinguished by exceptional characteristics, such as low weight and high strength, compliance with specified characteristics. The only drawback is the low resistance of the structure to impact loads due to its fragility. However, today the cost of budget products does not exceed 3,000 rubles for very decent quality and that is why it can be recommended to beginners. Fiberglass spinning rods are usually made telescopic, are obsolete, heavy and are used mainly as a unit for traveling as they take up very little space.
Guide rings on the rod blank are also made of different materials, but all-metal ones are increasingly leaving their positions, and their place is being taken by designs with various spacers made of ceramics, Teflon, etc. This innovation eliminates the unpleasant phenomenon of the fishing line rubbing against the ring material, followed by breakage and loss of valuable bait.
Recommended reading: Equipment
Summarizing the characteristics of a spinning rod for fishing from the shore, we can highlight general tips for choosing a blank. First, the parameters and price segment are determined, from which several copies are subsequently selected, preferably from different manufacturers. Secondly, the structures are checked for integrity, there should be no chips anywhere, all surfaces must be smooth and polished, the form must be uniform and straight along its entire length. The reel holder must have a strong and reliable fastening ring, the thread is intact, the moving elements can be put on easily, but without play. The handle must be made of cork or high-quality polymer, and the location of the reel seat must be such as to maintain balance with the blank, otherwise after hundreds of casts the hand will “fall off”. The plug connection should also not have any play. Small bonuses like an eye for catching a hook will be very nice.
Do you have a FisherGoMan self-hooking fishing rod?
Yes
Catching peaceful fish with a spinning rod
Catching white fish with a spinning rod is carried out mainly with bottom gear: a feeder and a donka. These two species have their own equipment depending on the desired catch.
But both fly fishing and casting can also be classified as types of fishing for “white” fish using spinning rods. You can also catch peaceful fish while trolling, fishing with edible rubber, wobblers and other options for hunting predators, but this is mostly an accidental bycatch rather than the rule.
How to properly equip a spinning rod
The spinning rod is equipped with a reel on which a cord or fishing line is wound, passed through guide rings and the equipment is tied. Gear is selected according to the characteristics of the spinning rod.
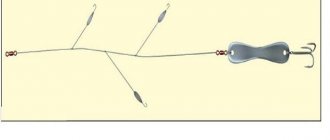
If there is a pike in the reservoir, then a leash is used, which is tied to a cord, and the bait is attached to the carabiner of the leash.
Reels can be inertial, inertial-free, multiplier.
Multiplier rods are the most powerful, so they are equipped with spinning rods for trolling and for catching catfish and other large fish.
Inertial ones are used in fly fishing and in the bottom version of spinning fishing.
Inertia-free, as the main type used in hunting for predators, and in feeder fishing, in carp fishing, etc. They are popular due to the ability to fine-tune the friction brake, with the help of which you can bring out impressive trophies on delicate tackle. Because of such emotions, real fishermen go to the pond. The simplest reels, like the Nevskaya, are suitable for fish harvesters.
The choice of cord or monofilament depends on the fishing method and location.
For example, for jig fishing, the extreme sensitivity of the gear is important. The fisherman controls the movement of the bait and the bite tactilely - through the form and visually - along the tip of the rod. The cord has no stretch, which ensures the best signal transmission from the bait to the form and then into the angler’s hand.
The monofilament, in turn, has stretchability and thereby dampens sudden jerks of the fish. This property, coupled with the flexibility of the rod and a properly configured clutch, helps to bring out the trophy without annoying derailments.
Expert opinion
Vladimir Poltoranin
Fisherman - expert
What type of base to equip a fishing rod needs to be determined for each individual case. There can be many factors - this is a littered reservoir (braid collects garbage like a vacuum cleaner), the presence of a shell (monofilament is less susceptible to cuts on sharp edges), weak fish lips (the line is stretchable and handles jerks better), pike teeth cut braid perfectly and do not always cope with fluorocarbon (fluorocarbon fishing line).
Small in appearance, but not in importance, are the auxiliary equipment elements:
- swivels;
- carbines;
- winding rings;
- fasteners
The comfort and reliability of the gear depends on their quality and proper selection and installation. A poor-quality swivel will ultimately result in twisting of the fishing line, which will lead to its tangling, the so-called “beard”. And instead of enjoying fishing, you will waste time and nerves redoing the gear.
