Climate and nature
Before conducting an economic assessment of the natural conditions and resources of Japan, let us characterize the climate of this country. It is diverse: the north is characterized by low temperatures and long winters. In the southeast, winters are mild, summers are hot, and there is a large amount of precipitation.
On the coast of the Sea of Japan there is heavy snowfall in winter, but in summer it is quite warm here. The central part is characterized by sharp temperature changes both in winter and summer, and day and night.
Volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, and earthquakes are frequent in this state.
Water resources
Japan's natural water resources are represented by an abundance of underwater waters, lakes and rivers. Numerous mountain rivers are quite deep, short and fast. Japanese rivers are not suitable for ferrying ships, but they have found use in hydropower. They are also used to irrigate agricultural land.
The largest rivers are the Shinano, 367 kilometers long, and the Tone, 322 kilometers long, both located on the island of Honshu. There are 24 major rivers in total, including Yoshino (Shikoku Island), Chikugo and Kuma (Kyushu) and others. Different areas are characterized by winter or summer high water, which often leads to floods.
The country has both coastal shallow and deep-water mountain lakes. Some of them, for example Cuttiaro, Tovado, are of volcanic origin. Saroma and Kasumigaura are lagoonal. Japan's largest freshwater lake Biwa (670 sq. km.) is located on the island of Honshu.
Minerals
Let's begin our consideration of Japan's natural resources by getting acquainted with mineral deposits, of which there are not many here.
We present information about what resources are available in this unusual country and what are missing in the table. Mineral Resources of Japan
| Available on site | Imported |
| Sulfur | Iron ore |
| Manganese ore | Oil |
| Barite | Natural gas |
| Iodine |
Interestingly, Japan, which is generally poor in minerals, is one of the world leaders in iodine production. On the territory of this country there are also small deposits of uranium, vanadium, lithium, titanium ores, and very modest reserves of gold and silver ore.
Japan's natural resources include sands, limestones and pyrites, which have long been used in the production of Japanese steel, famous throughout the world. Surprisingly sharp blades for edged weapons were made from it.
To summarize, mineral wealth is very diverse, but there is little of it, so minerals necessary for industrial development have to be purchased abroad.
Forest resources
Forests are Japan's natural resources, of which the country has plenty. They cover more than 65% of the territory. Approximately a third of forests are artificial plantations. More than 2,500 plant species grow in the country. Subtropical forests grow in the southern mountainous regions, coniferous species predominate in the north, and mixed forests are located in the central part.
Tropical vegetation is found on the islands: palm trees, ferns, fruit trees. Sweet potatoes and sugar cane grow on the Ryukyu Islands. Pine, fir, and evergreen oak trees grow in mountainous areas. The country has a large number of endemics, including Japanese cypress and cryptomeria. Here you can see a relict ginkgo tree.
At the foot of the mountains on the islands of Honshu and Hokkaido, such as Fuji, broad-leaved forests predominate. At an altitude of more than one kilometer, a zone of alpine bushes begins, which give way to alpine meadows. Vast areas are occupied by bamboo forests grown for furniture production.
Forest wealth
Let's consider the natural conditions and resources of Japan. More than half the area of this island state is occupied by forests, in which more than 2,000 species of flora grow. What kind of plants are these?
- Japan has many mountains in which pine, oak and fir trees grow.
- A variety of coniferous species can be found in the north of the country.
- There are also plants typical of the tropics: ferns, palm trees, and numerous fruit trees.
- Sweet potatoes are found on the territory of the Ryukyu Islands.
However, the country cannot fully provide itself with timber, so timber also has to be imported. Due to the development of agriculture, forest land has shrunk, so trees had to be planted artificially.
Forest plantations
Forests in Japan occupy 65% of the country's territory. The third part of it consists of artificial plantings. The following types of forests are present here:
- Conifers. Representatives are fir and spruce.
- Deciduous. Among them there are oak, maple, ash, chestnut.
- Evergreens. These include camphor tree and Japanese cypress.
- Monsoon forests. These are ficus, palm trees, tree ferns.
Since forest resources are insufficient, Japan has a government program to increase them. The grown wood is used in the wood processing industry. Since such raw materials are not enough for Japan, they are actively supplied from Russia.
