Currently, dishes that use raw, pickled or smoked fish (sushi, rolls, sashimi, etc.) are becoming increasingly popular among the population, especially in Asian cuisine. However, it is necessary to know and remember that fish (both sea and freshwater) are often infected with helminths, most often in their larval stage. Some of them are harmless to humans, but there are also those whose infection poses a great danger to health and can cause serious consequences.
Routes of infection for fish and humans
Statistics say that up to 90% of marine and freshwater raw materials are infected with various types of parasites. Fish usually become a temporary host for worms. Parasite eggs released in the feces of various mammals and birds end up in the water. The larvae hatching from the eggs are eaten by crustaceans and snails, which themselves then become food.
On a note!
The larvae of worms that enter the intestines of the fish begin to invade the organs inside the body. Human infection occurs by eating raw or lightly processed foods. Lightly salted, smoked, dried, marinated fish preparations, caviar and liver can also become a source of infection.
General classification of worms
Infectious disease specialists divide parasites in fish into those that are relatively safe for humans and those that are dangerous. Conditionally safe include:
- Helminths . Almost all types of helminths that parasitize fish do not cause anything other than eating disorders in humans. There will be no danger at all if, before preparing the dish, you remove the fish intestines and wash the carcass thoroughly. Next, the fish must be well cooked. In this case, you will get a tasty and healthy dish that will be completely safe.
- Cystidicolafarionis . This parasite is most often found in smelt fish of the salmon family. It is not dangerous to humans, but heat treatment must be carried out at the proper level.
- Schistocephalmoses in most cases infect crucian carp; this parasite does not pose a danger to humans, however, if pets become infected, this will lead to serious consequences, therefore, after cleaning the fish, the entrails must be properly disposed of, preferably buried.
- Trienophorus nodulosus is often found when cutting burbot, but it can also parasitize other species. It cannot cause any problems in humans if the fish is well thermally processed.
- Philometra parasitizes inside carp. It poses a great threat to freshwater inhabitants, but is safe for humans.
Parasites in fish that are dangerous to humans:
- Diffylbothryum dendriticum . Found in freshwater bodies of water. Fish is an intermediate host for this parasite; after the larvae enter the human body, they grow into a worm 1 m long.
- Diphyllobothriumalatum lives in the gills of burbot, perch and pike. In the human body, the larva develops into an adult up to 50 m long.
- Tapeworms in fish are also dangerous to humans. It can be found in different types of fish: herring, bream, roach, blue bream, pike and many others.
Safe parasites
You can often hear the question: is it possible to eat fish if it contains worms? There are worms that do not pose any danger to humans, here is an example:
- Diplostomiasis or parasite of the trematode class. When cleaning fish, a person may notice black spots all over the body of the fish, they are localized either in the eyes or in the brain.
- Philometridosis or parasite of the nematode class. The larvae are localized directly in the liver, kidneys, and swim bladder of the fish. After reaching the sexually mature stage, it moves into muscle tissue. The meat of such fish can be eaten, but before eating, rinse thoroughly and heat treat it.
- Schistocephalos or worms that do not reach more than one and a half to 2 cm. They are found in the intestines of trout or salmon. Worms are dangerous to humans; if you eat the product without prior preparation, the risk of helminthiasis increases several times. Before use, the fish is thoroughly cleaned and washed, heat treated and can be eaten.
All varieties of fish that are affected by worms visually look exhausted and swim near the surface closer to the shore.
The most common fish parasites
Recently, cases of detection of dangerous parasitic infestations among the inhabitants of water bodies have become more frequent. If several decades ago there were isolated cases of fish diseases caused by various helminths, today infected fish are being caught more and more often. Perhaps this is due to ecology and environmental pollution or something else, scientists have not yet come to a consensus. Be that as it may, the fish continues to get sick, and the most common parasites that infect it are the following:
- Eustrongylides, belonging to the genus of Dioctoform nematodes.
Adult Eustrongylides parasites in the stomachs of birds that feed on fish. They have intermediate hosts in the form of fish. The worm appears in the form of threads of red or red-white color, up to 50 mm long, located in fibrous cysts in the abdomen, in muscle tissue, in the stomach and intestines, as well as in the liver and testes. In cases where there are many larvae, they can lead to hyperemia and hardening of the stomach tissues in catfish, damage to the milk of perches, and cause kidney destruction in sturgeon. Infection with this type of parasite, when sufficient heat treatment is used, eliminates the danger for consumption and leaves the fish meat edible. - Philometra, a parasite, which is a long red thin worm, Philometra
parasitizes the body of a fish in the area of \u200b\u200bthe fins and head. Any inhabitants of water bodies, such as carp, bream, carp, crucian carp, perch, and pike, are susceptible to infection that causes the disease phylometroidosis. As it develops, at the beginning of the summer period, a fertilized, sexually mature individual releases more than 200 thousand of its larvae into the surrounding waters. They feed on crustaceans, which, in turn, are swallowed by fish. The larvae of worms enter the intestines of fish, and from there into all their internal organs, where they continue their development. Infection with this type of worms that live in the body of fish is not dangerous to humans, but the fish suffer significantly from their presence, becoming inactive. Fish meat, due to toxins released by the vital processes of parasites, becomes tasteless and unsuitable for consumption. - Another red thin worm, similar to filomentra, but with a more pronounced bright
red color and a length of 15 cm to a meter, is found in fresh water reservoirs. Fish infected by the worm are an intermediate link to humans, however, the disease caused by it is quite rare, poses a danger to humans and has a disappointing outcome. This representative of helminthiasis is still little known and its study continues.
What fish have parasites?
People often wonder whether there are parasites in sea fish. It will be a discovery for many, but helminths are found not only in freshwater fish; there are also dangerous worms in sea fish and other seafood. In this case, a parasite can enter the body, which, in principle, does not live in this type of fish. This happens as a result of large fish feeding on smaller fish. If you follow safe cooking techniques from seafood, all parasites die, and the dish becomes absolutely safe. Only those who like to enjoy rolls, sushi and other treats that are prepared without heat treatment of the product take risks. They are at risk of anisakids, which will cause problems with the gastrointestinal tract, and subsequently provoke a stomach ulcer. Getting rid of parasites and the diseases they cause will require a lot of time, effort and money, is a piece of roll worth such sacrifices?
Parasites in pollock include Chinese fluke, Siberian fluke, broad tapeworm and some others. Red fish: pink salmon, salmon, chum salmon contain tapeworms, roundworms, cat fluke, phylometroidosis and others.