This also applies to other installation elements. High-quality fittings contribute to the overall balance of the gear; you should not skimp on these small things.
Spinning fishing technique
Using artificial baits, the fisherman needs to “deceive” the predator and make him believe that in front of him is a living object of his diet. To do this, various wiring is used, forcing the bait to move in one or another amplitude, direction and speed.
Spinning wires
Basic wiring techniques:
- Uniform – suitable for spinners and silicone lures. It is carried out by uniformly winding the fishing line onto the reel. The closer the bait is to the surface of the water, the faster the retrieve rate. In the bottom layers, bait is carried out very slowly.
- Uneven - alternating bait movement and pauses. Suitable for fishing with oscillating spoons and silicone. A correctly selected ratio of the speed of posting and the duration of pauses gives excellent results.
- Stepped – for bottom baits. The bait sinks to the bottom, then sharply, by moving the tip of the rod, rises at an angle (at this time the cord is wound on the reel) and falls again. The secret of retrieving lies in the timing of the movement of the bait from the top point to the bottom - the predator often attacks at this moment.
- Twitching is a jerking drive that involves active movement of the form from side to side. The amplitude and depth of the bait's immersion varies, which presupposes the spinning angler's skills. Very good for wiring wobblers.
- Jig is a type of stepped wiring. The difference is that the movement of the bait is provided by the reel, without the participation of the blank. The speed of the drive and the duration of pauses change. Used for fishing with jig heads.
Different wiring techniques are used for different types of baits. But we must not forget that fishing is creativity, and this is projected onto the options and elements of wiring. You always need to improvise, look for the right technique right now. By mixing styles, changing established criteria, you will always find the key to the object of the hunt.
How to cast a spinning rod correctly
Spinning is a tackle that has its own characteristics. The casting is performed with a sharp throw without stopping. The casting technique depends on the reel that is installed. Let's consider a spinning coil.
Casting options:
- Vertical.
- Horizontal.
- Pendulum.
- Ejection.
Vertical cast.
The most common technique that allows you to deliver the bait to the designated place, applicable when there is no interference with the swing. Highest casting distance.
- We begin casting by searching the surface of the water for the bait delivery point.
- Using a reel, we wind the cord so that the bait is twenty centimeters from the tip.
- After this, the cord is pressed against the rod with the index finger, and the line-laying arc opens.
- The rod is thrown behind the back, a sharp movement of the hands so that the rod plays and a sharp feed forward of the bait, which “shoots” in the desired direction, at the same time the cord is released.
- While the bait is flying, the cord falls freely in rings from the spool, the tip of the rod points in the direction chosen for casting.
- When the bait touches the surface of the water, the line-laying arm is returned to its original position and they wait until the bait takes the desired position in the water column, then the retrieval is carried out.
Horizontal (side) cast.
It is used when tree branches are in the way above the spinner’s head and/or there is high overhanging vegetation at the casting point. The casting range is slightly less than in the previous case, but the accuracy is high.
The casting technique differs from the previous one in that the spinning rod is wound up to cast not behind the head, but to the side. The accuracy of the bait's flight directly depends on the moment when the cord is released.
Pendulum cast.
It is carried out when the branches are located very low above the water and the bait must be delivered as if from below, under the branches.
- We mark the point where we need to deliver the bait.
- We pull the bait to the tip of the rod by 20-30 cm.
- Fix the cord with your finger and open the line handle.
- We swing the bait and with a sharp movement “from under ourselves” we direct the bait to the desired point.
- We track the moment when you need to release the cord by the amplitude of the bait’s swing.
- We return the bow to its original position and carry out the wiring.
Catapult cast.
The cast is quite difficult to execute and unpredictable. Designed for hard to reach places. Reminds me of shooting with a slingshot. Requires high skill.
- The bait drops just below half the length of the rod,
- The line-laying bow is retracted and the cord is fixed with a finger.
- You need to grab the bait with your hand so as not to catch on the hook, pull the cord until the tip of the rod bends,
- First, release the bait with a throw, then release the line.
- Close the shackle and make the wiring.
