Tomsk region was formed in 1782. This subject of the Russian Federation is one of the regions with natural population growth.
The relief of the Tomsk region consists of swampy plains with hills no higher than 200 meters above sea level. The total area of the region is 314,000 km², of which 53,000 km² is occupied by the largest Vasyugan swamp in the world. But the region is notable not only for the presence of swamps.
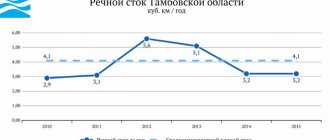
There are over 570 rivers of various sizes on its territory. All of them belong to the Middle Ob basin, whose area is 39,000 km². The length of only three reservoirs exceeds 1000 kilometers. One of them is Katya.
Description
The length of the Keti is 1621 kilometers; only 805 kilometers flow in the Tomsk region. The basin area exceeds 94,000 km². The channel runs through the territory of the Tomsk region and part of the Krasnoyarsk Territory. This is the second largest body of water in the region.
Ket
Its name comes from the name of the ancient chum salmon tribe, who lived on this land in the 16th-17th centuries. There is a legend according to which the Kets fought for their independence. During one of the battles, a brave warrior lured the enemy army onto thin ice. By sacrificing his life and destroying his enemies, the warrior saved his people. The river is named Ketyu in honor of him.
Rafting on the Ket River
In the diary of Nikolai Spafariy there is a description of the r. Keti, the voyage along which lasted a month: “... the Ket River is dreary because there is no elani tree or field along it, just impenetrable forest, swamps and lakes, and therefore in Keti the water is black, and there is little dry space.” (Spafariy N., 1960, p. 68). The traveler noted details of the Ket nature, for example, that on the right bank of the river there is little forest, and on the left there is a cedar forest, a willow forest, a fir, an aspen forest and “a lot of other forests” (the left and right sides of the Keti river are indicated by N. G. Spafariy along the way movement along the river); "on the river There are many ravines and channels in the Ket.” (Spafari, 1882).
Source
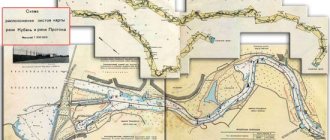
The Ket River on the map of Western Siberia
On the map of Western Siberia the mighty Ob River stretches out with many of its tributaries. The Ket is the right tributary of the Ob and, when it flows into it, it is divided into two branches. They are called Togurskaya and Kopylovskaya Kety.
The source is a remote taiga swampy area of the Krasnoyarsk Territory at the confluence of the Bolshaya Ket and Malaya Ket rivers - the Ob-Yenisei watershed. The riverbed is surrounded by coniferous forests, which predominate on the West Siberian Plain. In the lower part, the winding current is divided into numerous streams. They dry out when there is no rain.
Almost a century ago, the Ob-Yenisei Canal was built there. The goal was to connect the Keti tributary with the Yenisei tributary to unite these two reservoirs. But the waterway did not acquire practical significance. The decision was made to close it.
The Ket, like most rivers of the Ob basin, is located on the territory of a natural reserve. There is a route for travelers along the shore, and the riverbed is excellent for tourist rafting. Even the inaccessible taiga terrain and the lack of roads on the approach to the reservoir do not stop amateurs.
The Ket River in the Tomsk region
Geography and hydrology of the Ket River The Ket River is the right tributary of the high-water Ob and flows into it in two branches - the Togurskaya and Kopylovskaya Ket. The Ket originates from the remote taiga swampy area of the Ob-Yenisei watershed and is called the Big Ket. Connecting with Malaya Ketya, the river flows through flat wetlands, surrounded by coniferous forest. The length of the Ket River is 1621 km, the water basin is 94 thousand square meters. km. The river flows through the territory of the West Siberian Plain, the lands of the Tomsk region and the Krasnoyarsk Territory. Until the Orlovka River flows into Ket, its channel is very winding. After merging with Orlovka, the Ket spreads into many channels, which often dry up if there is no rain. A huge number of right and left tributaries fill the water basin of the Ket River. Ket freezes at the end of October, and opens at the end of April. Flood occurs in the period May-August. On the coastal territories after the confluence of the Malaya and Bolshaya Ket there are numerous settlements - Bely Yar, Aidar, Ust-Ozernoye, Togur, Novoselovo, etc. The river is considered navigable after 700 km from the mouth.
