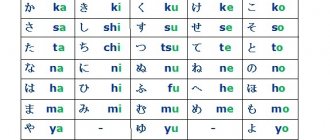
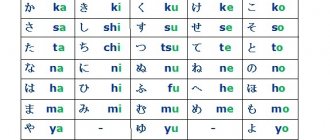
Studying abroad has long been available. Among numerous universities in Europe, Asia and America, higher education institutions in Japan are very popular. One such place is the University of Tokyo.
Where it is located? How can a Russian student enter Tokyo University? How much does it cost to study? We will consider all this and much other useful information for applicants in the article. So why do Russian youth strive to go abroad? Let's try to answer this and other questions.
Study abroad: benefits
- Receiving an education that is highly valued throughout the world.
- Invaluable experience of living in a different cultural environment, especially for Russian students.
- Improving foreign language skills.
- Increased professional level.
- Obtaining an international diploma.
- Acquaintance with the traditions, history, way of life and culture of other peoples and countries.
- Making new interesting friends.
- There are chances for employment in Europe and other countries.
How to enter a university in Japan
The Japanese government strives to attract as many students as possible from abroad (the goal is 300 thousand foreigners in the coming years) and favorable conditions are created for this. For example, the process of applying to local universities is simplified, and the number of courses that are partially or completely taught in English is increasing. However, most training programs require proficiency in Japanese.
To obtain detailed information about admission requirements and the list of documents, you must contact a specific Japanese university, but general conditions can be highlighted.
- At least 18 years of age.
- Secondary education obtained abroad must be at least 12 years. Otherwise, it is necessary to take special preparatory courses in Japanese educational institutions accredited by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (hereinafter referred to as MOKSST). An alternative option is to have a higher education diploma of at least a bachelor's degree.
- A mandatory requirement for admission to a Japanese university is to successfully pass a standardized test - Examination for Japanese University Admission for International Students (EJU).
According to some estimates, about 95% of national and 65% of public universities in Japan require international students to take the above test. During testing, knowledge of foreign languages, Japanese history and culture, as well as such areas as geography, mathematics, chemistry, physics, biology, economics and some others are tested. The choice of disciplines depends on the university and area of study.
The exam is held annually in mid-January over two days at special centers operating throughout the country. The candidate has only one attempt. Registration fee is around $60-$80. Additional requirements for foreigners entering Japanese universities relate to the correct application and preparation of documents, confirmation of sufficient financial resources and obtaining a student visa.
Tokyo is the capital of Japan
This city is one of the largest metropolises in the world. But it is not only this fact that attracts increased interest. Technical progress triumphs here. High-speed trains, advanced technology, robotic housewives and many other scientific inventions that serve people. In order to have someone to invent technical miracles, the University of Tokyo was built at the end of the 19th century.
It is one of the oldest educational institutions in the country and has held the title of Imperial for more than half a century. The university was formed by the merger of three institutions: Soheiko, Kaiseigo and Igakuso. There are a large number of famous people among the graduates of the University of Tokyo: writers - Kobo Abe, Akutagawa, Kizaburo Oe; politicians - Yoshida Shigeru and Yasuhiro Nakasone, and many others. Among them were a large number of Nobel laureates.
University of Tokyo: faculties
This educational institution is considered the most prestigious in Japan. After all, it is the University of Tokyo that produces the most qualified specialists to work in the government of the country, as well as in the largest companies. More than 30 thousand students from Japan and other countries of the world study here. The university has the following faculties:
- philological;
- legal;
- economic;
- pharmaceutical;
- medical;
- technical;
- scientific;
- Agriculture;
- arts;
- pedagogical;
- historical.
History of the creation and development of the University of Tokyo
The essence of the education of the University of Tokyo is based on the fact that at one time there was a merger of three educational institutions:
- Soheiko , which was founded in 1790 and represented a special center for Confucianism;
- Kaiseigo , founded in 1855 and specializing in the study of Western culture;
- Igakuso was founded in 1863. Students there studied Western medicine.
Since the merger of these three educational institutions, the University of Tokyo has been an official public educational institution.
Admission conditions and prospects
In order to become a student at the University of Tokyo, you must meet the following requirements:
- Documented knowledge of the Japanese language.
- Have a 12-year secondary education course. For applicants from Russia - one course of higher education.
- Pass the national entrance exam.
- Submit the following documents: medical certificate of health, application, certificate of education, photographs.
- Having a bank account with enough money to pay for tuition and living expenses.
- Get a student visa.