Casting distance is affected by:
- Length and structure of the form;
- Size, type of reel and spool shape;
- The diameter of the cord and the quality of its winding;
- Diameter and location of passage rings;
- Casting technique, environmental and weather conditions.
Catching pike perch at night
Let's start with our main night hero - the pike perch, which leads a stormy night life. If in the fall (including at night) we usually catch the fanged in the area of deep snags, then in the summer the picture is different - the predator can move around a lot, while making quick raids on the shallows, including coastal ones. It is normally caught in the area of shallow capes of the river and even on coastal shoals overgrown with grass. The latter circumstance suggests that the fanged one does not shy away from the grass at all if there are enough small fish there. Often bites occurred on the rifts.
The most active entry into shallow water occurs on the eve of night and then just before sunrise, including at dusk, when the sun goes beyond the horizon, but complete darkness has not yet arrived. At night (usually from 1 to 3 o’clock), the fanged one goes to deeper points, to holes or simply to riverbed areas, but continues to bite, although less often.
It is not easy to understand where to fish on a particular night, because going to a certain place the next night may not be repeated, since the small fish are also actively moving along the river, looking for the best conditions for themselves. It’s hard to say what’s the best thing to do: show the steely restraint of an experienced pike-perch fisher and take a long time to “iron” a promising place, or actively move around the water area, looking for cool spots. After all, you can work on some sandbank half the night, and, without waiting for a bite, leave this place, and the bite will begin after 20-30 minutes, and this has happened. And it also happens that a promising sandbank is quite long and a predator comes to it a little lower or a little higher upstream, and to be successful all you need to do is move a little. It’s great if the pike perch makes its presence known by splashes, perfectly audible on a windless night. The predator splashes most often on dark nights. In bright moonlight, you can already see the surface of the shallow waters. Sometimes you see that the small fish are playing too “intensely”, and this indicates a high probability of the presence of pike perch. It happens that you can even see the “whiskers” of a predator walking above. Naturally, having seen (and heard) the place where the fanged fish are fattened, you fish this area first. But such trips to specific shallow water can be very fleeting, often no more than 5-7 minutes, after which the school of pike perch leaves.
A good reference point when searching for a fishing spot can be the dense concentrations of breams on the shore, most of which catch bream during the day. Why? The fact is that bream very often stays close to fanged ones. Or maybe the latter is drawn to bream? Who knows, you can’t ask a fish. But the fact remains: in important bream areas, pike perch is found quite often at night, or rather, near the depths, on the edges leading to the shallows.
However, in most cases, the concentration of a predator can only be detected by test catches. I try to fish the area purposefully. I noticed that before entering the shallows, the predator concentrates on the edge adjacent to the shallows, usually in its upper part. If you put a jig bait with a weight suitable for tapping the entire edge, then in the end you will regularly roughly catch the upper ridge of the drop. In this case, you cannot wait for the grip, this can only frighten the predator, who at such a moment is still very careful. Therefore, first of all, I fish the upper part of the edge with a lighter head, and not with a step, but with a uniform retrieve, both along the drop and across it, depending on how you stand on the shore and how you can cast. If there is no grip, then you should replace the jig head with a more massive one and tap the entire shaft. However, with such tactics, which we profess in the evening twilight, the fish usually comes across is medium-sized, rarely more than a kilogram. The main action begins only with the onset of complete darkness, when the fanged ones begin to enter the shallow waters en masse and forget about caution during the hunt. But this does not mean that any type of wiring will do in such areas. If the pike perch hunt is visible on the surface, then I cast bait in the upper horizons. If there is no grip, then I check all layers of water. Many anglers make the mistake of thinking that if the fish is active, then it needs to be offered a quick retrieve; on the contrary, for night pike perch, a leisurely, even retrieve is best suited.
As for baits, many industrial models are not very suitable for night fishing for pike perch and spinners have to make suitable baits themselves. My friend uses one of these baits and doesn’t complain about his catches. It harmoniously combines many of the developments of home-made people, and there are not even small contradictions in the design - I would like to find fault, but I can’t. Although the load in the design is not removable, and when fishing conditions change, you have to put on another spoon - with a smaller or larger load. On the other hand, there are no completely universal baits.
