Description
Loach
The length of some types of loaches reaches 30 centimeters, but on average these fish do not exceed 15-18 centimeters. Loaches are covered with small but noticeable scales. The body is elongated, serpentine in shape. The loach is a squeaking fish: if you take it out of the water, it will begin to wriggle and squeak very strongly. The tail fin of fish from the loach family is small and has a rounded shape. The mouth has from 6 to 12 antennae. The nostrils are elongated into small tubes.
Unlike females, males have a thickened and elongated second ray of the pectoral fin. There is also a thickening on the sides, behind the dorsal fin, which is formed by adipose tissue. The lifespan of loaches is about 10 years.
The loach fish is the main representative of a small group of fish that are characterized by an elongated body covered with very small scales, and sometimes without scales at all. In appearance, the loach fish resembles an eel fish or a snake. Its name itself shows the ability of the fish to wriggle.
Another name for this fish is the squeak, which is its distinctive ability to make a faint squeak when you pick it up. This, obviously, comes from the ability to draw air into the food intake channel, which is confirmed by loaches that are kept in a jar with not entirely fresh water: then from time to time they come to the surface, stick their heads out of the water, swallow air and immediately release it with a noise through the back hole. This passage of air through the food intake channel, as it were, replaces breathing with gills.
The loach readily bites on the worm; this fish can be caught both day and night. Loach fish is a very good and extremely tenacious bait for pike, catfish and especially eel, which almost prefers loaches more than other fish. He is also a pond cleaner, eating fish waste.
In some areas, fishermen, knowing well the taste of the loach, vitality, unpretentiousness, as well as the ability to live in small ponds and reservoirs, specially breed it in tiny ponds - dugouts. And there is one more very valuable advantage of the loach: it devours a huge number of mosquito larvae, including malaria, and is not inferior in this to the mosquito fish, which was brought from America and acclimatized in our country precisely for these purposes.
The loach has another interesting feature: it reacts very sensitively to changes in atmospheric pressure. Before bad weather, he begins to worry and constantly pokes his head to the surface (10 - 15 times per minute). For this property, the loach is called a living barometer. In a number of countries, particularly in Japan, loaches, like other meteorological fish, are specially kept in aquariums. By their behavior, scientists often learn not only about changing weather conditions, but also about the approach of natural disasters such as tsunamis and earthquakes.
Common types of loaches
Let's get acquainted with the common types of fish described. For the convenience of users, the information is presented in table form.
Table. Overview of common loach fish species.
| Name, photo | Short description |
| Common loach (lat. Misgurnus fossilis) | A species widely distributed in fresh water bodies of Europe and Asia. Moreover, the fish prefer muddy reservoirs. Misgurnus fossilis is unpretentious to living conditions, and therefore can easily live where there are no other species. |
| Common (Siberian) spined loach (lat. Cobitis taenia) | The smallest representative of the loach family. Lives in reservoirs of almost all of Europe, with the exception of northern countries, as well as in some Asian countries. The body length can reach 10 cm. The color is light yellow, with large spots on the sides, merging into a stripe. |
| Amur loach (lat. Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) | Lives in Japan, China, Sakhalin. Can grow up to 25 cm in length. The body of the Amur loach can be yellowish-copper or light brown in color. |
Kinds
The loach family includes 177 species of fish, grouped into 26 genera, as well as 2 subfamilies.
The most common types of loaches:
- The common loachfish (lat. Cobitis taenia) is the smallest representative of the fish of the loach family. It lives throughout Europe, with the exception of Norway, Ireland, Sweden, and Scotland. It is widespread in the CIS countries, as well as in Northern China, Japan and Asia Minor. The length of this type of loach reaches only 10 cm. The main body color is light yellow, on the sides there are large spots that merge into a common stripe.
- Common loach (lat. Misgurnus fossilis), lives in muddy reservoirs of Europe and Asia. The body length of the common loach is from 15 to 30 cm. Its color depends on the living conditions. Basically, the back is brown, with a large number of dark spots, the belly is yellow, spotted. In the middle of the loach’s body there is a dark wide stripe, and above and below it there are narrow stripes.
- The Amur loach (lat. Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) naturally lives in water bodies of northeast Asia, Siberia, Sakhalin, as well as China and Japan. In its natural habitat, this species grows up to 25 cm, and in aquarium conditions up to 15-18 cm. The color of the Amur loach is mainly yellowish-copper or light brown tones.