There are also enough parasites in river fish; most often helminths can be found in grayling; it is not expensive, which means it is in demand among the population. When you cut a grayling, you can often see whiteworm in it. Often nematodes can be seen in the liver of crucian carp; helminth larvae look like small balls and are quite easy to see. However, in freshwater fish you can often find worms, which, although they look like parasites, are not freshwater leeches. With sufficient heat treatment, all freshwater fish parasites die. Parasites in river fish: Chinese fluke, trematodes, tapeworm, broad tapeworm, plerocycloids and others.
It is impossible to unequivocally answer the question of which fish are free of parasites; we can only say that helminths are less common in fish that live in the sea and even in those that swim in very cold water. However, it is impossible to name a type of fish that is not susceptible to helminthic infestations.
Helminths in freshwater fish
Most often, flatworms and roundworms parasitize the inhabitants of rivers and lakes. The route of infection is the same as in marine ones. River fish with worms are caught very often, but this is not always detected visually. Infestation of humans by parasites of river fish can cause a number of serious diseases. The most common diseases are:
- Opisthorchiasis. The causative agents are several types of liver flukes (cat fluke or Siberian fluke). The body of the parasite has the shape of a leaf, 4-18 mm long and up to 3 mm wide. Fluke eggs are very small, slightly yellowish, oval in shape. Human infection occurs through the carp family. The risk group includes asp, carp, tench, bream, roach and other species. Flukes in the human body affect the liver and bile ducts.
- Clonorchiasis. The disease is associated with the ingestion of a parasite such as the Chinese fluke. Symptoms resemble opisthorchiasis. The carriers of worms are the inhabitants of the Far Eastern rivers: crucian carp, gudgeon, carp, Amur ide.
- Diphyllobothriasis. Infection occurs when infected with a broad tapeworm. Parasitic larvae are most often found in muscle tissues of ruffe, perch, burbot, pike and in the salmon group. Eating pike caviar prepared in violation of technology poses a huge danger. The clinical manifestations include nausea, flatulence, abdominal pain, loose stools, physical and nervous exhaustion, and an allergic rash.
Helminths in freshwater fish
- Nanophyetosis and metagonimiasis. Caused by parasites from the group of trematodes. Small worms no larger than 1.5-2 mm settle in the human small intestine, causing continuous diarrhea, severe weakness, dehydration, anemia, and allergic rash. The source of infection for people is the Far Eastern grayling, chum salmon, minnow, Amur broadmouth and whitefish, taimen, and trout.
- Ligulosis. The disease is caused by a tapeworm in the fish Ligamentum vulgare, from the intestines of roach, roach, rudd, bream, and silver bream. Parasites in the human body have a destructive effect on all internal organs.
- Dioctophimosis. The occurrence of the disease is provoked by the consumption of nematode-infected giant ide. Adult worms, especially females, can reach one meter in length with a thickness of 0.5-1 cm. The eggs are very small, less than 0.1 mm, oval, yellow-brown in color. Helminths affect the urinary and excretory systems, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract.
Fish in aquariums are not immune from infection with worms. Infestation of domestic fish is caused by the use of live food, dirty water, and the acquisition of already sick individuals.
Important!
Worms do not pass from aquarium pets to humans; for prevention, it is enough to wash your hands with soap and water.
Diphyllobothriasis
Diphyllobothriasis
The causative agent is the broad tapeworm. In the human intestine, a worm 812 m or more in length grows from the larva. Usually a person lives with one, or less often several, tapeworms, but cases of parasitism of 100 or more individuals are described. The lifespan of a parasite is calculated in years: 10, 20 or more years. In this case, periodically, part of the end section of the strobila is torn off and is excreted in the form of a ribbon with feces during defecation.
Source of infection: perch, ruffe, pike, burbot, Far Eastern salmon caught in the Volga, rivers of Siberia, the Far East and the north of the European part of Russia.
Manifestations of the disease: changes in appetite, weakness, nausea (especially on an empty stomach), less often vomiting, salivation, belching, heartburn, rumbling in the abdomen, pressure in the abdomen, unstable stools, headache, irritability, and sometimes an itchy rash.
Pike caviar and parasites
Pike caviar contains larvae of the same dangerous diseases as the fish itself. You can become infected with worms if the caviar is poorly processed: not salted enough, not treated with boiling water before salting, or not sufficiently heat treated.
Can there be parasites in smoked or salted pike?
Dried, lightly salted, smoked pike, as a rule, is a source of infection with helminths. Never give it to children!
When eating dried, lightly salted, smoked pike, think about whether the momentary pleasure of eating is worth the treatment of dangerous helminthic diseases.
Do not neglect the information contained in this article. Don't be careless
Worms in sea fish
Marine fish are infected with parasites slightly less frequently than freshwater fish. But you shouldn’t hope that salt water protects it from infection.
Anisakids and broad tapeworm in marine fish
The following types of worms in marine fish are most dangerous to human health:
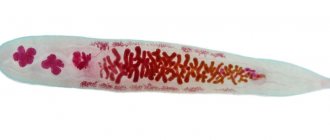
- Anisakids. Spindle-shaped white worms from 1.5 to 6 cm long. Initially they are found in the intestines, and after catching they migrate to muscle tissue, milt, and caviar. Worms look like a spiral in fish. Most often, different types of herring, halibut, capelin, chum salmon, cod, and greenling are infected. In humans, worms invade the mucous membrane of the stomach and small intestine. The site of penetration becomes inflamed and swollen. Granulomas and tissue necrosis may appear. The most dangerous consequences of anisakid infection include peritonitis caused by perforation of the gastrointestinal tract walls by the larvae. The invasion is complemented by a strong toxic and allergic effect on the body. Parasites live in the human body from 2 weeks to 3 months.
- Wide tape. An adult tapeworm reaches several meters in length. The muscles, eggs and liver most often become infected in the salmon family. The larvae are found as white worms in the meat measuring 1 or 2 cm, as well as translucent cysts on the viscera about 0.5 cm in diameter. When they enter the human body, the larvae attach themselves to the intestinal walls with suction cups. During growth, they intensively absorb nutrients entering the digestive tract. Tapeworms cause severe group B vitamin deficiency, necrosis of intestinal tissue, and damage to the central nervous system.
- Herring worm. Nematode of the genus anisakid. The worm is whitish in color, up to 30 cm long. It is found in herring, mackerel, herring, sprats, silver hake, and pollock. A person most often becomes infected by eating herring with improper salting technology.
- Nanophyetus (salmon fluke). A small parasite of the trematode class, pear-shaped, yellowish in color, measuring 1.5 by 0.8 mm. You can become infected by consuming insufficiently heat-treated foods or orally through your hands when cleaning and cutting up a carcass. Affects the entire group of salmonids.