Earth
The next type of natural resources in Japan that you should pay attention to is soil. The country is entirely covered with mountains, but agriculture is thriving here, so the Japanese manage to almost completely meet their food needs. Only about 30% is imported, which is quite a high figure for a mountainous island state. What soils are typical for Japan?
- Meadow-swamp and podzolic soils are typical for the northern zones.
- Brown forests - in the south, in temperate regions.
- Red soils and yellow soils are common in the tropics and subtropics.
The Japanese grow rice, wheat, barley, and various types of vegetables. Often the harvest can be obtained twice a year.
Flora of the country
Due to its island isolation and mountainous terrain, Japan's biological natural resources are somewhat impoverished. Mostly relict and endemic species are present here. Brown bear, wolves, foxes, and sable are often found on the islands of Hokkaido and Honshu. Closer to the south live white-breasted bears, Japanese macaques, antelopes, and gigantic salamanders.
Japanese territory is characterized by the presence of a large number of birds. Here you can see blackbirds, hawks, cranes, eagle, large-billed and black crows, owls, jays.
The rivers are home to carp, eel, and catfish. Considering that Japan is surrounded on all sides by sea waters, fishing is developed here. The Japanese diet includes fish such as iwashi, flounder, and Pacific herring. Prawns, crabs and oysters are harvested.
Water wealth
There are a huge number of small rivers on the territory of the country, which are not suitable for navigation, but are actively used for irrigating agricultural crops. Due to the fact that the rivers are mountainous and full-flowing, they become sources of hydropower. Japan also has a lot of lakes and groundwater, which generally has a positive effect on the development of agriculture. The country is rich in mineral and thermal springs.
Water resources can bring a lot of problems to the country's residents, since frequent typhoons here are often accompanied by floods.
general characteristics
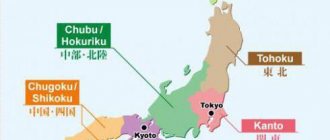
Geographically, the country is located in the Japanese archipelago. The map of this territory covers about 7,000 thousand islands. The history of their appearance is associated with the processes of volcanic activity in the earth's crust. For this reason, some of them are uninhabited. Among them, the main 4 stand out:
- Hokkaido.
- Honshu.
- Kyushu.
- Shikoku.
The bulk of the population is located on them. The state is washed by seas on all sides:
- Japanese.
- Okhotsky.
- East China.
Japan borders Russia, South Korea, China and the Philippines. In the world it is called the Land of the Rising Sun. The total area of the territory is 377944 km2. 127 million people live here.
The main city of Tokyo is located on the island of Honshu.
Modern developments
An assessment of Japan's natural resources suggests that this country is highly dependent on imports. Thus, it is necessary to import minerals and minerals, wood and even food products. To reduce this dependence, the Japanese are working on creating alternative energy sources:
- Sunny.
- One.
- Wind.
Such work is highly effective. The country has all the makings for this: there are many sunny days a year, there are regular winds, there are also enough rivers and lakes on Japanese territory.
Despite the fact that the country as a whole is poor in natural resources, it is one of the strongest economic powers. The Japanese have learned to effectively use the wealth they have. The standard of living here is also very high, the average life expectancy is more than 80 years, and infant mortality is minimal.
The geographical location and landscape features have made Japan a country poor in natural resources. This, however, did not stop her from becoming one of the world leaders. The Japanese purchase everything necessary for the development of industry abroad, and also learn to use the wealth that is located on the territory of the island state.
Water expanses
The nature of Japan is rich in the presence of rivers and lakes. Among them, the Sinano and Toni rivers are particularly large in size. Their waters, in addition to irrigation of agricultural land, are used for the development of hydropower. Japan has fully developed hydropower potential. In this respect, it is the largest producer of electric fuel.
There are a large number of lakes in the country. The largest of them are Biwa, Saroma, Kasumigaura, and Towado.
The state has more than 2 thousand hot springs for bathing. They are hydrogen sulfide, ferrous, and carbonated. This attracts a large number of tourists to the country. For Japan, such a business brings significant income to the treasury.
Agroclimatic resources of the country of Japan
Area - 372.8 thousand km2.
