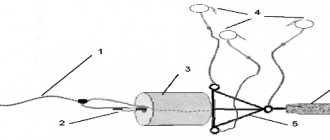
Making tackle
As you can guess from the name, the tackle consists of two paired spinning rods equipped with inertial reels. One or more leashes with bait in the form of fresh insects are attached to a common fishing line. Grasshoppers, butterflies, locusts, and dragonflies are used as bait. If you plan to catch predatory fish, use live bait.
The process of making a bale does not require special skills and is carried out directly at the fishing site.
Before fishing begins, anglers are located in their positions, on different banks of the reservoir, within line of sight. Next, one of them throws, or (if possible) transports his line and sinker to the other side of the river. The second fisherman removes the sinker and both lines are tied together. Leaving a knot connecting both lines approximately in the middle, one of the anglers ties several, usually 2-3, leashes. As such, pieces of fishing line with a diameter of approximately 0.18-0.25 mm are used. Hooks are attached to the ends of the leashes. The tackle is ready.
Baler
“Tyukalka”, “tug” and probably there are several other variants of local names for the well-known and popular, especially in the provinces, fishing tackle.
The gear is old and, quite likely, existed in some variants before the advent of reels and spinning rods. Its principle of operation is in many ways similar to the “boat”, but unlike the Siberian version, due to its partner and manual traction, it works even in areas with a barely noticeable current. It is usually used on small and medium-sized rivers where it is possible to “reach” the opposite bank with a regular cast or swim, although if you have a boat it can be successfully used on rivers with large water areas.
Equipment. Take two short (1.5–2 m) and “oak” spinning rods, their material can be anything - composite, aluminum, fiberglass, jerk sticks, old-fashioned (thick) bamboo, a broken carbon fiber rod or its lower leg are quite suitable. The simplest inertial reels with a large drum (Nevskaya type) are installed on them. 100 m of inexpensive and better rigid monofilament with a diameter of 0.4–0.5 mm is wound onto reels. At the end of one of the fishing lines, a loop is made and two auxiliary ones (at a distance of 1.5–2 m from each other), on which the leashes will be fixed in the future.
In the Ryazan and Tambov regions they traditionally fish with two leashes, but I have often seen a bale with four leashes.
This amount, in my opinion, is too much, since when the same chub bites at the same time, one of the fish often leaves and scares the already cautious members of the flock.
But a rig with multiple leads has another advantage - the ability to simultaneously use different baits (insects, streamers, or both), and just a couple of grasshoppers jumping on the water gives additional confidence and certainly looks more appetizing.
The thickness of the fishing line used for leashes is 0.2–0.25 mm. Their length usually ranges from 1.5 m. Depending on the fishing conditions, it may be slightly larger or smaller, but, in my opinion, this is a secondary issue.
The leashes can either simply be tied to the main line or (for their quick removal and replacement) attached using the “loop-to-loop” method.
The process of fishing with a twin spinning rod
Insects or live bait are attached to hooks and delivered by air to the place where fishing is planned. This is done like this: one of the fishermen, the one who is on the far shore, winds the fishing line onto his reel. At the same time, the other one slightly slows down his reel, thereby creating tension in the line.
The bait is delivered to the selected fishing spot and placed on the surface of the water. In order to create the impression that the bait, butterfly, grasshopper is alive, it is brought to life. To do this, periodically, alternately, the fishing line is twitched (baled). This creates the appearance that the bait has actually fallen to the surface of the water and is trying to take off.
Deceived by easy prey, the fish rises to the surface and swallows the bait. Next, winding the fishing line onto the reel of one of the spinning rods, the prey is pulled ashore. The process is repeated.
Baits and lures
Lures for drag fishing can be either artificial or natural.
Fly fishing flies are usually used for artificial baits.
As for natural baits, the best results are obtained from insects during the period of their flight when fishing occurs.
Various butterflies, flies, horseflies, moths, beetles and bugs, dragonflies of all kinds - all this is food for insectivorous fish. From mid-May the caddisfly begins to fly out. Emergence continues until mid-September as caddisfly species emerge in a specific sequence. This is an excellent bait for drag fishing.
With the advent of grasshoppers, they become the main bait. However, there are days when the fish reacts very weakly to the grasshopper, or even ignores it completely. But one of the surest baits is the cabbage butterfly. This white butterfly is very noticeable, often flutters near the surface of the water and is a common hunting object, primarily for chub. Night moths are very effective as bait.