After completing their studies and receiving a state diploma, graduates have several options:
- Apply for a job. With a diploma from the University of Tokyo, this is not so difficult.
- Continue to graduate school and achieve advanced degrees and awards.
Arts and Education: Tokyo University of the Arts
Tokyo University of the Arts (東京芸術大学), more popularly abbreviated as Geidai, is one of Japan's oldest and most prestigious universities in the field of art.
This public university was founded in 1949 as a result of the merger of the Tokyo School of Fine Arts and the Tokyo School of Music, which, in turn, existed in the capital since 1887. At first, the doors of the new university were open only to men; women began to be admitted a little later. In April 2004, Geidai became the Tokyo National University of Fine Arts and Music, and acquired its current name on April 1, 2008.
Departments of bachelor's, master's, postgraduate and doctoral studies have been opened at Geidai. There are three faculties:
- Faculty of Fine Arts (departments: Japanese painting; oil painting; sculpture; crafts; design; architecture and planning; aesthetics and art theory; restoration; Inter-Media Arts)
- Faculty of Cinematography and New Media (departments: animation; film production; new media)
- Faculty of Music (departments: composition; conducting; vocals; musicology; traditional Japanese music; musical creativity and environment; performance)
The university is proud of its infrastructure: an art museum, academic library, opera, orchestra, art media center, Sogakuto concert hall, Institute for the Study of Ancient Arts, Center for the Performing Arts, Center for Musicological Research.
The main campus of the University is located in the picturesque Ueno Park, Tokyo. Additional corps were deployed to Taito, Torida, Adachi, Ibaraka, Kanagawa and Yokohama. The dormitory for international students is located in Matsudo.
Gaidai has student exchange agreements with such institutions as, for example, the Art Institute of Chicago (USA), the Royal Academy of Music (UK), the Australian University of Sydney, the Queensland College of Art and Griffith University, the Korean National University of the Arts (Republic of Korea) , Central Academy of Fine Arts (PRC).
Over the years, our compatriot, the famous pianist Leonid Kreutzer, the sculptor Takamura Koun, and the film director and actor Takeshi Kitano taught at Geidai.
More information: Official website of Tokyo University of the Arts
Distinctive features of studying at the University of Tokyo
- The opportunity to use the rich library of the educational institution.
- Much attention is paid to the physical development of students. There are sports sections and organizations.
- The research laboratories in which students study are equipped with the most modern technology.
- Dormitory accommodation is provided and costs about 14 thousand yen per month.
- A large number of hobby groups and clubs for students to study in their free time.
- The training time is from four to six years, and the cost is from 500 to 800 thousand Japanese yen per year.
- Study here begins on April 1 and ends on March 31.
Student reviews
High quality knowledge and confidence in the future - that’s what the University of Tokyo is all about. The cost of training, of course, is very high, but the education received is worth the money. In addition, there are always opportunities to receive scholarships or grants, although for this you will have to work hard.
Japan is a country that obeys only its own laws, which are largely incomprehensible to foreigners. If you want to study traditions and get into business circles, then the best and surest way is to study at the University of Tokyo. An interesting fact is that everyone here chooses their subjects themselves, and the usual schedule for Russian students does not exist at all.
To successfully graduate from the University of Tokyo, you must complete a certain number of hours. According to students, they can be obtained when you pass an exam or test. Japanese students usually do not use cheat sheets, because if they are discovered, the punishment will be very severe - an exception.
Higher education in Japan
Japan's economy ranks third in the world after the United States and China. The successful development of the state became possible largely due to the introduction of advanced research developments of local scientists into all industries and the incredible working capacity of Japanese citizens in general. Therefore, today residents of all corners of the planet have the opportunity to use high-tech products from companies such as Nissan, Toyota, Honda, Panasonic and Sony.
Japan's higher education system includes numerous specialized schools, colleges and about 800 universities , which are divided into three types:
- National . There are about 90 national universities in Japan, fully funded by the state. The largest are Tokyo and Kyoto, which are among the three best Japanese universities. The cost of training in national higher educational institutions is considered the most reasonable.
- State (Public) . The main difference between state universities and national universities is the structure of management and financing. Universities of this type are governed by the prefecture at their location, and the budget is formed from taxes of local residents. There are currently about 100 public universities in Japan.
- Private . The most expensive education in Japan is offered by the largest group (about 600) of higher education institutions, which are called private. The average cost of 4-year courses is 60–70 thousand dollars. Popular private universities in Japan are Keio University and Waseda University.
