The Japanese economy developed at an accelerated pace in the 60s–80s of the last century. However, the last decade of the 20th century is considered to be a “lost decade” for the Land of the Rising Sun. At that time, there was a significant decline in economic growth due to the so-called explosion of the price bubble for the assets available in the country. The Japanese government took drastic measures. As a result, by 2005 the country’s economic growth rate began to exceed the value of this indicator in the European Union and the United States.
Features of the economic and geographical location
Japan is located on 4 large islands - Honshu, Kyushu, Shikoku and Hokkaido, as well as on more than 6 thousand smaller ones. Its total area is 378 km2.
The subsoil of Japan is poor in mineral resources. On its territory, mining is carried out mainly:
- limestone;
- sulfur;
- oil;
- zinc and lead ores;
- coal.
The peculiarities of Japan's economy are a direct consequence of the fact that it is located in the center of the Asia-Pacific region (APR). This factor opens up broad prospects for the country to participate in the international division of labor.
Despite the lack of natural resources (raw materials for a large number of industrial sectors are imported from abroad), Japan occupies a leading position in some manufacturing sectors. For example, in terms of steel production volumes in the global ferrous metallurgy, its share accounts for 23%.
And the phrase Made in Japan is firmly associated with the high quality of a variety of products.
Japan GDP by year
Gross domestic product is the most important indicator of economic productivity. Japan's GDP for 2021 has not yet been presented on the websites of leading statistical agencies; only forecast data is available. The International Bank provides data only for 2015. Thus, Japan's GDP last year amounted to $4,123.26 billion. This is about 6.65% of global gross domestic product.
Between 1960 and 2015, Japan's average GDP was US$2,549.58 billion. A record low figure was recorded in 2012. Then the GDP reached $5957.25 billion. The highest figure was recorded in 1960 – 44.31 billion US dollars. Between 1980 and September 2021, Japan's average GDP growth was 0.48%. The record high was recorded in the second quarter of 1990. Then GDP growth was 3.2%. The record low figure occurred in 1990 – -4.1%.
Characteristics and structure of the Japanese economy
The economy of the island state is developing in accordance with the doctrine adopted in the mid-20th century.
At that time, the flagship of Japan's industry was light industry. Today, heavy industry has also become a priority. The area of high-tech developments was singled out as a special niche. Combined with a high level of exports and low unemployment, the country confidently holds third place in the world in terms of GDP.
The gradual and at the same time competent implementation of this doctrine has borne fruit. Let us consider only the main characteristics reflecting the level of economic development of Japan.
GDP size
In terms of GDP, Japan at the beginning of 2021 ranked third in the world and was second only to the United States and China. The dynamics of changes in this indicator in 2010-2018 are presented in the diagram. The unit of measurement is billion dollars.
The size of Japan's GDP is significantly influenced by the volume of exports of electrical, electronics, and mechanical engineering products. Interestingly, even during the global crisis of 2008-2012, the state's gross domestic product increased. And in the next 3 years, a decrease in this indicator by 16.8% was recorded.
Experts explain this phenomenon by unfavorable fluctuations in the exchange rate of the American currency, which caused a drop in demand for cars from Japanese manufacturers in the global car market.
In per capita terms, Japan's GDP at the end of 2021 was $39,306. Over the year, the value of this indicator increased by 2.51%. Such low growth rates are a consequence of the fact that, at a certain level of technology, the Japanese economy has reached a development threshold. That is, in the coming years, GDP will increase relatively slowly.
The World Bank announced the following forecast: within 3 years, annual GDP growth in Japan will average from 0.4 to 1.5%. In numbers it looks like this:
- 2021 – up to $4.992 trillion;
- 2021 – $5.008 trillion;
- 2021 – $5.015 trillion.
Formation of the state budget
The state budget of the Land of the Rising Sun for 2021 was approved for a record amount - about 101.5 trillion yen ($950 billion). The government plans to increase defense spending by 1.93% to $48.1 billion. The need for this is due to the instability of the situation on the Korean Peninsula.
A record high amount of 31.884 trillion yen (about $300 billion) will be allocated to social needs, the rapid growth of which is due to the aging population of Japan.
By the way, for this reason, in March 2021, the country's public debt reached 1103 trillion yen ($10.38 trillion). The fact is that the government cannot cover social expenses only through taxes, and therefore is forced to issue government bonds. These funds are also expected to finance free preschool education.
As for the revenue side of the state budget, according to the calculations of the Japanese government, in 2021 its size will be 99.113 trillion yen ($932.567 billion).