By and large, the spoon is a very sophisticated jig head for the iconic ripper - a seven-centimeter “hoof”. A wire frame (0.8 mm) is rigidly fixed in the front weight - inserted during casting (a simpler option for a homemade worker is to solder it into a cut made in an ordinary round “Cheburashka”). The second ring of the “Cheburashka” was removed as unnecessary, although it does not particularly interfere. The weight (14 g) is round - the most compact shape, and therefore minimally interferes with the operation of the petal. It is small (2.3 by 1.8 mm), spoon-shaped, “Colorado” type - one of the most stubborn when wiring of all known. This is important, because the spinner tends to produce fairly strong vibrations when fishing for pike perch at night. At the same time, it affects the vision of the fanged one - two large beads on a wire frame are luminous. I charged it a little with a flashlight, and they shine in the dark with a bright green color, highlighting the shiny chrome petal. True, among pike perch fishermen there is an opinion that the predator does not like excessive glare. Therefore, the surface of the spoon’s petal is ribbed to disperse excess glare.
The front luminous bead is round and slides freely between the back one and two miniature beads that act as a kind of bearing for the petal clamp. The back luminous oblong works as a lock for the wire lock, thanks to which the hook is quick-release - the wire piece is pressed with a finger to the main frame, and the bead is tightly pushed onto the double wire, preventing the lock from opening under significant loads on the hook. It is double, in the working position the tips look up, sharply reducing the number of hooks - the scourge of front-loaded turntables with a tee.
And one more important point regarding rotating spinners with front loading is that the hook gets caught in the line when casting. This is simply the problem with such decoys, which have a hinged joint in their design and fold in flight. This problem can be solved in different ways. Some people simply practice a special throwing technique, and they don’t get overwhelmed. Some people prefer spinners where there is a free hinge only between the weight and the frame, and the hook is rigidly fixed, pressed with a cambric to the frame or even soldered to it. This spoon has one hinge at the rear. Adherents of such designs claim that this option is the best for complex jig wiring. Thanks to the rigid front part, this lure for pike perch is very well controlled, and the rear hinge better stabilizes the bait, especially when additional bait is used on the hook (large fly, Christmas tree rain, silicone, etc.), working as a quickdraw when retrieving. The only drawback of this design is that it is difficult to get rid of overlaps between the hook and the fishing line or even the front part of the frame! Typically, such overlaps haunt the spinning angler when the hook is completely free. But in this design, my friend completely limited the folding of the rear part of the bait - the body of the ripper rests against an oblong bead.
Spinning fishing tactics
The tactics of spinning fishing are practically the same in any body of water: be it a large or small river, lake, reservoir, etc.; Whether you are fishing from the shore or from a boat, with an active spinning rod or feeder, with a donkey or a casting rod, you will be subject to the following components:
- Finding a fishing spot (choosing a fishing spot);
- Duration of reconnaissance (fishing) of an unfamiliar (or familiar) place;
- Variety in the choice of baits and complementary foods (selection);
- Varying the degree of immersion of baits (for active spinning);
- Animation of baits by combining the type of postings (for active spinning).
Finding a fishing spot
It involves choosing a place in the territory of which the fish you have chosen can stand (feed) or hunt.
If this is a predator, then we will choose dumps, edges, bottom holes, boundaries of vegetation and clean water, steep shore, etc., i.e. those places where it is convenient for a predator to make an ambush.
If we catch peaceful fish, then we choose places for active feeding (or we feed in places that are familiar to fish and convenient for fishing) depending on the time of day: if night fishing is in shallow water, daytime fishing is in deeper fishing areas.
Duration of the catch
The time you will spend searching for actively feeding fish or stimulating their activity.
This parameter depends on the time of year. In winter, late autumn, early spring - there is a greater dependence on weather conditions and seasonality of behavior: if you find a fish site and cannot catch it, then the fishing time will be quite long, because... All tactics will need to be tested.
In late spring, summer, early autumn, when the fish are active, the time for fishing is reduced significantly. To search for active fish, three or four casts to each promising place are enough.
Selection of baits
It all depends on the preferences of the fish at a particular moment.
For example, the choice of the size of a wobbler or silicone will depend on the length of the fry near the shore. This is the main food supply of the predator in the fishing area.