Unlike many other countries in the world, the academic year in most higher education institutions in Japan lasts from April to March . Nevertheless, there are enough universities in the country with a system of education that is more familiar to foreign students, where the academic year begins in September or October. In addition, to help and quickly adapt foreigners, local universities recruit a large number of teachers from countries outside Japan.
The most popular universities in Europe
Based on numerous student reviews, we can compile a list of the most popular higher education institutions. These include:
- University of Bologna in Italy. This is the oldest university in Europe. Dante Alighieri, Francesco Petrarch, Coluccio Salutati, Nicolaus Copernicus studied here. The university's educational program covers all possible areas of knowledge. Although Roman law was originally taught.
- Oxford University. One of the most prestigious universities is located in the UK. On its territory there are churches, museums, theaters, and libraries. Fun fact: The Harry Potter movie featured the main dining hall at Oxford University. In 2021, it entered the top ten best higher education institutions in the world.
- Al-Azhar University in Egypt. Here they pay great attention to the study of religious disciplines.
- Salaman University. It is located in Spain. This is one of the first universities to have a public library.
- California Institute of Technology. One of the leading universities in the USA. Space developments are carried out here.
- Cambridge university. A huge number of its graduates become Nobel laureates.
- Harvard University. In the USA, it is the oldest educational institution in the country.
Universities in Tokyo: Todai, Meiji University and others
Tokyo is one of the largest metropolises on Earth and is the capital of Japan. It is home to many educational institutions, including universities in Tokyo that are very prestigious around the world. One of the oldest is the University of Tokyo, abbreviated as Todai (official website www.u-tokyo.ac.jp), founded in 1877, and until 1949 had the status of an Imperial University. It has 10 faculties, 12 graduate schools, the number of students is about ten thousand, two of which are foreigners studying there. The university area is divided into two campuses.
Sights of the University of Tokyo
The University of Tokyo (Tokyo Daigaku), known as Todai , is the most prestigious university in Japan. Todai has five campuses, with a total of about 3,000 students studying in ten faculties, of which 2,100 are foreigners. According to the Academic Ranking of World Universities, Todai is ranked top in Asia and 21st among the best universities in the world.
Kyoto University ranks second among Asian higher education institutions, Osaka University - seventh.
The classification of universities in Japan itself is interesting . So, Todai , of course, beyond any comparison, the private Keio University (Tokyo) , next in prestige, which, by the way, graduated from Junichiro Koizumi, is known for the fact that its graduates are independent, creative, innovative thinkers. But the private Waseda University (Tokyo) , also one of the prestigious universities, but for some reason they believe that it produces, although talented, but very obedient type of cooperative workers.
Although in general, Waseda and Keio are considered excellent institutions and are designated as Japan's Harvard and Yale universities .
Todai , created during the Meiji era in 1877 by merging the Medical School with the Kasei School founded under the Tokugawa shogunate, was originally called the Imperial University (teihoku daigaku) and was the first modern university in the country. In 1886 it was renamed Tokyo Imperial University (Tokyo Teihoku Daigaku) .
Like the famous universities in Kyoto and Osaka, Todai is a national educational institution. Its graduates include many high-ranking officials, businessmen, scientists, and engineers.
About 30 percent of the government members, 60 percent of the commercial and financial elite in their youth prepared for the start of the school year by buying stationery and other school supplies in order to go to lectures in Todai .
Five Nobel laureates studied at the University of Tokyo (Kyoto University is also proud of its five Nobel laureates).
The University of Tokyo's engineering department currently runs the Nobel Prize program, which rewards promising scientists with 10 million yen a year for research, allowing access to expensive equipment like laser generators, with the hope that scientists will soon make discoveries worthy of a Nobel Prize. .
The main campus in Hongo (Tokyo's Bunkyo-ku area) is housed in buildings owned by the Maeda family (daimyo in the Edo era). One of the most famous signs of the university is the Red Gate (Akamon), preserved from that era.
The symbol of Todai is the ginkgo leaf, and ginkgo trees can be seen throughout the area.
Another cultural and historical landmark of Hongo that is generally recognized as a study area is Sanshiro Ike - Sanshiro Pond , dating back to 1615.
After the fall of Osaka Castle, the shogun handed over both the pond and the surrounding garden to Maeda Toshitsune. Over time, the garden was recognized as the most beautiful in the city, including eight traditional landscapes - Ikutoku-en (Garden of Teaching Virtue). Since the pond is in the shape of a heart, the garden was officially named Ikutoku-en Shinjiike (shin-heart). It began to be called Sanshiro Ike after the novel “Sansiro” by Natsume Soseki.