In the sectoral structure of the economy of the island state, the service sector accounts for up to 70% of GDP. Most firms of this type operate in retail and wholesale trade, communications, and information networks. Industrial production contributes approximately 18% to GDP. But the share of the agricultural sector is only 1.5%.
What is made in Japan
Japanese industry specializes in the production of materials and various goods based on high modern technologies. Despite its relatively small territory, 12% of world production is produced in the Land of the Rising Sun.
Those made in Japan are in greatest demand today:
- cars;
- vessels, ships and other types of watercraft;
- robotics;
- personal computers, consumer electronics;
- plastics, chemical fibers, synthetic rubber.
A conversation about what Japan produces would be incomplete without mentioning the products of the military industry. Yes, despite the pacifist constitution, this industry is very developed here. The special forces, police and self-defense forces of this country are armed with Miroku Liberty Chief revolvers, sniper rifles, machine guns, locally produced Howa Type 89 and Howa Type 64 assault rifles.
Origins of Japanese civilization
The very first human settlements on the territory of what is now Japan arose approximately forty thousand years BC, even before the separation of the Japanese islands from the mainland. For a long time, Japan lived in isolation from the rest of the world. Relations with neighboring China and Korea were difficult. Early Japanese civilization was greatly influenced by Chinese culture; suffice it to say about the hieroglyphs that came from the Middle Kingdom. But subsequently, Japan built its own unique state and legal structure, the development of which was greatly influenced by ancient traditions.
- In the I-II centuries. the basis of the Japanese social hierarchy were clans
, consisting of several (up to 70) thousand people. The clan was headed by an elder, who also served as a priest. In the clans there was a class division into lower (geko) and “big” (daijin) people. The clans themselves were also divided into lower and higher. - From the end of the 2nd - beginning of the 3rd centuries. of proto-states
begins . Power began to be inherited. At the same time, the Japanese rulers recognized themselves as vassals in relation to China. Over time, one of these proto-states gained dominance over the others. - Asuka
period (mid-5th to early 7th centuries), when the typical proto-state
of Yamato
.
Statehood develops and Buddhism
. The king (okimi) began to bear the title of emperor, possessing religious and state power, and subsequently began to perform the functions of the supreme judge. - Early Nara
(second half of the 7th - beginning of the 8th centuries) is characterized by the great influence of Chinese culture, writing, and bureaucratic management practice. The first sets of laws are created, the land is divided into plots. - Nara
(until the end of the 8th century).
The first permanent capital appears in Japan - Nara. The country receives a new name Nihon (“land of the rising sun”). The first written monuments - collections of myths - date back to this period. The confrontation between Chinese and Korean representatives of the nobility and the local aristocracy is intensifying, which contributed to the weakening of Buddhism and the emergence of Shintoism
. - Heian
(late 8th - early 12th centuries). The new capital was Heian (now Kyoto). The land passes from a state monopoly to the private ownership of the aristocracy, like estates. Ties with China and Korea are finally weakening. Powerful development of culture, the appearance of brilliant examples of aristocratic literature. The Fujiwara family comes to the fore. - Kamakura
(XII - mid-XIV centuries).
Period of the Minomoto shogunate. The leadership of the military ruler (shogun) Minomoto Yorimoto. Supreme power belonged to the samurai
, although the title of chief priest of Shinto always remained with the emperor.
After two Mongol invasions in Japan, the level of national identity rises sharply. Zen Buddhism,
is spreading throughout the country . - Muromachi
(late 14th - mid 16th centuries). Ashikaga shogunate period. Development of urban civilization and connections with Europe through the mediation of missionaries. - Edo
(beginning of the 17th - second half of the 19th centuries).
Period of the Togukawa shogunate. The end of the civil war, the fight against Christianity and the eviction of Europeans, the complete isolation of Japan from the outside world. Powerful population growth, further development of cities and the economy. The emergence of Neo-Coifucianism
. Strict and final regulation of all spheres of social life. - Meiji
(mid-19th - early 20th centuries). Under the influence of Europe, Japan is recovering imperial power, lost during the period of samurai rule. National isolation, but at the same time rapid industrial development. Military expansion of Korea and China.
Main components of the Japanese economy
Many people do not understand how a small state, occupying an archipelago that does not have significant mineral deposits, has been among the leaders of the world economy for decades.
But since the 70s of the last century, industries that have become basic in the economic sphere of the country began to develop leading themes here. Let us briefly consider the main components that the structure of the Japanese economy includes.