Origin of the name of the Ket River There are several assumptions why the river is called that way. One of the most beautiful legends says that a long time ago the Kets, a people living on the banks of the Ket River, fought for their territories with one particularly hostile tribe. Each battle ended with heavy losses and there were fewer and fewer Kets left. One of the young leaders of the Kets, whose name was Ketil, lured a large enemy detachment onto the thin ice of the river. The ice began to break under the weight of the enemies and the cold water swallowed them all. Ketilu died along with everyone else, but grateful residents began to call the savior river Ket.
Features of fishing on the Ket River The waters of the Ket River abound with various types of fish. Nelma, pike, burbot, sturgeon, ide, sterlet, crucian carp, bream, gudgeon, tench, ruffe, chebak and other types of fish inhabit this river (about 20 species). The most valuable fish species are considered to be nelma, sturgeon and sterlet. After the flood, the sturgeon goes to the Ob. In this regard, Ket is one of the most favorite places for fishermen. However, fishing on Keti is not easy. It begins in mid-June when the water level drops and continues until mid-December, when icing begins. Ide, perch and pike can be easily caught using a spinning rod; avid fishermen prefer to catch other fish using a fishing rod. There are many lakes near the river, where crucian carp are often caught. The weight of the fish can reach 4 kg. There is also tench there. It is difficult to get to the Ket River for fishing - there are almost no car descents to the river. Often you need to use special equipment designed for off-road travel, or use watercraft along neighboring rivers.
Loading…
Tags: Rivers of Siberia, Rivers of the Tomsk region
Geography
The Ket flows through the West Siberian Plain. More than 2,000 large and small rivers flow through the harsh continental climate, which is influenced by the Arctic Ocean. All of them belong to the basin of this ocean. The largest rivers in the region are the Ob, Yenisei and Irtysh, and their numerous tributaries. The channels lie in well-developed valleys up to 80 meters deep.
There are many lakes on the plain, most of which give rise to river streams. There is also a record number of swamps here. Coniferous forests grow among these reservoirs. Tree species that are typical for the taiga include fir, cedar, and aspen. Moreover, the left bank is more wooded than the right side of the river.
The pool is well populated. There are many modern villages there, including Novoselovo, Stepanovka, Bely Yar and Togur. Most of the settlements were formed below the confluence of the Big and Small Ket.
Information and literature about the Ket River
Contents:
Ket River - Encyclopedic reference
Ket is a river flowing in Siberia. It is the right tributary of the Ob. The length is 1621 km, the area of its basin is 94200 sq km. The source is located in the Ob-Yenisei watershed. It flows through the West Siberian Plain, through the territories of the Krasnoyarsk Territory and the Tomsk Region. Before the confluence of the Orlovka River it is very winding, below it it breaks into numerous channels. The Ket flows into the Ob through two branches - the Togurskaya Ket and the Kopylovskaya Ket, flowing along the Ob to Narym. Some tributaries: right - Shaitanka, Ivashkova, Sochur, Kelma, Ozernaya, Chagiseyka, Togolika, Orlovka, Lisitsa, Nalimya, Chichulina, Tolodya, Eltyreva; left - Malaya Ket, Kelchigeyka, Mendel, Sterlyazhya, Elovaya, Olenka, Kassayga.
Literature about the Ket River
Ket River - POEMS
Ket - a playful river Nikolai Vershinin 2
Ket is a playful river, You run from afar. And, frightening us with trouble, You wash away the ravine with water.
The Ket is a playful river, and so easy to work with. We all remember how you carried rafts into the distance with the forest.
Ket is a playful river, capricious and lively. It’s deep, you won’t find a ford, the people feed on fish.
Ket is a playful river, The boy’s eyes are bright: How can you not overlook that one girl, Ket?
Ket is a playful river, You will survive for now We are confident, loving: The world is colorless without you!
Ket the great river Alexander Ivanov 79
Ket is a great river. Where it is shallow, where it is deep, Where it is wide, where it is not very much, The length is stable.