Population - 127.5 million people Constitutional monarchy - 47 prefectures. Capital -. Tokyo
. Japan is an island state . Most of the state's territory is located on islands. Hokkaido. Honshu,. Kyushu and Shikoku, which is washed by the seas. Pacific Ocean. In addition, it owns about 7 thousand small islands
B. Japan is geographically the closest. Russia,. South. Korea,. DPRK. China,. Taiwan. Neighboring states are very different in political systems and economic potential. South. Korea and Taiwan is a new industry real country of the first wave with high rates of economic development. China and. North Korea is a socialist country, however. China combines command and market economic models. Japan is an active member
UN,. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation
The country is located near rich mineral resources. China and. Russia, which is for. Japan is very important important for. Japan's "storehouse" of minerals -. Australia, located on convenient sea pu. Yahah v. Country. Ascendant to go.
Japan is the center of economic development not only in the region, but also in the world. Most neighboring countries are developing dynamically and have significant resource and economic potential and, over time, naturally played a leading role in the world.
Population
In Japan, a type of population reproduction has been formed, the characteristic features of which are low birth rates (9 per 1000 people), low annual population growth (0.2%), and the process of “aging of the nation” (average life expectancy is 81 years). Country first in. Asia has made a demographic transition from the traditional type of population reproduction and has approached a state of population stabilization. Insignificant size and migration (migration balance at the beginning of the third millennium close to 00).
The Japanese make up 99.4% of the state's population. They belong to the Mongoloid race. The Japanese language forms a separate language family, since it is completely different from the languages of neighboring peoples. In the north of Hokkaido is home to a small number of aboriginal people (about 20 thousand people). Japan - Ainu. The main religions are Shintoism and Buddhism.
Japan is a densely populated country (about 337 people per km2). The population density is especially high in the southern coastal regions of the city. Honshu and in the north. Kyushu - more than 500 people per 1 km2. In the mountainous regions and in the north of the country, the population density is 60 people per 1 km2.
. Japan is one of the most urbanized countries in the world - 78% of the population lives in cities . There are ten millionaire cities in the country. Three largest agglomerations. Japan are merging into the largest metropolis. Tokkaido has a population of over 600 km and has a population of over 600 km.
About 66 million economically active people (52%) are employed. Of these, more than 25% are in industry, 5% in agriculture and about 70% in the service sector. For. Japan is characterized by a relatively small number of unemployed (1.3 million people).
Natural conditions and resources
Japan is poor in mineral resources. Only coal, insignificant reserves of oil, gas, and non-ferrous metal ores (copper, lead, arsenic, bismuth, zinc) are of industrial importance. The chemical industry uses its own sulfur, the construction industry uses dolomite, gypsum, and limestone. The needs of most types of mineral raw materials are met through imports: oil and gas - 99%, coal - 90%, copper - 3/4, iron ore - 99.9%, more than half - lead and zinc
Rivers in In Japan, their mountainous resources are mainly used for both irrigation and electricity generation. Numerous small lakes are an important source of drinking water
Forests cover 63% of the territory. Japan. Coniferous, broad-leaved and subtropical forests predominate. However, our own forest resources are also not enough to meet production needs!
Japan is a mountainous country. Mountains occupy over 3/5 of the territory. In many places they come very close to the sea. Above the central part of the. Honshu is a towering volcano. Fuji (3776 m). The very plains of the races located in the central part of the island. Honshu (plain. Kanto) they are crossed by numerous irrigation canals. The difficult terrain forces the construction of numerous underground transport tunnels. The decline of flat lands makes it necessary to reclaim land in the bays for the development of large coastal localities.
Robotics
Along with the development of electronics, the robotics industry began to develop rapidly. The first robot in the world was created in Japan in the mid-60s. Now this industry is one of the leading in the country and has practically no competitors in the world.
The government takes an active part in the development of the industry, providing inventors with preferential working conditions.
Currently, Japan produces about 45% of the world's total industrial robots. Leading organizations in the development of robotics are the national universities of Aizu, Iwasaki, Tohoku, Tsukuba, Hokkaido, Ritsumeikan, Kagawa, as well as the polytechnic institute in the city of Shibaura. The military of Japan and the United States are showing particular interest in remotely controlled robotics.