Varieties of loach
The loach family includes many species of fish, there are 177 of them. Let's look at the most common types of loaches:
| Type of loach | Description |
| Common spined loach | The smallest fish belonging to the loach family. They live in almost all of Europe, with the exception of some countries. Most often, this variety can be found in the CIS, Northern China, Japan, and Asia. The length of the fish does not exceed 10 cm. The color of the body is light yellow, and there are large spots on one and the other side. |
| Common loach | The location of such a loach is muddy reservoirs in Europe and Asia. The back has a brown color, where there are many dark spots. The length of the fish is 15 cm, sometimes up to 30 cm. The color depends on the location and living conditions; the majority of loaches have a brown back with a large number of dark spots, and the belly is yellow and also has many spots. In the center of the body there is a thick dark stripe, from which narrow stripes extend. |
| Amur loach | This fish can be found in northeast Asia, Siberia, Sakhalin, Japan and China. One of the largest fish of the loach family, reaching 25 cm or more. And those fish that live in the aquarium, their length does not exceed 18 cm. The color of the fish is yellow-copper or light brownish. |
Lifestyle
The loach leads a sedentary lifestyle, often burrowing into the silt. Mainly adheres to swampy, slowly flowing or standing waters. In rivers it prefers muddy areas overgrown with dense aquatic vegetation, often in channels, bays or oxbow lakes. It even lives in swampy lakes and ditches where there are no other fish, not even crucian carp. In such swampy reservoirs, the loach often rises to the very surface of the water, releases exhaust air and swallows a new portion, while emitting a characteristic squeak.
First of all, what is striking about him is his extraordinary vitality and amazing resourcefulness. It is very unpretentious to the oxygen content in water; for this it has additional intestinal respiration. It happens that small lakes dry up completely in very dry years. The inhabitants of these reservoirs for the most part either die or become easy prey for birds and humans. It would seem that the loach should share this fate. But then the rainy season comes, the lake bowl is filled with water again and, like a phoenix bird, the loach is resurrected in it. This fish has the rare ability to burrow into the mud to a depth of one to two meters and hibernate. which continues until water appears again. In general, the loach can live in almost any standing water, and even in swamp water.
The rare ability of the loach to remain alive for a long time without water is explained by the fact that, unlike most fish, it can breathe not only with its gills, but also with the help of its skin and intestines. Its intestinal walls are rich in blood vessels and perform respiratory functions when the body lacks oxygen. Swallowing air, the loach passes it through the digestive canal and then releases it through the respiratory opening (this is precisely what explains the squeak of loaches when they are pulled out of the water). Some fishermen claim that large loaches, like eels, can crawl from one body of water to another, nearby, in the dewy morning hours.
The loach has another interesting feature: it is sensitive to changes in atmospheric pressure. Before bad weather, he begins to worry and constantly pokes his head to the surface (10-15 times per minute). For this property, the loach is called a living barometer. In a number of countries, particularly in Japan, loaches, like other meteorological fish, are specially kept in aquariums. By their behavior, scientists often learn not only about changing weather conditions, but also about the approach of natural disasters such as tsunamis and earthquakes.
Distribution and habitats
Loach fishing
The loach is found exclusively in the waters of Central and East Asia. The Western, Northern and South-Eastern parts of Europe are not at all rich in this fish. Very rarely found in reservoirs of eastern France. The loach does not visit England and the northern part of our country at all. Also, the loach was not recorded in Siberia and Turkmenistan. However, some sources say that it was seen in the area of the city of Yekaterinburg and in certain small rivers located near the eastern slope of the Yekaterinburg Urals, where, most likely, it came quite recently.
Most likely, the transition to these areas is due to the fact that the loach is found much more often than other fish in almost dry swamps. However, it is a known fact that the Ural swamps give rise to the largest rivers in the Asian part of our country. In the region of the western slope of the Urals, almost all swampy and muddy rivers are rich in this fish. In the waters of rivers flowing into the White Sea and the Arctic Ocean, as well as in the waters of Finland, there is much less loach. In the waters of the Leningrad region, the loach is a very rare fish; only in the area of Kronstadt Bay and Peypus is it found somewhat more often.
Swampy rivers, swamps and ditches are bodies of water where the loach is especially common. The Pinsk swamps and Polesie are especially rich in this fish: fishing there is more common. Fishing is also carried out in large quantities in the area of the Dnepropetrovsk bays. So far, the loach has not been found in the lower reaches of the Volga, which is very strange. In the Kuban region, catching this representative of the ichthyofauna is common, however, it is not found at all in the rivers of the Crimea and the Caucasus.
The loach prefers to live in quiet water with a muddy bottom, which explains the high population in swampy, slow-flowing rivers, quiet backwaters of large rivers, remote tributaries, silty ponds and lakes. Often the loach is found in ditches and swamps where the existence of any other fish is simply unthinkable, if you do not take into account the unpretentiousness of crucian carp. Thanks to its incredible vitality, the loach can live for quite a long time not only in wet mud, but can also survive at the bottom of a dry lake, pit or swamp. In general, the loach spends most of its life in mud or silt, however, this fish has such an interesting feature that with the onset of bad weather the loach floats to the upper layers of the water. As a matter of fact, the loach can be called the most reliable and accessible barometer.