Settlements settled along its entire course. I wouldn’t be too lazy to describe them, but there are too many villages. Here are Palochka, and Rybinsk, and Fox, and Makzyr, Kataiga, Central, Druzhny, And so on and so forth... We are not childishly serious, But our district is Verkhneketsky. Both young and old live here, and the capital is Bely Yar. We are not spoiled by the weather, we are accustomed to any weather. And at any time of the year we are pleased with ourselves. Minus forty – relaxation, Thirty plus – babbling. We are not difficult guys, we are characterized by kindness. There is a “quota” for work these days. It’s not a problem for us either. Where is fishing, where is hunting We are always accompanied. The main principle is not to be lazy, the rest is nonsense. Water helps us in these difficult years. Wild plants help out: Cones, berries, mushrooms. We are not striving for millions, our destiny is enough for us. The Ket united us all - the mushroom picker and the fisherman, and that’s why, guys, the Ket is a great river!
Tributaries
The river basin is cut by numerous tributaries. The largest are:
- Ivashkova.
- Ozernaya.
- Orlovka.
- Burbot.
- Malaya Ket.
- Mendel.
- Spruce.
- Katayka.
The most winding section of the river is before the confluence of the Orlovka. The current then divides into branches, which can dry out in dry weather. Floods occur between May and August; the river floods nearby valleys and populated areas.
It freezes heavily at the end of October. The lower the temperature drops, the thicker the ice cover becomes. In the spring (April and May) there is a deafening roar on the Keti, blocks of cracked ice move along the river until they completely melt.
Rafting on the Ket River
In the diary of Nikolai Spafariy there is a description of the r. Keti, the voyage along which lasted a month: “... the Ket River is dreary because there is no elani tree or field along it, just impenetrable forest, swamps and lakes, and therefore in Keti the water is black, and there is little dry space.” (Spafariy N., 1960, p. 68). The traveler noted details of the Ket nature, for example, that on the right bank of the river there is little forest, and on the left there is a cedar forest, a willow forest, a fir, an aspen forest and “a lot of other forests” (the left and right sides of the Keti river are indicated by N. G. Spafariy along the way movement along the river); "on the river There are many ravines and channels in the Ket.” (Spafari, 1882).
Map of the Ket River
Definition of coordinates: Map center: Scale:
Map of the Ket River with attractions - you can navigate around the map using the mouse, and also zoom in and out of the map using the '+' and '-' buttons. Ket map, Ket river map, Ob map, diagram, area plan, borders, roads, railway, railway communication, bridge, seas, rivers, lakes, cities, settlements near the Ket river, river, Ob satellite map, railway, fields, mountains, satellite view, scale, Yandex map - World Ocean. Arctic Ocean. Kara Sea. Ob. Ket
Ket (river)
Ket
(Selkup. Ӄet, Ӄet [2]; in the upper reaches -
Bolshaya Ket
) is a river in Siberia, the right tributary of the Ob.
Length - 1621 km, basin area - 94.2 thousand km². It originates from the swamps of the Ob-Yenisei watershed. It flows through the West Siberian Plain, through the territories of the Krasnoyarsk Territory and the Tomsk Region. Before the confluence of the Orlovka River it is very winding, below it it is divided into numerous channels, which are replete with riffles and often dry up in low water. The Ket flows into the Ob through two branches - the Togurskaya Ket (below the city of Kolpashevo) and the Kopylovskaya Ket, flowing along the Ob to Narym.
The average long-term annual flow is 560 m³/s, 17.7 km³/year. High water from May to August. It freezes in late October - early November, opens in late April - early May.
- Right
- Shaitanka, Ivashkova, Sochur, Kelma, Ozernaya, Chagiseyka, Togolika, Orlovka, Lisitsa, Krasnaya (?), Alset, Kuzurova, Nalimya, Panovskaya, Chichulina, Tolodya, Eltyreva, Parga, Pingasan, Kolosok, Pikovka, Paidugina. - Left
- Malaya Ket, Krasnaya (?), Eremskaya, Kelchigeyka, Mendel, Sterlyazhya, Elovaya, Olenka, Kassaiga, Kataiga, Laiga, Poludenovka, Duck, Chachamga, Karbinskaya Anga, Suiga, Kasatka, Sungoto, Pizik.
In 1596, the Ket fort was founded on the river, and the Ket who lived in these places began to pay yasak (tribute in furs). In the second half of the 17th century, the fort was moved to a new location, more convenient for life.
At the end of the 19th century, the Ob-Yenisei Canal was built, connecting the river of the Keti Lomovataya basin through the Kas River with the Yenisei. The waterway did not acquire practical significance and was closed in 1917.
Source