Find out what abilities robots are endowed with in the video below.
Robots are no less in demand in everyday life. Caring for the disabled and elderly is already practiced automatically. Human-like robots are being created that can perform the functions of social workers.
Innovation has also come in handy in the medical industry. The main developers and manufacturers of robots are Sony, Honda, Toyota, Mitsubishi Electric, Panasonic, Kawasaki and Yamaha.
*Mitsubishi Research Institute made a report in 2021 according to which by 2030 robots will take 7.4 million human jobs in the country.
Chemical industry
The chemical industry felt its main impetus in the 60s. with an increased demand for energy, which was generated from gas and oil products. It is waste oil products that have become an excellent raw material for the chemical industry.
At this time, the Japanese chemical industry is a favorite in the Asian market and ranks second in the world. The main producers of goods in this segment are the following corporations:
- Asahi Chemical;
- Asahi Glass;
- Fuji Photo Film;
- Sekisui Chemical;
- Mitsubishi Chemical.
Almost all companies are involved in petrochemicals. Depending on their specialization, enterprises produce synthetic rubber, polymers, chemical fibers and more. In addition to petrochemicals, corporations are engaged in the production of biochemicals, which include medicines and fertilizers.
The largest diversified areas of the chemical industry
It is also worth mentioning the ecology of the country. Find out more about ecology here.
Light industry
Another of Japan's oldest industries is light industry. This national sector has always been in the spectrum of interests both within the country and abroad. The main hobby was the production of silk yarn and the manufacture of ceramics.
During this period, almost all products are produced in large factories equipped with robotic machines. Instead of silk products, priority is given to cotton and woolen products.
Ceramics remained more conservative, but were also produced on an industrial scale. Almost 75% of products are exported. Many admirers of ceramic products note with sadness that the influence of the West can be discerned in modern Japanese works.
Food industry
Japan is forced to produce most of its food products from imported raw materials. Apart from the gifts of the ocean and rice plantations, the country has rather limited opportunities for producing its own raw materials. Almost everything that is manufactured remains on the domestic market.
Among the Japanese, it is fashionable to eat organic foods as part of a healthy diet.
Agriculture
Almost 6.5% of Japan's population is employed in agriculture. Thanks to this industry, the country's GDP receives 2%. The industry is largely focused on the production of food products.
Learn more about farming in the video below.
Almost 13% of the archipelago’s territory is allocated for agricultural land. The main crop grown is rice. Many areas are sown with fruit and vegetable crops. In addition to crop farming, farmers keep cattle, pigs and poultry.
A significant part of the coastal population is engaged in fishing and maintaining farms for growing marine animals and plants. Marine flora and fauna are also intended for consumption.
Japan has about 400,000 registered fishing vessels and has built over 3,000 ports for unloading fish.
Energy
There are no oil fields on Japanese territory or in territorial waters. The country is forced to buy almost 95% of gas and oil to meet its needs. But their status as a consumer does not prevent the Japanese from occupying third place in the world in electricity generation, behind China and the United States.
The vast majority of power plants in the country are thermal power plants, with a slightly smaller number of hydroelectric power stations. Since the mid-70s, Japan has operated nuclear power plants. There are currently 17 nuclear power plants in the country, including the most powerful in the world, Kashiwazaki-Kariwa.
The electric power industry in Japan includes the generation, transmission, distribution and sale of electrical energy in the country.
Of the total number of power units, 42 reactors, only nine are in operation. The rest are undergoing certification and conservation after the explosion at the Fukushima-1 nuclear power plant in 2011. Nuclear experts are reviewing safety parameters given the threat of seismic activity.
The production of solar energy has become very popular. In the near future, the government wants to achieve a complete transition of the country's energy system to solar energy, abandoning nuclear energy.
Japan is now in fourth place in the world in terms of total electricity capacity produced from solar panels with a volume of 13 GW. Germany, China and Italy are in the lead.
Metallurgy
The main boom in ferrous metallurgy occurred in the 60–70s of the twentieth century. However, after the fuel crisis of 1973–1974. the demand for metal began to gradually decline.
The archipelago does not have its own reserves of ferrous and non-ferrous ore. Despite this, metallurgical plants continue to operate in the country, most of which are full-cycle production facilities.