Herring worm and salmon fluke
On a note!
Not all parasites in fish can be detected visually. Not only the intestines are infected, but also the liver, caviar, muscle tissue, and organs of vision. Therefore, you should not risk your health by eating poorly processed seafood.
Clonorchiasis
The Chinese fluke is the causative agent of the disease clonorchiasis. The main region of the disease is East Asia; in other areas, cases of infection are much less common. The intermediate host of the helminth is mainly the carp family, less commonly goby species, herring and shrimp. Once inside a person along with contaminated meat, the tapeworm can live in the body for up to 40 years.
Complications that clonorchiasis can cause have severe forms: stomach and pancreatic cancer, chronic hepatitis, peptic ulcers of the gastrointestinal tract. Anthelmintic drugs are used to treat the disease. Treatment is also prescribed depending on the symptoms: immunoboosting drugs, antispasmodics, sorbents.
Parasitic diseases of fish
These larvae are invisible to the naked eye and therefore pose a hidden danger.
A person becomes infected by eating raw, undercooked or fried fish containing the larvae of parasitic worms. In the body, these larvae settle in various organs: liver, pancreas, gall bladder, kidneys, intestines, causing severe, often difficult to cure, diseases. Opisthorchiasis is the most common helminthic disease of humans and fish-eating animals, caused by a flat helminth up to 1.5 cm long and up to 2 mm wide. The disease is characterized by damage to the liver and gallbladder, and less commonly to the pancreas. Parasites cause inflammatory processes in the bile ducts, as a result of which mucus accumulates there, the ducts thicken, the passage of bile becomes difficult, and sometimes becomes completely impossible as a result of the accumulation of a large number of helminths. There may be cases when single parasites die and gallstone salts are deposited around them, which can lead to the formation of stones. There are cases of liver cancer as a result of constant mechanical irritation of tissues during the movement of helminths.
In addition, parasites secrete waste products that have a detrimental effect on nearby liver cells, which leads to their degeneration and dysfunction.
A person with severe infection experiences paroxysmal pain in the right hypochondrium, not associated with food intake, and possible nausea and dizziness. Later, yellowness of the mucous membranes and digestive disorders are noted. The development of the helminth occurs with the participation of three hosts: the final one - man, cat, dog, fox, wolf, otter; additionally - fish from the carp family: ide, dace, tench, roach and others (26 species in total); intermediate - the mollusk Bitinia. In the body of humans and animals, sexually mature parasites secrete eggs, which enter the intestines with bile, and from there come out with feces. Further development of eggs occurs only when they fall into water. In the water, the eggs are swallowed by mollusks, in whose body, after 2.5-3 months, up to 30 living larvae, called cercariae, freely floating in the water, emerge from one egg through a series of transformations. The larvae are invisible to the naked eye. Their massive release from shellfish is observed in the spring and summer.
They live in water for two to three days. The larvae have a sharp stylet at the head end, with the help of which they penetrate the skin of fish; for movement they have a tail twice the length of the body. The larvae pierce the skin of the fish, their tail falls off, and they penetrate the muscles, where they are surrounded by two shells.
When helminth larvae enter the stomach of a person or animal, their shell dissolves, the larvae, having special sensitivity to bile, rush into the bile duct and after three hours are found in the bile ducts of the liver, where after two weeks they grow into sexually mature parasites and begin to produce eggs. The larvae of these parasites most often infect ide, dace, and less commonly - tench, roach, and bream.
To avoid infection with these parasites, it is necessary to eat well-cooked or fried fish. When preparing fish soup, small fish (up to 0.5-1.5 cm thick at the back) should be cooked for 20-30 minutes after boiling, larger fish (2 cm thick or more) - 40-60 minutes. In order for the fish to be better fried, it should be cut into small pieces and fried for 20-30 and 40-60 minutes, respectively. Drying and cold smoking do not kill parasites; they can only be neutralized by salting. Therefore, small fish infected with helminth larvae must be kept in a 12% solution of table salt for 7-10 days before drying or smoking, and larger fish for 14-20 days. In well-dried fish, the larvae die.
It should be remembered that parasites are resistant to freezing. At a temperature of minus 8-12° they die only on the fourth or fifth day, and in the meat of large fish only after two to three weeks. When cooking fish, you should not try raw minced meat: the meat of certain types of fish contains up to 20 thousand larvae. To better imagine the epizootic role of infected mammals, it is enough to note that one sexually mature parasite in the body of humans and animals is capable of releasing up to 1 thousand eggs into the external environment during the course of a day. In the liver and other organs of mammals, up to 10-5 thousand of these parasites can accumulate, and the parasites live up to 10 years.
Animals that are weakly infected release up to 20 thousand parasite eggs into the external environment every day; with severe infection - up to 15 million or more. Fish caught from water bodies unfavorable for helminthiasis can be fed to animals only in a proven form. Animals that periodically consume fish from unfavorable bodies of water must be given chloroxyl or hexachloroethane at least twice a year. These drugs kill and expel parasites from the liver.
Measures to prevent opisthorchiasis also include the destruction of stray dogs and stray cats, and timely treatment of domestic animals against this disease.
Methorchiasis is a widespread disease of piscivorous animals caused by a pear-shaped flat helminth. Its length is 2.5-3.5 mm, width is 11.2-1.6 mm. The helminth affects the bile ducts of the liver and gallbladder. Infection of humans and animals is possible only through fish. The development of the parasite occurs with the participation of three hosts: the main one is a cat, a dog, a fox and other animals; additionally - fish from the carp family (ide, roach, rudd, bleak); intermediate - mollusks. The timing of development of metorchis in the host organism is close to that of opisthorchis. Metorchis also causes significant changes in the liver. In cats affected by Metorchis, thickening and inflammation of the bile ducts and an enlargement of the bile duct (up to 1 cm in diameter) are possible. Metorchises are more often found in fish and animals living in lakes, oxbow lakes, reservoirs, and river basins. Measures to combat and prevent these diseases are the same as for opisthorchiasis.
What to do if a worm or larva is found in fish
If you cannot accurately determine the type of parasite, and do not know whether it is dangerous for humans or not, then it is better not to eat such fish. But if you still decide to cook it, you must follow the following rules:
- Infection with helminths occurs when eating poorly fried or poorly cooked fish. Therefore, you need to cook or fry the fish for at least 20-25 minutes; when baking in the oven, the fish needs to be kept for 30-40 minutes.
- Not all parasites die in salted fish, this must be remembered well, and those that die die only after 15-20 days. When frozen, parasites die in 6 hours at a temperature of -30 C, in 3 days at a temperature of -20 C and in 4 days at a temperature of -12 C.