Useful little things
Fish tend to behave cautiously. A person who is on the shore of a reservoir makes her wary, therefore, in order not to be left without a catch, it is advisable to use camouflage. This is especially true when fishing on small, narrow rivers. Therefore, if possible, it is advisable to use shelter on the ground, for example, hide behind the trunks of trees growing near a pond. Use bushes, tall reeds, and grass as shelter. In the absence of natural shelters, both anglers can move away from the shore, or, as a last resort, sit down.
Don't forget about clothes. It should hide the fisherman, make him invisible against the general natural background. You should also worry about silence. Loud sounds will make the fish go deeper. It is advisable to initially agree on gestures so as not to shout to each other, scaring the fish.
As a rule, fishing with a paired spinning rod is quite effective. The catch is often large specimens of such fish: ide, grayling, char, large chub, trout.
Arrangement of hauling tackle and fishing with it
Most likely, the harness evolved from the saddle with the advent of spinning rods. These gears are similar in principle of operation, although they are designed for fishing at different depth levels. The attitude of fishermen towards them is also ambiguous - some believe that drag fishing is a poaching method of fishing, and consider its use unacceptable, while others argue that in terms of catchability it is not superior to other conventional gear and at the same time requires skill for effective use. One way or another, fishing with a tug-baler (sometimes this tackle is called that) is sometimes practiced on small rivers. In this case, the baler works most effectively precisely for fish that find food in the surface layers of the reservoir. It is advisable to fish with a partner, however, you can use this gear alone, although this is much less convenient, and limits the maneuverability of the hauling, and can negatively affect the quality of the feed bait
Pull fishing technique
The best time to fish with a drag line is in June. You shouldn’t pay attention to the saying “June – don’t give a damn about fishing”, because it is during this period that insects actively reproduce. The waters are swarming with horseflies, dragonflies, and mosquitoes, and mediocre pilots—chafer bugs—flop into the water. Spawned fish happily take advantage of the circumstances, and you need to catch them from the surface. The fisherman’s task is to carefully and as naturally as possible deliver the bait to the places where the fish “play.”
When fishermen work in pairs, coordination comes to the fore. One attaches the bait and begins to gradually remove the line. His partner from the opposite bank must reel it in so that it does not touch the water. Once the leads are correctly positioned above the surface, you can choose one of two tactics:
- "Dipping".
Both fishermen synchronously lower the bait into the water and raise it, waiting for a bite. The one closest to which it pecked catches the fish.
- "Drawing".
The leashes are immersed in the water, and one of the anglers begins to reel in the line, provoking the fish to react. This wiring is suitable for asp fishing.
When fishing without a partner, it is important to correctly calculate the length of the main line and the possibilities of the elastic. The gear must be prepared in such a way that the fisherman can pull the leashes towards him without breaking. Having set the bait, the fishing line is slowly released until the leashes take the desired position. Then you can use one of the fishing tactics described above.
It is important to remember: when fishing with a drag, you need camouflage and silence.
Principle of gear design
The tug tackle is quite simple. It is nothing more than a piece of fishing line wound on the reels of two spinning rods, to which a dozen or more hooks are tied.
The rods carry out all the maneuvers, and if it is necessary to remove the catch from the hook, part of the fishing line is wound onto the reel that is closest to it. Sinkers or foam floats are sometimes used as additional elements - these devices help keep the tackle on the working horizon. But this is true if two anglers are fishing with a tug, but fishing with a bale is possible alone. The tackle differs from the option for two in that a piece of elastic band (round in cross-section or tape, there is no difference) is tied to the end of the fishing line, thanks to which it will be possible to return the tackle to the fishing site.
The animation of the bait is carried out by synchronized lifting of the rods, the equipment is periodically literally hit on the water (baled, one of the names of the gear comes from this method of supplying the bait), primarily attracting predators like chub that feed at the surface.
Photo 1. Scheme of the gear operation.
Catching pike perch in winter using a 'snitch'
Pike perch, especially large ones, are undoubtedly the most desirable prey in the Moscow region. Nevertheless, it is found in catches much less frequently than other predators. Few of the lure anglers can boast that they purposefully catch pike perch using “pieces of iron.” With girders, the situation is a little better, but only if the tackle is properly equipped, and the hook on the hook is not a traditional crucian carp, but a bleak or a minnow. In a word, catching pike perch with baits is troublesome, but with spoons it is ineffective. However, a long time ago, fishermen invented a very simple tackle that combines the mobility of a spinner with the attractiveness of live bait. Under the name baler or squealer, it has survived practically unchanged to this day.