You will vary the bait on the hooks of the feeder or donkey, just like the complementary food in the feeders. Everything will depend on the gastronomic preferences of the selected fish.
Degree of immersion of baits
More relevant to active spinning fishing, since it is necessary to find fish sites in layers of water. We consistently study by varying the depth of the postings, experimenting with equipment (jig heads, wobblers, spinners, spoons). This is more about a predator than a peaceful fish. Her preferences will depend on weather conditions, time of year and day.
Lure animation
It is more important during the period of least fish activity, as is the choice of color, shape and size of baits. To stir up a sluggish predator, it needs to be qualitatively stimulated to attack the bait by changing or combining the methods of wiring to create a more attractive animation for the predator. It would be very appropriate to experiment here. This requires time and skill.
Basic spinning fishing from the shore
We already know that the standard pattern for fishing from the shore is to move along potential catching “points.” Spot fishing is practiced relatively rarely, since there are very few places left from which you can fish all day. Mixed tactics are used much more often - uninteresting places are skipped, more promising areas are “combed” at the required intervals, and successful “points” are fished in the most thorough manner.
A characteristic feature of coastal fishing is that you can easily scare away fish standing near the shore with your careless actions. Moreover, this probability is quite high. After all, in the evening and early in the morning, many predators, especially pike, like to approach the shallowest water. And in such reservoirs as artificial canals and quarries - where there is a rapid drop into depth, and then there is a flat bed - most fish stay in the coastal zone. Here, predators often stand just a meter from the shore and even closer if they are “covered” by grass or bushes. Moreover, if the fish is not disturbed, it can stand for a long time in such shallows that the dorsal fin sticks out. But as soon as even one person “stomps” or appears within sight, the predator immediately goes deeper. How many times only whirlpools and clouds of turbidity told us that a large fish had just stood here. And we could have caught her...
In addition, the fry constantly stays near the shore, and various insects fall from trees and bushes into the water - therefore, almost all predators either periodically “stand watch” here or make raids on the coastal border. Moreover, pike and pike perch can even go out into vast shallow waters at night. But asp, ide, chub and perch prefer shores with relative depth and especially like to stand in “quiet spots” behind obstacles or under overhanging bushes.
Conclusion: in interesting places, before going to the very shore, try to fish the border water area with short casts. And before moving on, be sure to make one or two trips along the shore itself. I have had cases when the majority of the catch was collected in this way.
Please note one more important point. If you return today or plan to visit these places in the near future, mark the bite spots. This can be done in different ways: bend or plan a branch on a bush, tie a polyethylene ribbon or a bright rag, stick a noticeable “peg”, put a stick across it, trample on more traces, write a “dot” on a diagram map in a notebook.
The notebook is also good because by entering catchable places into it, you can simultaneously note the time of bites and the fish caught. In this way, “two birds with one stone are killed,” and at the end of the fishing, together with the diagram map, we have an exact “schedule” of biting for different predators. No marks will tell us this, and you won’t find them later. And so, after several trips, so much useful information may accumulate that our schematic map will become more expensive than the map of treasure island.
How to fish at night with a spinning rod
More comfortable night fishing in summer. Traditionally, this is fishing for pike perch, but in the July heat, catching pike can also be successful. You can also catch a good bite of asp, chub, ide, catfish and other fish.
At night, the fish more willingly goes into shallow water; you should look for it not far from the daytime anchorages. It is better to study promising places during the day for the presence of bottom snags, vegetation, and bottom topography. The bite can be good throughout the night, but the hours immediately after sunset and just before dawn stand out.
Illumination of the reservoir: on clear moonlit nights, the natural light of the moon is enough; in cloudy weather, you can use an electric flashlight.
Baits are chosen depending on the light level: on clear nights, use all types of silver-colored spinners of at least No. 5, jig baits from 3 to 7 cm; in cloudy weather - wobblers with a rattle, popping poppers; Glowing rubber is used when fishing for pike perch.
Placing baits at night forgives all mistakes; you can move any bait evenly and slowly - and this is the main advantage of night fishing.
Winter spinning fishing
With the advent of abnormally warm winters, spinning fishing in open water is becoming increasingly popular and has its advantages.