Signs of fishworm infestation
Signs indicating that there are parasites in the human body do not appear immediately. In the process of evolution, worms have learned not to reveal themselves and not to disrupt the life of the host. Therefore, at the larval stages, the symptoms are rather vague, and often a person does not attach importance to the ailment or does not associate it with parasites.
The most common habitat and breeding ground for parasites is the intestines; here, infection with helminths can manifest itself as follows:
- diarrhea and constipation;
- abdominal pain and bloating;
- weight loss;
- intestinal obstruction;
- sleep disturbance, irritability;
- irritable bowel syndrome.
Parasites are not often localized in the stomach, since the acidic environment and enzymes are not very favorable conditions for the life of worms, however, if they do settle there, the symptoms may be as follows:
- nausea and vomiting;
- bloating;
- belching;
- feeling of heaviness;
- in severe cases, heartburn and stomach bleeding.
As for the liver, parasites settle in it very often, and the following symptoms occur:
- nausea and vomiting;
- pain on the right under the ribs;
- yellowness of the skin;
- allergic reactions;
- anemia;
- constant fatigue and weakness;
- nervousness;
- hair loss.
If the parasites infect the lungs, a dry cough develops, and if the alveoli are affected, the cough is accompanied by the production of sputum streaked with blood. Damage to the skin causes itching and rashes; when parasites actively multiply, abscesses, swelling and redness can occur. If they attack the eyes, then the person’s vision deteriorates sharply, shadows and glare appear before the eyes. These are dangerous symptoms, since in some cases parasites can deprive a person of vision, and this process is irreversible.
With the bloodstream, larvae and adults can enter the heart, this is extremely dangerous, as it can be fatal. Parasites worsen the patency of blood vessels, and ischemia develops, the nutrition of the heart becomes insufficient, and the functioning of the organ is disrupted.
Is it possible to eat fish if it has worms, and what do they look like?
Marine or freshwater fish very often become a place for the development and reproduction of many types of helminths. Some species may not pose a danger to humans. But in most other cases they cause serious illness and unpleasant symptoms. Worms in fish do not die when smoked, pickled or salted, especially since an infected product cannot be eaten raw.
Manifestations of helminthic infestation
Symptoms characteristic of infection with worms after eating infected fish.
- A large accumulation of worms in the human body leads to intestinal obstruction and stagnation of bile. Constipation and abdominal pain develop.
- Fish helminths cause disturbances in peristalsis, change the microflora, and frequent loose stools develop.
- When the mucous membrane of the small intestine is damaged, flatulence and bloating develop.
- As helminths move through the body, a person may feel pain in the muscles and joints.
- During their life, worms release toxins that cause allergic reactions. From a simple rash to Quincke's edema. The number of eosinophils in a person's blood increases.
- Many parasites feed on blood, sucking out all nutrients, including iron. Anemia develops, which is characterized by pale skin, increased fatigue, apathy, and drowsiness.
- Sleep is disturbed, teeth grinding during sleep and night drooling are observed.
- Eating a fish product with helminths can lead to inflammation of the respiratory tract. Cough, asthma, runny nose, shortness of breath may occur. Bronchitis and pneumonia develop.
- Immunity decreases. People often suffer from colds and dysbacteriosis appears.
- If helminthic infestation lasts for a long time, it can develop into cancer.
If at least one of these signs appears, you need to undergo an examination. Another characteristic sign of fish worms entering various human organs is loss of appetite and weight loss.
Types of worms found in aquatic inhabitants
Are there parasitic microorganisms in the body of aquatic inhabitants? There is a greater chance of becoming infected with helminths from river fish than from marine species. There are also dangerous diseases for humans that can be contracted from fish.
Opisthorchiasis. The disease is caused by the cat fluke. Fish are only intermediate hosts. Dogs and cats are considered carriers. The size of the worm reaches 12 mm, parasitizes the liver, gall bladder, and pancreas. Can exist in carp breeds.
If you eat fish infected with cat fluke, the first symptoms will appear only after 2-3 weeks. The main symptoms are fatigue, pain in the head, muscles, and joints. The respiratory system is affected. Cough and difficulty breathing appear. The digestive organs become enlarged, the liver and spleen are especially affected. I am concerned about the rash and itching of the body. Body temperature can rise to 39-40 degrees.
The acute phase lasts only a few days and then passes into the chronic latent stage, slowly destroying all the internal organs of a person. When the first signs appear, you need to contact a specialist.
Diphyllobothriasis. The disease is caused by the wide tapeworm, which can reach 12 meters in length. The main carriers of parasites are: river fish, salmon, perch, pike.
The incubation period can last up to 2 months. And only then the first symptoms will appear. Body temperature stays no higher than 38 degrees for a long time. Fatigue, fatigue, loss of appetite, stool problems. The patient feels nauseous and may vomit. A coating appears on the tongue.
Clonorchiasis. The causative agent is the Chinese fluke. Most often it can be found in the body of minnows, crucian carp, and carp. Only after 2-4 weeks do the first symptoms appear in the form of high fever, muscle pain, and skin rashes. The liver is enlarged, the upper right part of the abdomen hurts. I am concerned about the increased formation of gases and flatulence. Vomiting and diarrhea occur.
Metagonimiasis. The causative agents are trematodes only 2.5 mm long. A week after the larvae enter the human digestive organs, a rash appears on the body, appetite is disrupted, body weight decreases, vomiting, diarrhea, and pain in the central part of the abdomen occur.
Anisakidosis. Helminths in fish such as anisakids parasitize the intestines. Most cases are found in marine fish. You can become infected by eating a lightly salted product, in particular herring. After a few hours or days, pain in the head begins to bother you, and body temperature can rise to 38 degrees. The patient is worried about nausea, which then turns into vomiting, abdominal pain appears, and there is no appetite. A common characteristic symptom is an allergic rash throughout the body.
Ligulosis. The disease is caused by a tapeworm - the common Ligulidae. It can reach one meter in length. Causes diseases of all internal organs. Dizziness, headaches appear, body temperature rises, vomiting and diarrhea bother you.
Dioctophimosis. Helminths are localized in the organs of the urinary system and disrupt its functioning. Weakness, vomiting, diarrhea appear, the digestive organs become enlarged, the bladder becomes inflamed, and pyelonephritis develops.
Nanophyetosis. The disease is caused by small trematode worms. Adults live in the small intestine. I am worried about pain in the lower abdomen, diarrhea, flatulence.
Worms that people don’t need to be afraid of
There are fish helminths that pose a danger only to themselves. In the human body they do not find favorable conditions for development and die.