Banking sector
The banking system of the Land of the Rising Sun is based on the American model and consists of the following three levels:
- Central Bank (Bank of Japan). Manages the activities of all credit and financial institutions in Japan, including 11 public and all private banking institutions.
- Commercial national banks. These are the following types of financial organizations:
- long-term lending banks;
- trust banks;
- regional and city banks;
- foreign banks.
These monetary institutions form the basis of the Japanese banking system: they account for 80% of its total capital.
- Cooperative credit institutions. This group includes:
- labor credit cooperatives;
- credit cooperatives;
- credit associations.
They are designed to provide financial support to small businesses in various areas of the Japanese economy.
The most famous include the following banks in the Land of the Rising Sun:
- Mizuho Corporate Bank;
- Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group;
- Industrial Bank of Japan, etc.
The article “How can a foreigner open an account in a US bank” will tell you what the US banking system is like.
Industry sector
The leaders of the world economy are Japanese companies such as Fujitsu Limited, Toshiba Corporation, Honda Motor Co. Ltd, Sony Corporation, Panasonic Corporation, Toyota Motor Corporation.
One of the main Japanese exports is automotive products. The whole world knows vehicles of the brands “Mitsubishi”, “Suzuki”, “Nissan”, “Toyota”, “Honda”, “Mazda”.
At the beginning of the 21st century, about 8 million people worked on a permanent basis in this industry. It was during that period that assembly branches of Japanese automakers were opened en masse in Asia.
Shipbuilding is a traditional industry in the island state. The largest factories operate in the cities of Hakodate (Hokkaido island), Yokohama, Yokosuka, Kobe, Onomichi (all on the island of Honshu), Sakaida (Shikoku island), Nagasaki (Kyushu island). The leading shipbuilding companies in Japan include Kawasaki, Mitsubishi, and Sasebo.
In the electrical field, corporations such as Yamaha, Sharp, Pioneer, Konica, Hitachi, JVC, Casio, and Canon have received well-deserved fame.
Agricultural industry
Only 12% of the land in the archipelago is suitable for cultivation. Flood fields occupy most of these lands. They are used for rice cultivation.
On average, 1 farm has 1.8 hectares of arable land. Hokkaido is far behind this indicator - 18 hectares, while the remaining 46 prefectures have only 1.3 hectares.
Traditional crafts for the Land of the Rising Sun since Neolithic times have been fishing and seafood processing.
For a long time, the greatest profit was brought by such activities in the Sanriku Sea (northeast of Honshu Island). There, the warm Kuroshio Current meets the cold Kuril Current. But due to the accident that occurred at the nearby Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant, fishing in this area was temporarily suspended.
Another area of the Japanese archipelago rich in seafood is the south and north of the Western Pacific Ocean
Transport sector
Japan has a modern and efficient transport system. The total length of highways in the archipelago is 1.2 million km. Large cities are connected by a single network of high-speed toll roads. It is administered by organizations authorized to collect tolls.
Dozens of railway companies compete in local and regional passenger transportation markets, such as Keio Corporation, Kintetsu Corporation, JR Group, Seibu Railway Company. All their trains are famous for their precision.
Some numbers:
- The total length of railways is 27,182 km.
- Electrified: 2893.1 km of roads with standard gauge;
- 89.8 km of narrow gauge roads.
There are many airports in Japan. The main international airports are Narita (Tokyo area), Chubu (Nagoya area) and Kansai (Kyoto/Kobe/Osaka area).
The main domestic hub is Tokyo Haneda Airport. According to statistics, this is the busiest airport in Asia and the 4th busiest airport in the world.
There are two main airlines in Japan: Japan Airlines and All Nippon Airways.
All the basic information about Japan Airlines (JAL), the world's leading carrier that operates scheduled international and domestic flights to 125 airports around the world, is presented in the article “Japan Airlines - one of the largest airlines in Asia.”
Other passenger carriers include Fuji Dream Airlines, Star Flyer, Air Do, Skynet Asia Airways and Skymark Airlines.
Historically, domestic air travel within the Japanese archipelago has been strictly regulated. The three largest airlines (JAS, ANA and JAL) have been assigned specific routes since 1972.
Up until 2000, airfare was determined by the government. However, since 1995, airlines have had the opportunity to regulate standard fares (at that time discounts of up to 50% were allowed). Today, an air carrier can set its own price for a flight, but the government has a veto right if the cost turns out to be very high.
Employment rate
The best unemployment rate in Japan was observed in 1960, when the country's economy was developing at a rapid pace. Officially, 1% of people were considered unemployed, which means that almost full employment was achieved. And the so-called oil crisis that occurred in 1973 led to massive job losses.