The main importers of resources are India, South Africa and the USA, supplying 99% of the required ore. The main metalworking centers are located on the coast of the country, near port areas. And some plants are located not on the shore, but on sites specially reclaimed for metallurgical plants.
For example, the largest plant in Fukuyama is located between two piers - one that receives raw materials and one that ships finished products. In total, after processing, Japan exports about 25 million tons of steel per year.
Not everything can be done by robots; manual labor still exists in manufacturing in Japan. You can learn more about this from the video below.
General economic and geographical characteristics of Japan
Japan, which the Japanese themselves call the Land of the Rising Sun, is one of the economic leaders of the modern world.
Territory area - 372 thousand square meters. km.
The form of government is a constitutional monarchy.
The form of administrative-territorial division is federation.
Economic and geographical characteristics of the country:
1) economic and geographical location: Japan is located on the eastern coast of Eurasia. This state is an archipelago located on 4 large islands (Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, Kyushu) and almost 4 thousand small ones.
The country is located at the crossroads of the sea routes of the Asia-Pacific region, which provides great opportunities for its participation in the international geographical division of labor.
2) natural conditions and resources are poor:
· relief: mountainous, lowlands occupy less than 1/2 of the area;
· mineral resources: poor; only local resources;
· soils: brown forest soils, yellow soils, red soils;
· land resources: depleted; most of the land is occupied by industrial development, arable land and pastures;
· climate: climatic zones: subtropical and moderate monsoon; temperatures: summer +16 - + 24 degrees, winter -8 - +8 degrees; precipitation amount - 500-3000 mm;
· agroclimatic resources: favorable for growing rice, vegetables, tea;
· waters: numerous rapids small rivers;
· water resources: used to generate electrical energy and irrigate fields; resource availability of total river flow per capita is 2.5-5 thousand cubic meters per year (average value);
· forest resources: occupy 2/3 of the territory;
· resources of the World Ocean: near the Japanese islands, coal, iron ore and natural gas are mined from the bottom of the sea. The energy of ebbs and flows, ocean currents, sun and wind is used.
a) number - 125 million people;
b) population density is high - 300 people per square meter. km, most of the inhabitants are on the coasts;
c) type of reproduction - II; birth rate, mortality rate, natural increase are low;
d) there are more women than men;
e) general aging of the population; the world's highest average life expectancy - about 80 years;
f) national composition - 99% Japanese;
g) religion - Buddhism, Shintoism;
g) level of urbanization - 76% of the population.
Large cities: Tokyo, Osaka, Nagoya; the agglomerations formed around them together form the largest megalopolis of Tokaido (average population density - 800-1000 people per sq. km);
h) labor resources - highly qualified; more are employed in the non-productive sector, less in agriculture and fishing.
Japan is the second industrial power in the world and ranks third in exports of products after the USA and Germany.
Conditions that influenced the development of the country:
— development of a well-thought-out national economic development strategy taking into account local conditions;
— a combination of large mass production with small supplying enterprises;
— purchase and implementation of scientific and technical inventions;
— high level of the education system;
- limiting military spending;
- traditional Japanese hard work.
Natural resources of Japan (table)
| Name | Example | Application |
| Forest | mixed, tropical, subtropical, coniferous forests | woodworking, export |
| Water | mountain rivers (Shinano, Tone, Mimi, Gokase, Yoshino, Chiguko), deep and shallow lakes | hydropower, irrigation, domestic water supply |
| Soils | red soils, yellow soils, brown soils, peaty, slightly podzolic, alluvial soils | cultivation of rice and other grains (wheat, corn, barley), horticulture |
| Biological | 260 species of mammals, 700 species of birds, 100 species of reptiles, 600 species of fish, more than 1000 species of mollusks | fishing, catching crabs, oysters, shrimp |
| Minerals (used mainly with imported raw materials) | large quantities: limestone, sand, dolomite, pyrite, iodine; small: coal, iron ore, nickel, lead, gold, silver, lithium, tungsten, copper, tin, molybdenum, mercury, manganese, barite, chromium, etc. | industry (metallurgy, mechanical engineering, chemical); energy |
| Energy | sea waves, winds, rivers, sunny days | alternative energy |