Diplostomiasis is caused by helminths of the trematode class. The main manifestation is black spots all over the body of freshwater fish. They are localized either in the organs of vision or in the brain. Wild birds become the source of infection. The feces of infected birds fall into the water, the eggs penetrate the shellfish, and larvae emerge from them, capable of penetrating the fish’s body through the skin.
Philometroidosis is caused by nematode worms. The larvae are localized in the liver, kidneys, swim bladder, and adults move into muscle tissue. After eating an infected cyclops crustacean, the fish itself becomes ill. Inflammation of all internal organs occurs. Infected meat can be eaten; first you need to clean the belly, remove the liver and rinse well with water. Be sure to heat-treat before use.
Helminths such as schistocephamos reach a length of no more than 2 cm. Most often they can be found in the intestines of red fish, for example, trout or salmon. They are not hazardous to human health. Fish with worms of this type just need to be gutted, washed with running water and thoroughly boiled or fried.
Trienophorosis. Sexually mature helminths are most often found in the intestines of pikes, and less commonly of perches or omuls. The larvae infect the internal organs of trout, perch, burbot, ide and other fish. When cutting infected fish, white balls can be found in the internal organs. When the membrane ruptures, the flatworm emerges. Such accumulations should be removed and the meat should continue to be processed before consumption.
All fish infected with helminths look exhausted, swim near the surface of the water, closer to the shore and become easy prey for birds.
How to neutralize fish from parasites
There are several ways to neutralize fillets from parasites to avoid infection. Fish needs to be properly:
- cook,
- freezing,
- salt,
- dry,
- fry,
- stew.
Freezing kills the adult parasites and larvae. But this must be done correctly, since different types of helminths can die when exposed to cold for different durations. After freezing, the fillets need to be boiled or cooked to completely kill the parasites.
Freezing
A reliable way to neutralize carcasses is to freeze them. Almost no viable parasites are found in frozen fillets. Therefore, the caught fish (if it is not cooked immediately) is frozen. How long you should freeze fish to remove parasites depends on the temperature. The table provides the time and temperature for freezing raw materials weighing 2 kg.
| Time, h | Temperature *C |
| 12 | -27 |
| 18 | -22 |
| 36 | -16 |
| 72 | -12 |
| 7 days | -8 |
| 10 days | -4 |
Opisthorchids are killed by temperatures of -40*C for 3 hours and -30*C for 6 hours. The larger the fish, the longer it needs to be frozen. Small fillets less than a kilogram can be frozen at home in a regular freezer for at least 10 hours. To destroy the tapeworm, the fish should be frozen for a day. The deep freezing method is also used (keeping the meat for 3-4 days). If the chamber maintains a temperature of -12*, then the raw materials must be kept for at least 20 days.
Do worms in fish die when frozen?
This happens when all freezing rules are followed. Exposure to cold has a detrimental effect on adult and larval helminths.
Salting, smoking, drying
These are the most favorite ways to cook fish. In this form, it is brought as a gift, or bought when visiting fish markets. The effects of salt and smoke have been known for a long time. But this processing method does not always pay off. It is necessary to strictly adhere to the technology so that the finished product is safe for consumption:
- hot salting (16*C) 5-9 days,
- cold salting (6*C) 6-13 days.
Dry salting is done at the rate of 20% salt per 1 kg of fish. Gutted carcasses are kept in this mixture for 7-12 days, and whole ones for 9 to 13 days.
Cold or hot smoking kills all parasites by the time they are fully cooked. The fish is dried for 21 days. On the eve of the cooking process, the fillets are kept in a 15% saline solution for 72 hours.
Information! At home, it is difficult to smoke fish correctly, since it is impossible to maintain the desired temperature for a long period. Therefore, it is necessary to refuse to prepare raw materials in this way at home.
Boiling, frying, baking
Almost all river inhabitants contain parasites. Heat treatment is a simple and reliable way to destroy unwanted residents in meat. How long should you cook river fish to kill parasites, depending on its size. The larger the fish, the longer it is processed. This also applies to frying and baking. In order not to doubt the correct preparation, you should cut the carcasses, cut them into small pieces and cook for at least 30 minutes after boiling. Boiled fish is not dangerous to eat. How long should you cook sea fish to kill parasites? It must be prepared in the same way as river fish.
Fry the fillet under the lid. This will create a high temperature, and the parasites will be completely neutralized. The cooking time depends on the size of the product pieces:
- small fish 10 minutes,
- 700-1200g, as well as fillets 2-4 cm thick, cook for 15-20 minutes,
- carcasses with a backbone or thickness of 5-6 cm are fried for at least 40 minutes.
Fans of pies with fish filling should bake them for at least half an hour. You need to bake the fillet in an oven, maintaining a temperature of 200*C for 35-40 minutes.
Do parasites in fish die when frozen?
Meat and fish are valuable food products. Their main nutrient is protein, which is necessary for the normal functioning of the body. They also contain various micro and macroelements, vitamins and fatty acids, which help maintain normal health.
Fish of any species that have grown in natural conditions may contain parasitic worms. They choose not only the intestines as a localization site, but also the head, gills and muscle tissue.
The risk of developing helminth infestation when eating fish is determined by the following indicators:
- The place where the parasite develops.
- Availability of its removal.
- Method of preparation.
- The state of the body of the final host.
Worth knowing! By infecting fish, parasitic worms lead to changes in their appearance. Often, specific diseases caused by worms affect the condition of the skin, fins and scales. Such fish can be visually distinguished from healthy ones. It cannot be eaten.
Main signs of infected fish:
- Spotting of unknown nature.
- Light or dark dots.
- Changing body shape.
- Enlargement or degeneration of individual organs.
Parasites in the human body. Read about the treatment of parasites with aspen bark here.
Read about broad-spectrum anti-parasitic medications at the following link:
Some helminths can be seen with the naked eye, but many of them are very small. That is why they cannot be determined even with a thorough examination. And worm larvae can almost always be seen only under special equipment.
To prevent helminthic infestation, fish products are subject to heat treatment. This allows you to destroy all microorganisms parasitizing in it and their larvae.
Do worms in fish and their larvae die when frozen? The unequivocal answer is yes. Adults and larvae of worms are destroyed when fish are exposed to low temperatures. This theory has been confirmed by medical scientists. Indeed, cold has a negative effect on helminths. To disinfect infected products, they must be frozen and kept in such conditions for at least three hours. After such processing, the products become safe.
Temperature conditions for the destruction of helminths:
- At -40 C, the worms die within 24 hours.
- At -25 C, parasites and their larvae die in three days.
- At -18 C, helminths are destroyed in 5-7 days.