The situation did not get out of control only thanks to the measures taken by the government to organize workplaces and a significant breakthrough in the field of medicine. The peak of unemployment - 5.3% - was recorded in 2021, and until now there has been a gradual decline.
As of the end of August 2021, it was 2.2%. A slightly different figure for young people is 3.8%. For comparison: for the same period of time in the United States, the unemployment rate was 8.5%.
The employment rate of the working-age population is important for the country's economy.
It is calculated using the following formula:
KZ = (CHZL/CHTN) × 100 (%), where
KZ – occupancy factor, the required parameter;
CHZL – number of employed people;
CHTN – the number of working-age population (age from 15 to 65 years).
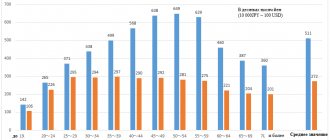
In Japan, at the beginning of 2021, the KZ was 59.2%. You can find out how Japanese employment has changed over the past 20 years by studying the graph. It shows that the maximum drop in the employment rate occurred in 2012, the last year of the global financial crisis.
The population of the Land of the Rising Sun is declining, but this does not mean that mortality is increasing. The health of elderly Japanese is better than that of elderly people in other countries.
Meanwhile, the demographic situation in Japan is by no means rosy. Today, the birth rate here is 1.46, while population reproduction will take place when this indicator per woman of reproductive age is no less than 2. And, according to all forecasts, at least in the foreseeable future, the birth rate will not become so .
Japan is a country of long-livers. Representatives of the local population are ready to work even after reaching retirement age.
They are also encouraged to do this by the rules established by the state for the payment of cash assistance to people of advanced age:
- upon retirement at the age of 60, the size of the basic pension payment is reduced by 0.5 percent for each month during which the person remained in retirement until he reaches the age of 65;
- A resident of Japan who retires at the age of 70 is entitled to a half-percent increase in the basic pension for each month during which he worked after the age of 65.
The minimum pension payment for elderly people in Japan is $600, while in China the average payment is about $14 for rural residents and about $350 for urban residents.
More detailed information about the pension system of the PRC is provided by the article “Pension and pension system in China.”
Economic development
Definition 1
Economic development is permanent gradual qualitative transformations in the country's economy.
It includes the transformation of relationships in society, which are built in accordance with the current system and principles of social communication. In essence, this is a process of improving the quality of life, which has a beneficial effect on the economy of the country as a whole.
For a long time, representatives of economic science were interested only in the quantitative side of economic activity. Scientists sought to evaluate the effectiveness of economic processes based on their results. Today, a quantitative assessment characterizes economic growth, which is the aggregate result of the economic activity of all business entities related to the national economy in question.
Finished works on a similar topic
Course work Modern trends in the development of the Japanese economy and forecasts for its development 490 ₽ Abstract Modern trends in the development of the Japanese economy and forecasts for its development 250 ₽ Examination Modern trends in the development of the Japanese economy and forecasts for its development 200 ₽
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
Development is a broader concept that is difficult to evaluate with any final indicators. It occurs gradually and leads to significant socio-economic improvements in society. Various parameters are used to assess economic development. For example, the human development index, which is calculated based on three criteria:
- Life expectancy of the population.
- Current level of literacy.
- Quality and standard of living, which is calculated using purchasing power parity.
Another indicator is gross domestic income per capita. According to it, all countries of the world are divided into developed, developing and underdeveloped. However, this indicator does not characterize the qualitative side, but indicates the distribution of total income in society.
Note 1
Thus, economic development represents qualitative changes in the national economy, which lead to structural transformation and the emergence of fundamentally new socio-economic characteristics.
Need advice on your academic work? Ask a question to the teacher and get an answer in 15 minutes! Ask a Question
Features of the structure of Japan's exports and imports
Japan takes an active part in international trade. The main exports of the state are vehicles. In terms of sales abroad of products in this category, Japan ranks 2nd in the world rankings (after Germany).
The article “Japanese car auctions: affordable quality” will tell you how you can purchase a high-quality Japanese-made car.
Electrical machines, mechanical devices and equipment are also important components of Japanese exports. The total volume of sales of these types of goods (including cars) to other countries is 55% of the total cost of supplies to other countries.
The main markets are Germany, Australia, countries of Southeast and East Asia, and the USA. As for Russia, in terms of exports from Japan it is in the third ten among all countries in the world. Moreover, in value terms, the majority of exports to the Russian Federation are vehicles.