The loach is also famous for another interesting feature, which is why this fish is also called the squeaker. This feature is typical for those individuals that live in completely polluted water bodies. Thanks to its ability to draw air into the food canal, the loach floats to the surface and emits a weak squeak, which is emitted through the anus. Thanks to the ability to use the digestive canal when breathing, the need to breathe through the gills is replaced.
Habitats and habits
Small groups and numerous schools of loach inhabit lowland and mountain rivers, lakes, ponds, reservoirs and even swamps with low oxygen content. The physiological characteristics of the fish allow it to survive in very shallow and drying up water bodies.
The additional mechanism of intestinal respiration is configured in such a way that bindweed, a fish living in polluted water bodies, can occasionally surface to the surface to grab a breath of clean air, and then do without full gill respiration for a long time.
That is why the piskun and other types of loaches can be found almost anywhere, even in ditches that remain after river floods. If the water level or contamination becomes critical, the fish burrows deep into the moist soil and waits out unfavorable conditions in safety. In addition, like an eel, it is capable of crawling to a neighboring body of water over dew-covered grass.
Favorite habitats are standing or slow waters. A prerequisite for normal life is also a soft bottom, which serves as a shelter and source of nutritional microorganisms.
Its unpretentiousness, peaceful nature, extravagant appearance and vitality of the species have made it a popular object for keeping in aquariums and landscape ponds. Under artificial conditions, all types of loaches develop quickly, but grow to half their possible size. Another feature of the fish is its sensitivity to decreases in barometric pressure. Long before the start of a thunderstorm, she shows hyperreactivity and makes sudden movements from the bottom to the surface and back.
Loaches can burrow into silt, and mucus protects them from direct contact with silt. Obviously, this is how loaches survive the winter; they are not even afraid of small ponds and reservoirs, since it is undemanding to living conditions and can withstand a significant lack of oxygen in the water. In this regard, it is more resilient compared to other types of fish.
Feeding
It feeds on invertebrates, insect larvae, small crustaceans and bottom mollusks. And there is one more very valuable advantage of the loach. It devours a huge number of mosquito larvae, including malaria, and is not inferior in this to the Gambusia, which was brought from America and acclimatized in our country precisely for these purposes.
The loach is voracious and greedily grabs bloodworms, raw meat, earthworms, ant eggs, and picks up food only from the bottom. He finds food by touch (on his head around his mouth he has 10 antennae, which serve as the main organs of touch).
Nutrition
It feeds on insect larvae (especially chironomids), crustaceans, worms, small mollusks, as well as detritus and partially bottom vegetation. In captivity it can live without food for up to six months. In addition, the loach is known as an active eater of alien eggs. Hardly any inhabitant of rivers and lakes can compete with it in its ability to find it at the bottom. He does this so actively that in small bodies of water other fish often completely disappear. Crucian carp, carp, and tench suffer the most from loaches.
In an aquarium, the loach is voracious (as in the wild) and greedily grabs bloodworms, raw meat, earthworms, ant eggs, and picks up food only from the bottom. He finds food by touch (on his head around his mouth he has 10 antennae, which serve as the main organs of touch).
Reproduction
The loach reproduces in the spring. Loaches spawn in their usual habitats near the coast, in dense thickets; in addition, loaches often go to the flood, and their larvae are then found far from a river or lake. The dimensions of the eggs are 1.7 -1.9 mm, the diameter of the embryo with the yolk is 1.2 -1.3 mm. The shell of the eggs is thin and slightly sticky.
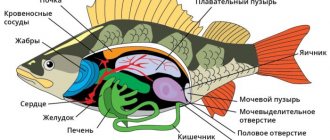
After hatching, the larvae, using adhesive organs located on the head, stick to the plants and hang quietly while there are yolk reserves. Development occurs in conditions of insufficient oxygen, and therefore the larvae develop a whole system of larval respiratory organs, which replace each other.
First, these are powerful vessels passing along the surface of the yolk sac, then long, thread-like external gills appear - thin leathery outgrowths riddled with blood vessels and protruding from under the gill covers. The external gills become smaller after a while and then disappear completely and true gills develop in their place.
In addition, in larvae the respiratory function is carried out by a dense network of blood vessels in the large pectoral fins, in the anal fin fold, and later in the posterior part of the intestine. Even before the yolk is completely absorbed, the larvae begin to actively search for food with the help of special sensory organs located around the mouth and on the antennae, which begin to develop very early. The network of capillaries is preserved in a small area of the intestine in an adult, as an adaptation to breathing atmospheric air.