After keeping the fish and meat products in the freezer for the recommended time, at the appropriate temperature, they can be disinfected.
If you use a standard freezer in the refrigerator, you should leave the fish or meat there for at least six days. Insufficiently deep freezing of these products can cause helminth infestation.
Remember! It is recommended to buy frozen fish and meat only in special stores. Their shelves are stocked with products that have undergone industrial antiparasitic treatment. In addition, the required temperature conditions are maintained in the refrigeration equipment.
When purchasing fresh meat or fish in the winter season, if possible, they are kept in natural frost for four days. Under normal conditions, it is enough to freeze them in the freezer of a standard refrigerator for the same period of time.
Cut raw or frozen fish and meat products on special boards and with a separate knife. Kitchen utensils that have been in contact with raw foods must be treated with boiling water or steam.
Despite the fact that freezing is a good way of disinfection, such fish and meat are not recommended to be consumed raw. They require heat treatment, the duration of which is selected depending on the cooking method, temperature and size of portioned pieces of fish or meat fillet.
Symptoms of infection
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9G9xF5QMqI0
The first clinical picture of helminthic infestation does not appear immediately and has vague signs. Symptoms depend on the incubation periods of helminth infections, which can range from 2 to 60 days. Common symptoms of parasitic infestation include:
- lethargic, drowsy state;
- excessive fatigue;
- nervousness;
- increase in low-grade fever;
- allergic reactions;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- disorders in the gastrointestinal tract;
- excessive gas formation;
- jumps in weight indicators;
- depressive state.
Tapeworms (cestodes class) are the largest in size. Causes enormous harm to the body.
Moreover, not only a certain organ suffers, but many digestive, circulatory, nervous, respiratory, and vascular systems.
Cestodes in humans can be of several types. The treatment is specific, so only a doctor can tell you how to get rid of tapeworms.
In some cases, surgery is required. The consequences of the presence of pathogenic neighbors in the body can be irreversible.
Treatment methods
Treatment of fish parasites can only be prescribed by a specialist in this field, namely a parasitologist or infectious disease specialist. When choosing a treatment regimen, the doctor is guided by the type of parasite, its location, the severity of symptoms, the general condition of the patient and many other factors. All drugs used in treatment are very toxic, so self-administration of these medications is not permissible. The dosage and special diet for the duration of treatment are selected by the doctor.
Treatment of tapeworm should be carried out only in a hospital setting, with the patient taking the medicine in stages, with breaks between them. As a result of treatment, the parasite dies and is eliminated from the body, while the patient may experience intestinal obstruction, and surgical intervention may be required, especially if the parasite is of an impressive size or there are several of them.
Populin or Ecorsol are used to treat opisthorchiasis; treatment of this disease is complex and must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. Clonorchiasis is treated with anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, choleretic, antihistamine drugs and sorbents.
For metagonimiasis, Cesolom or Biltricid is prescribed; without timely treatment, the disease can affect the heart, spinal cord and brain. Anisakidosis is treated with Albendazole or Mebendazole.
Basics of therapy
If you have eaten infected fish or you suspect that it contains worms, first of all, go to the doctor. He will prescribe the necessary tests, the results of which will confirm or refute the diagnosis.
Treatment of helminthiasis
The earlier the disease is detected, the more effective the treatment will be. Each type of parasite has its own medicine, which cannot be used against other helminths. Severe diseases are treated surgically, and some of them lead to death, despite qualified medical care.
If there were tapeworms or other parasites in the fish, therapy is carried out for all family members, since some worms are transmitted through one touch. In addition, there are diseases that occur without visible symptoms.
That is why it is necessary to have stool tested and undergo a course of treatment. To prevent re-infection, you must follow a diet and not violate the rules of hygiene.
Self-medication is strictly prohibited. Many anthelmintic drugs are toxic and can cause serious consequences if taken in the wrong dosage.
Folk remedies
Worms in fish are very dangerous for humans, and alternative medicine recipes can be used to combat them. But first you need to talk to your doctor.
One of the popular options is carrot juice, which has an anthelmintic effect. Garlic is often used to kill worms.
You can eat it or make cleansing enemas from the juice. But the most effective remedy is pumpkin seeds, recognized by official medicine.
They quickly kill parasites and ensure their removal from the body.
Preventive measures
To exclude the possibility of infection with parasites through fish, you must adhere to some recommendations:
- do not consume raw fish products;
- strictly adhere to the technology of salting, marinating and smoking;
- subject the raw materials to heat treatment for at least 20 minutes. with a temperature above 65°C;
- the filling for fish pies must undergo preliminary heat treatment or bake for at least 30 minutes;
- When purchasing, pay special attention to the appearance of the fish;
- Do not purchase fish from your own hands, caught in unknown waters.
The freezing process allows you to get rid of parasites invisible to the naked eye: 5 days at -20°C and below, or 1-4 with stronger freezing. After this, the worms in the frozen fish die completely.
On a note!
Many lovers of raw seafood dishes are interested in the question of which fish are free of worms and parasites. They can be advised to use sterlet in cooking or buy fish grown in artificial reservoirs, where the quality and health of the stock is constantly monitored.
Prevention measures
To ensure that contaminated fish does not end up on your table, it is necessary to regularly take certain preventive measures. Consumption of the product in its raw form is strictly prohibited.
If there is an urgent need for this, then certain rules are followed.
To be consumed raw, the product must be grown under artificial conditions. Her nutrition must be artificial. The product must be treated and regularly monitored for the absence of parasites.
If sea fish is used for cooking, it must be frozen on a fishing boat immediately after catching.
The product must be defrosted immediately before consumption. The product is also allowed to be eaten raw immediately after catching.
Almost all types of river fish are characterized by the presence of parasites that pose a danger to human health and life.
Only sterlet can be eaten raw . All other types of products must first undergo a salting, pickling or smoking process in accordance with the developed recommendations.
Only a product that has been thoroughly boiled or fried beforehand is considered safe . These rules must be followed, regardless of the type of fish, since it is impossible to see the presence of microscopic helminth larvae with the naked eye.
Cooking fish should be carried out for at least 20 minutes after it boils. The product must be fried in a well-heated frying pan for the same time. To ensure complete heat treatment, it is recommended to pre-cut the product along the ridge.
Baking pies that contain this product should take at least half an hour. If the product is hot smoked, this process completely kills the helminths before they are ready.
When buying fish, you should give preference to those options that have scales. It should have a characteristic shine and not puff up.
How to avoid getting infected with worms
Adult worms in fish can most often be seen independently. Larvae and eggs, which are much smaller in size, are detected only in laboratory tests. Once you see a photo of worms in fish, it is no longer possible to forget their terrifying appearance. Subsequently, the visual picture can always be compared with the found parasites in order to determine the degree of their harmfulness.