Squealer
A squealer is a very large jig that is baited with freshly killed fry. The shape of such a jig usually resembles a “Uralka”. As a rule, the fry is simply hooked, but some variants of hooks, used for careful biting, have another additional small tee. The fishing rod is an ordinary pike perch lure, which differs, perhaps, only in a stiffer whip and the obligatory presence of a nod. The fishing line should be thick enough, with a diameter of 0.25–0.30 mm, only monofilament. This choice is determined mainly by the fishing conditions: it is often carried out among snags, so hooks still happen. It’s not worth using braided cords, despite their attractiveness: in the cold they quickly freeze and the tackle loses sensitivity. You shouldn’t try to treat the braided line with any sprays or oils, as is often done in winter spinning rods, since they all have a strong odor. The smell will concentrate under the hole and drive the pike perch away from it. One more nuance. Although pike bites occur quite regularly when fishing with a bale, a metal leash is not needed. The pike perch has a very negative attitude towards the leash. A special issue is the whitebait. As always when fishing for pike perch, the choice of fry must be treated with special care. Bleak and gudgeon 6–7 cm in size are suitable, but it is not advisable to use roach. The reason is that the pike, as I have been convinced more than once, has a special love for it, which in our case is not at all pleasing. Malek must be fresh. Pike-perch is a very capricious fish: it can still take a fry that has recently fallen asleep, but I have not had a single case when it pecked at ice cream.
Fishing technique
Bale fishing is generally very similar to lure fishing, but the game should be softer. The bait with the fry smoothly sinks to the bottom, then light tapping on the bottom begins with small rises and pauses of 3-4 seconds. He lifted it - knocked it - stopped it, lifted it - knocked it - stopped it... An imitation of a fish is created, swarming at the bottom. Due to the movement and smell of the bait, the bait attracts pike perch. The bites are very different. The pike perch can crush the bait, it can grab it on the fly, but more often it tugs at the fry and often pulls it off the hook. For this reason, a decent supply of live bait is necessary. I usually take 20 pieces per day of fishing. The advantage of a bale is that it can cause a bite even in a passive predator. This makes certain adjustments to fishing tactics. If you work a point quickly enough with a spinner or a balancer - 10-15, maximum 20 strokes and if there are no bites you move on to the next hole - then there is no need to rush here. In a place on the hole that is attractive to a predator, you can linger for 10 minutes. It happens that there is no bite, but you feel the touch of the bait, the pressure - which means there is a fish, it is trying on, but for some reason does not risk daring to grab. In this case, you can change the game a little - increase the tempo or, conversely, increase the pause time to 10-15 seconds. After any bite, even a single one, the fish must be replaced, but when searching, if there is no grip, one intact fry can be used within half an hour.
Search and fishing tactics
The search for pike perch begins with a series of holes of 5–7 pieces. You need to find gentle slopes, pits, and, very preferably, snags. If there was a bite from a pike perch, and even more so if it was caught, it is advisable to drill the next hole nearby, 1.5–2 meters away, and, if possible, without much noise. Pike perch often stay in small groups, and after catching one of their comrades, the rest seem to move to the side. Therefore, you definitely need to check the neighboring hole. We must remember that pike perch is very afraid of extraneous sounds, and if you make 3-4 holes in a row nearby, it will move away. There can be no talk of any pumping of holes. Accordingly, if, having seen a caught pike perch, other fishermen come to you and want to share the success, then you can forget about catching pike perch: it will not be in this place for at least several hours.
The advantage of the snitch is that you can literally catch it between snags. Unlike a spinner, and especially a balancer, it practically does not give lateral deviation when playing. Of course, when fishing in a snag, a predator always has a chance to get the bait behind the snag and tangle the line, but the probability of a bite here is also much higher. In any case, it is very advisable to have a release with you. Pike perch go out to feed mainly in the morning and evening twilight. In cloudy weather, biting with varying intensity can continue throughout the day. I would like to especially emphasize that when fishing for pike perch, you should not rush to the shore after it begins to get dark. If possible, it’s worth staying and fishing for at least another hour and a half in the dark. Very often, this is the time when pike perch activity peaks.
Features of the place of use
Drag fishing is not possible in all bodies of water. First of all, this concerns the size of the river. Too long a fishing line when catching fish by hauling makes it difficult to maneuver the tackle and degrades the quality of bait delivery, and it is difficult to control bites over a long stretch; after all, this is tackle for small rivers.
Also, when using a tug for catfish or other fish, you need to select suitable areas of the shore. A lot of aquatic or terrestrial vegetation in the coastal zone easily makes the use of gear impossible. Too much difference in the height of the left and right banks can also worsen the supply of bait.
Photo 2. Convenient place for re-tying.
What kind of fish can be caught this way?