Loach fishing
It is rarely caught specifically with a fishing rod, but in reservoirs where there are a lot of it, it bites greedily. The loach readily grabs earthworms, and with this bait it can be caught using a simple float rod. The bait is a worm, pieces of a worm, large bloodworms, ant eggs.
Where there are a lot of loaches, the easiest way to catch them is by basting, capturing the top layer of silt with a net. They also come across wire mesh-tops. In small bodies of water it is best to catch it using a frequently woven basket or a diving net.
It is also known as a good bait for catching many predatory fish, especially perch, burbot, eel and catfish. And what’s interesting is that the loach is the catfish’s favorite delicacy, and of all the live bait, the catfish gives the greatest preference to it. However, in many reservoirs, predators are very reluctant to take on the loach.
Benefits of loaches
Loach is very rich in a wide variety of beneficial substances. Although its fat content is quite high, loach fat will only bring health benefits, since it is represented mainly by unsaturated fatty acids. This means that the loach will be useful for people with diseases of the cardiovascular system, including high blood cholesterol levels.
Loach protein contains all the essential amino acids, so it is highly nutritious. Among other things, loach is a valuable source of vitamin A, which is necessary for the human body to produce many hormones, and also ensures vision at dusk and the normal condition of mucous membranes, skin, hair and nails.
It also contains a lot of vitamin E, which is considered the most powerful antioxidant that protects cell membranes from destruction by free radicals and toxins. This effect of vitamin E helps to increase overall vitality and strengthen the heart muscle.
Loach is recommended to be consumed to prevent rickets, as it contains a lot of vitamin D. As for B vitamins, which play an important role in the functioning of the nervous system, in the processes of carbohydrate and protein metabolism, loach meat also contains plenty of them. Loach is saturated with mineral elements necessary for any person: calcium, magnesium, potassium, zinc, fluorine, chromium, iodine, etc.
Composition and beneficial properties
Loach fish
Loach contains many useful substances in its composition. These are mainly unsaturated fatty acids, as well as amino acids, which have a very beneficial effect on the activity of the cardiovascular system and also normalize cholesterol levels.
In addition, loach is a source of vitamin A, which is necessary for the production of sex hormones, and also ensures the health of the mucous membranes. Vitamin E contained in this fish increases overall tone and strengthens the heart muscle. And vitamin D ensures proper and healthy growth of the human skeleton, as well as teeth. Loach also contains B vitamins, which play a very important role in the proper functioning of the nervous system, as well as in the processes of carbohydrate and energy metabolism. In addition, loach is rich in useful elements such as magnesium, zinc, calcium, potassium, fluorine, chromium and iodine.
Useful properties of loach fish
Loach fish (the photo gives you the opportunity to admire it) is considered to be of little value and is only eaten occasionally, because it is greatly neglected, which, however, it does not deserve. Its meat is tasty and tender and resembles tench: without small bones, fatty, sweet, juicy. True, it almost always smells like mud, and in connection with this, some fishermen are engaged in breeding loaches in special digging ponds. Before cooking, it is advisable to rinse the fish thoroughly with running water, after clearing the mucus with ash. Most often, fish soup is made from loaches; They are fried very rarely, although in Japan and France this fish is specially grown and is considered a real delicacy. Cooked loach dishes are sources of many nutritional components:
- vitamin A, necessary to ensure the health of the mucous membranes and the process of producing sex hormones;
- vitamin B, which increases overall tone and strengthens the heart muscle;
- vitamin D, which ensures healthy and proper growth of the skeleton and teeth;
- vitamin B, which normalizes the functioning of the nervous system and the processes of carbohydrate and energy metabolism;
- magnesium, potassium, fluorine, zinc, calcium, iodine;
- unsaturated fatty acids and amino acids that favor the functioning of the cardiovascular system and normalize cholesterol levels.
Loach fish has another very useful quality: it eats large quantities of mosquito larvae, including malaria ones. In this ability, the fish is not inferior even to the gambusia, imported from America and acclimatized to local conditions specifically for this purpose.
Interesting Facts
- It is known that the loach fish can endure fasting without harm to its body for 3 to 5 months.
- The loach has the rare ability to remain without water for a long time, this is explained by the fact that this type of fish can breathe not only with gills, but with the help of the skin and intestines.
- Large loaches can crawl from one body of water to another; they do this mainly in the dewy morning hours.
- Loaches are excellent at predicting the weather, which is why they are even called barometers. A day before a thunderstorm, loaches rise to the surface and rush from side to side, simultaneously swallowing air through their mouths. By this sign, fishermen know that there will be a thunderstorm the next day. This throwing occurs due to the fact that the loaches sense changes in atmospheric pressure. Thanks to this ability, loaches are kept in aquariums. They are unpretentious in food, and aquarium owners always know about the approach of a thunderstorm or other manifestations of bad weather.