On a note!
Fish with worms is not always a source of infection. Some species, after removing the scales and entrails, become safe. But it's not worth the risk. It is better to get rid of an infected fish carcass.
Helminths in fish
Worms in fish - dangerous and safe, which fish do not contain parasites
What fish don't have worms? Recent studies show that all fish products are invaded. Even marine fish are parasitized by several species of helminths, in particular anisakids. Tapeworms in fish (cestodes) are not as rare as they might seem at first glance. In addition to cestodes, at least a dozen other varieties of helminths use marine and freshwater inhabitants, including crayfish and crabs, as intermediate or final hosts. Roundworms (nematodes) and also flatworms (trematodes) are often found in fish. Not all of them are dangerous to humans. Is it possible to eat fish with worms inside? Yes, if people prepare it correctly. What to do if a worm is found in fish already at home? There are 3 options - take it to the store, freeze it for a couple of weeks, fry it well or boil it.
Safe worms
Many types of parasites living in fish do not pose a particular threat to humans. This is due to the fact that:
- Not every worm parasitizing fish is dangerous to humans.
- The fish we buy in supermarkets and fish stores comes to us frozen. It can be considered safe if everything was done correctly on the fishing vessel. At what temperature are worms rendered harmless? When frozen at -20°C or below, most parasites die within 7-14 days.
- If you eat fried or cooked fish in accordance with accepted standards (not half-raw), 99% of any parasites will die after heat treatment.
The following parasites in fish do not pose a threat to humans even when alive: diplostomy (flat), pylometry (round), some types of tapeworms.
Diplostomy
Such fish parasites as Posthodiplostomum cuticola, Diplostomum spathaceum, Posthodiplostomum minimum belong to the family Diplostomatidae and belong to the class of trematodes or flatworms.
Diplostoma cuticola parasitizes near the eyes of fish - in the pectoral fins, gills, and sometimes in the eyeballs. This parasite is found throughout Russia in fresh water bodies, as well as in the Kursk Bay of the Baltic Sea. Diplostom is found in perch and cyprinid fish, in particular in perch and roach.
The worm Diplostomum spathaceum parasitizes exclusively in the lens. As a result, the fish's eyes become cloudy and lose vision due to an active inflammatory process. The following are especially susceptible to the disease:
- Salmonidae (in red fish: in chum salmon, salmon, salmon, coho salmon, sea trout, and also in pink salmon, diplostome can often be found).
- Cyprinids (bream, ide, crucian carp, tench, silver carp, roach).
- Perch (these parasites are found quite often in sea bass).
- Whitefish (whitefish, nelma).
Posthodiplostomum minimum is a widespread species of tiny fluke that lives in fish. The length of these worms does not exceed 1.2 mm. Widely distributed in Mexico and North America. The dwarf diplostoma has an anterior oval segment with a ventral depression, covered with numerous spines. The larvae of the parasites are found in the fish under the skin and in the tissues in the form of metacercariae and can be seen even with the naked eye.
Pilometra
Philometra fasciati or Philometra lethrini refers to nematodes that live in fish (photo below). These are red worms up to 0.1 meters long. They were first discovered in the South Pacific Ocean off the coast of New Caledonia. The worm most often lives in the scale pockets of females or in the membrane of the swim bladder of male cyprinids. When cleaning the scales, the helminth is removed, and the fish that was once wormed becomes fit for consumption.
Cestodes or tapeworms
Several species of these worms parasitize fish: Ligula intestinalis and Schistocephalus solidus.
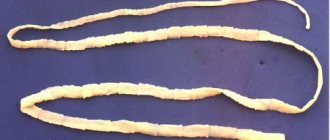
The first tapeworm is called the common strapworm. In the body of the fish, it resides in the form of the last larval stage (plerocercoid) and at the same time reaches a length of 100 cm.
Schistocephalus solidus is similar to the Ligulidae in its normal life cycle. The size of this parasite is very small - only a few centimeters. Parasitizes small fish.
Dangerous worms
It is imperative to remember that you can find uninvited guests not only in river fish, as well as crayfish, but also in sea fish. Therefore, it is better to be careful and refuse to buy lightly salted or cold/hot smoked herring and mackerel, and cook crustaceans for at least 20 minutes. Parasites in sea fish are not a myth, but a harsh reality (for example, cod or herring worms).
Among the huge number of worms that parasitize marine and freshwater fish, only some of their species are capable of infecting people. They belong to round, flat and tapeworms. Parasites living in fish that are dangerous to humans (see photo below):
- anisakids;
- diphylobothrium;
- clonorchis;
- opisthorchi.
Rare fish worms include Heterophyes heterophyes and Metagonimus yokogawai.
Anisakids
They are considered the most dangerous of those living in fish. In the human body they parasitize for a short time:
- Anisakis simplex – white herring worms. Such worms are very common in mackerel and herring. Parasites in pollock also belong to Anisakis simplex.
- Pseudoterranova decipiens. The worms in cod belong to this species of anisakid. They are often found even in frozen fish and are called cod worms.
The route of infection is oral. Herring worm larvae can enter the human body from raw or lightly salted fish (parasites in mackerel or herring, worms in pollock). The situation is similar with cod fish; you can get infected from them even faster if you regularly eat sushi made from halibut, trout, pink salmon, and also if you prepare burbot incorrectly (this fish is a cod fish). Very often, anisakid parasites are found in the liver of burbot.
Diphyllobothrium
Belongs to the class of cestodes that parasitize fish. There are about 13 varieties of Diphyllobothrium. You can become infected with 3 of them - Latum (wide tapeworm), Dendriticum and Nihonkaiense.
The broad tapeworm living in fish is one of the longest worms in the world. Its length reaches 10 m or more. The lifespan of the parasite is up to 20 years.
The life cycle of a worm is quite complex:
- An infested person releases immature eggs in the stool.
- The worm eggs enter the aquatic environment, where they mature for about 20 days, after which oncospheres emerge from them.
- After some time, the oncospheres produce coracidia - larvae that move in the aquatic environment and feed on intermediate hosts (crustaceans, fish).
- Crustaceans and marine fish eat coracidium. In their body, the parasite turns into a procercoid.
- The second intermediate host, a small fish, eats the crustacean. Here the procercoid becomes a plerocercoid. If a person eats sick fish raw, he will become infected.
It should be noted that minnows and other small fish are never eaten by humans. However, the danger of invasion remains because these fish species are food for predators such as pike or trout.