A bale is most effective when catching fish that feed primarily in the surface layers of a reservoir (although catching catfish by dragging is also sometimes practiced). First of all, these are the so-called “white predators” - chub and asp. In mountain rivers you can catch trout using this method. Among the peaceful fish that are caught on the hooks of the constriction are redfish, rudd, and saberfish.
To a large extent, species diversity depends on the bait used and the depth of fishing. Grasshoppers, various other insects and their larvae increase the likelihood of catching a chub, and if there is live bait on the hooks, then you can count on catching a pike or large perch. Well-coordinated teamwork and competent maneuvering of tackle with additional weight allow you to fish at depth. Reeling for catfish can also be used - to do this, you need to add a sinker to the tackle, and use frogs, leeches, or large bunches of crawlers as bait.
Gear used
Rod
Two strong rods with rigid tips are needed, since during fishing the tackle is under constant tension, and the tips are subject to a significant load. Usually these are spinning or plug rods; bamboo fly rods are also popular.
fishing line
The diameter of the main line on reels - from 0.50 mm - is due to the fact that the tackle works under heavy load, and since the fish does not see it and, accordingly, is not afraid, you can use a thick line. Its length depends on the length of the rods and the width of the reservoir.
Coil
Fishing rods require inertial reels with high line capacity. They must have a brake, which they often have to use while fishing.
Leash
Considering the length of the rods, the length of the leash should be at least 1-1.2 m, and the diameter is limited only by the inability to attach small baits to a thick fishing line, since the leash does not come into contact with the water and does not scare the fish, even if it has a large diameter.
For drag fishing, from one to ten leashes are used, depending on the width of the reservoir and the preferences of the fisherman.
Hook
For fishing with a bale, thin, very sharp single hooks are used.
Fishing with a drag for two or alone
It is most convenient to fish with a bale together with a partner. One fisherman on a boat crosses the river along a bridge, or wades or swims along with his piece of gear. Next, the fishing line is pulled over the water in promising areas of the reservoir, and the tackle is periodically immersed or raised. With well-coordinated teamwork, the moment the bait touches the water, they look as natural as possible and provoke even such a cautious fish as a chub to attack.
After fishing one point, you can smoothly move up or downstream, thus covering a significant area. With a good knowledge of the bottom topography, as well as with additional weight, you can play with a tug in the water column, as well as at the very bottom, thereby provoking the inhabitants of the near-bottom layers to bite.
Chub fishing can also be done from boats, which increases the maneuverability of the gear and makes it possible to fish promising sections of rivers. However, such fishing requires stable swimming equipment, otherwise it is difficult and dangerous to maintain balance while standing on a single-seat inflatable and at the same time work with the tackle. That is why this method of using constriction is not very popular.
You can also fish with a bale alone. This is somewhat more difficult, and the maneuverability of the gear is lost, but it is possible. To do this, you need to secure a fishing line with a piece of elastic band tied to it on the opposite bank (to a tree trunk, or to a peg driven into the ground). Otherwise, solo fishing with a tug is the same as with a partner, but in order to change the place where the tug is used, you will have to swim across the pond again and tie it in a new place, which will take a lot of time.
Fishing with a rope (baler)
Fishing with a rope (baler) is practically not described in the fishing literature; there are only isolated mentions. The 1992 Recreational Angler's Handbook gives only a brief description of the constriction.
Some authors strive to impart a certain scientific quality to fishing terminology, which is why this method of fishing is also defined as “fishing with twin spinning rods.” Fishermen often call this tackle briefly, “tightening” or “baling”. The name “hauling” is given because the tackle must be pulled from one bank to the other, and “baling” comes from the fishing technique itself, since artificial or natural bait is dipped into the water and “baled” on the surface.
Similar tackle - saddle
Sling and drag are sometimes confused, and in some regions these tackles are called the other way around. But it is generally accepted that the seine is distinguished by the presence of floats, sinkers, and also by the fact that it is a passive method of fishing - the tackle is simply fixed so that it remains buried to a certain depth. The bait is often live bait, a bunch of crawlers, leeches, and other options that can interest large river predators like catfish, pike or pike perch. The main difference lies primarily in the fact that the line is always under water in one position, while the drag is constantly moved by anglers, both when changing the fishing point and during retrieving.
Sources:
https://fffishing.com/tyukalka-rybalka-sparennym-spinningom-ili-lovlya-na-peretyazhku https://www.ohotniki.ru/fishing/spinning/article/2017/07/19/648732-kak-lovit -tyukalkoy.html https://fishelovka.ru/gear/ustrojstvo-snasti-peretyaga-i-lovlya-ryby-na-nee