The main product groups imported into Japan are petroleum products and mineral fuels. According to data at the beginning of 2021, they were supplied mainly from:
- Russia – 6.8%:
- Qatar – 7.7%;
- United Arab Emirates - 14.1%;
- Australia - 18.2%;
- Saudi Arabia - 18.9%.
Japan also imports electrical machines, mechanical devices and equipment. About half of these goods traditionally come from China. In general, products from the Middle Kingdom account for about 25% of the value of total imports to the Japanese market.
High growth period (mid 1950-1973)
It was during this period that the so-called The “Japanese economic miracle” is the strongest impetus for the development of the Japanese economy. Over 15 years (1958-1973), GNP increased 6.5 times, industrial production - 10 times.
Already at the end of 1960 and the beginning of 1970, Japan overtook (in terms of GNP and industrial production) countries such as Germany, France, Canada, Italy and the UK, taking a clear second place in the world economy, second only to the USA. The growth rate of the “Japanese economic miracle” was colossal and amounted to 11.0% per year, this was the highest growth rate among developed capitalist countries.
During this period, Japan discovered new industries, such as: radio-electronic industry, petrochemicals, production of plastics, synthetic rubber, synthetics. fibers, etc.
The Japanese economy at that time involved very large amounts of capital investment, especially in machinery and equipment. In the period 1950-1971, Japan bought about 15,000 patents, the main share (60%) of which came from the United States. At the same time, technologies acquired abroad were usually processed and brought to perfection! As a result, Japanese technology has taken the lead on many issues.
By the end of this period, Japan was one of the largest automotive powers in the world.
A total of nine national economic plans were developed during this period. With the early implementation of the plan, new ones were adjusted:
- 1951 - “Three-year plan for economic independence”;
- 1955 - “Five-year plan for achieving economic independence”;
- 1957 - “New Long-Term Economic Development Plan”;
- 1960 - “Plan for Doubling National Income”;
- 1965 - “Medium-term economic development plan”;
- 1967 - “Plan for Economic and Social Development”;
- 1969 - “New comprehensive plan for regional development”;
- 1970 - “New Comprehensive Plan for Economic and Social Development”;
- 1972 - “Plan for the reconstruction of the Japanese islands.”
Unfortunately, not everything went according to plan. In 1973-1974 Japan faced an energy crisis that brought an end to its period of high growth. After wartime, this crisis seemed to be the largest of all time since the end of 1945.
Traditions as a feature of market relations
This feature is based on the historical and cultural development of the nation. In the country in general, and in business in particular, “grouping” supported by the state is extremely developed.
Society is characterized by the presence of trade and business traditions based on the philosophy of group goals and aspirations that can only be realized collectively. The concept of grouping is to bring together a number of partners who know each other well. Within the framework of such a group association, a mutual expectation of a certain behavior of partners develops, mutual trust is formed, which leads to strong cooperative relationships.
Note 2
In addition, in Japan it is customary to reinforce such close, strong relationships between business partners with a system of fines, which inevitably increases the level of responsibility in the case of “ungentlemanly” behavior, and is also a serious mechanism that constrains moral principles.
Industry structure
If we consider gross domestic product by sectors in which added value is created, the picture looks like this:
- Industry – 18% of GDP.
- Real estate sector – 13.2%.
- Wholesale and retail trade – 12.5%.
- Transport and communications – 6.8%.
- Public administration – 6.2%.
- Construction sector – 6.2%.
- Financial and insurance sector – 5.8%.
- Electricity, gas and water supply – 0.7%.
- Government services – 0.7%.
- Mining industry – 0.05%.
- Other – 23.5%.
Agriculture contributes about 1.4% of gross domestic product. Only 12% of Japanese land is suitable for cultivation. Therefore, small farms often use a terrace system to grow crops. The agricultural sector is subsidized by the state. Preference is given to small farming.
Japan's industry is well diversified. Many cutting-edge industries are extremely successful. Industry contributes about 24% of gross domestic product. The main industries are the production of household appliances, automobiles, semiconductors, optical media, fax and copy machines. However, more and more Japanese companies are experiencing competition from American, South Korean and Chinese manufacturers.
The service sector accounts for three quarters of the gross domestic product. Its most important industries are banking, insurance, real estate, retail, transport, and telecommunications. Four of the five most read newspapers in the world are Japanese. Tourism is also an important sector of the country's economy. The government aims to attract 20 million foreigners to the Summer Olympics, which will be held here in 2021. The financial sector is also widely developed in the state. The Tokyo Exchange has the fourth largest market capitalization in the world.