After swallowing infected fish, they become carriers of plerocercoids. Here the wide tapeworm is localized in the meat of the fish. Having eaten poorly cooked or fried trout or pike with parasites, a person becomes the final owner of the broad tapeworm.
Trematodes
There are about a little more than 3 dozen varieties of flatworms, but only a few of them pose a real threat to humans. This includes parasites of freshwater fish such as Clonorchis sinensis (clonorchis) and Opisthorchis spp (opisthorchis). The intermediate hosts in this case are bithiniid mollusks and cyprinids (roach, carp, carp, bream and others).
In addition, small trematodes are dangerous to humans, one of the intermediate hosts of which is fish, and the final host is birds of prey and mammals. These are representatives of the Heterophyidae family. The most common pathogens are helminths of the species Heterophyes heterophyes and Metagonimus yokogawai.
You will be surprised how many parasites will come out if you drink a glass of regular...
Parasites will leave the body in 3 days! You just need to drink on an empty stomach...
Diseases caused by fish worms
Worms in fish often cause various helminthiasis in humans. This is due to the fact that this product (fish) is considered to be the safest in comparison with cattle meat or poultry. Among helminthic infestations caused by fish worms:
- anisakidosis;
- diphylobothriasis;
- clonorchiasis;
- opisthorchiasis;
- heterophyosis (Heterophyes heterophyes);
- metagonimiasis (Metagonimus yokogawai).
Anisakidosis
Anisakid larvae (worms from pollock, herring, cod) are adapted for life in the body of fish and are not adapted for long-term residence in the human body. Immediately after getting into it, the worms try to get out as quickly as possible. However, during their short visit they can cause great harm to human health. The most pronounced intestinal or gastric symptoms depend on where the parasite temporarily stopped:
- Vomiting, persistent nausea.
- General weakness.
- Temperature rises to subfebrile.
- Diarrhea.
- Accumulation of gases in the intestines.
- Epigastric pain.
- Allergic reactions to the release of toxins by parasites - Quincke's edema, urticaria.
Anisakids can migrate to the liver or esophagus. In the first case, inflammation of the bile ducts and bladder is observed, in the second there is pain in the esophagus, which is accompanied by a cough.
Diphyllotbothriasis
Diphyllobothriums live in fish, and are perfectly adapted for long-term residence in the human body. He is their final master. In his intestines, a worm like a wide tapeworm can grow to a gigantic size - 12 meters, and live for at least 10 years.
Diphyllobothriasis can be asymptomatic. Although in fact nonspecific symptoms in the form of abdominal pain, nausea, and belching are present. But the patient pays attention to it only after he notices a piece of worm tape in the feces. Other symptoms include:
- Pathologies in the systems: digestion, hematopoiesis, nervous.
- Weakness, drowsiness.
- Stool disorder.
- Incomprehensible taste sensations when eating sour, spicy, salty foods.
- Possible allergic rashes - urticaria.
- Vomiting, loss of appetite.
- Weight loss.
- B12 deficiency anemia.
- Paresthesia.
When diagnosed, in 9 out of 10 cases, patients are diagnosed with achylia - atrophy of the gastric glands that produce digestive juice, as well as thrombocytopenia, leukopenia.
Clonorchiasis
Clonorchid worms (Chinese flukes) are based mainly in the human stomach and liver. Symptoms are similar to opisthorchiasis:
- General weakness, high temperature, inflammation of the lymph nodes. Palpation reveals an enlarged liver, less often the spleen. This condition lasts up to a month. This is due to the life cycle of the parasite.
- A month later, Chinese fluke eggs are found in the patient’s stool.
- In advanced cases, the patient develops biliary dyskinesia, hepatitis, pancreatitis, angiocholitis, liver cirrhosis in critical cases.
Clonorchiasis is chronic, with periods of exacerbation and remission.
Opisthorchiasis
Opisthorchid worms live in the bile ducts of the liver, but are also found in the pancreas. The symptoms associated with their presence in the human body are divided into allergic, which is associated with the release of toxic substances by worms, and traumatic - when the worm is fixed in the organ and moves, it causes great damage. With a large concentration of worms, complete blockage of the bile duct is possible.
Symptoms:
- A sharp rise in temperature to +38 and above. Lasts up to 3 weeks.
- Joint, muscle, headaches.
- Hives.
- Diarrhea, vomiting, nausea.
- Insomnia, lethargy, or vice versa - overexcitement.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Jaundice.
- Pain in the right hypochondrium.
The disease can last a long time, without obvious periods of exacerbation. In this case, patients gradually develop chronic hepatitis and more severe conditions - hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis of the liver.
If the worm is caught in the pancreas, the symptoms are different:
- Girdle pain radiating to the left side of the chest.
- Depression, sleep disturbances, headaches.
- Sudden change of mood.
If the worm has entered the intestines or stomach, ulcers, gastroduodenitis, and chronic gastritis develop.
Heterophyosis
The main location of the Heterophyes heterophyes worm is the human intestine. However, its eggs can also enter the brain.
The disease is characterized by intestinal and allergic symptoms:
- Stool disorder (diarrhea, constipation).
- Hives.
- Headache.
- Vomiting, nausea.
The chronic course is characterized by persistent diarrhea, salivation, and pain localized in the abdomen. Heterophyosis provokes the development of enteritis.
Metagonimiasis
The symptoms of this helminthiasis are similar to heterophyosis. The onset of the course is acute, characterized by a rise in temperature, fever, and allergic reactions in the form of skin itching. Next, enteritis develops, which is characterized by abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and prolonged diarrhea.
Are helminths in fish dangerous and is it safe to eat? If hygiene standards are not violated, the product is safe. But whether to eat it or throw it away is something everyone decides individually. Knowing what certain worms look like, you can determine their type and understand whether they are dangerous to humans or not. If worms are found in fresh frozen fish purchased at the store, do not be alarmed. Gut it, wash it and heat it well. After this, even the parasites remaining in the carcass will be neutralized.
Precautionary measures
Is it possible to eat a fish product that contains helminths? There is a high probability that a person can become infected with worms from fish. Unpleasant symptoms appear associated with dysfunction of internal organs. Contaminated fish should not be eaten lightly salted, smoked or dried.
Worms die in the freezer at temperatures below -25 degrees or during heat treatment above +100 degrees. We can conclude that if fish is frozen or well-heat-treated, it becomes safe for human health and can be eaten.
You need to boil the fish for at least 35 minutes, fry for at least 25 minutes, and bake for about 45 minutes. If the fish is large, it is recommended to make cuts so that the meat inside is also cooked well.
It is recommended to dry the fish for three weeks and salt it for two weeks. Freeze at temperatures below 25 degrees for at least a day.